Energy
We will discuss here about energy.
We have seen in a rail shed or shipyard that huge cranes are engaged there in lifting very heavy articles and placing those articles to somewhere else. Similarly, we might have followed a small ant carrying a piece of food in its jaws, which is much heavier than the ant weighs itself. In both the cases some works are associated with and to perform this work, be it a huge machine or a tiny ant, it needs energy. So we can treat energy as an ability to do some work or an ability to make things happen. A machine gets the energy from fuel and a living organism gets it from food.
When you switch on a light, it glows. Here electrical energy is transformed into light energy. If we rub our palms against each other for a while, we w0ould feel hot. Here heat energy is generated from mechanical energy. From here we conclude that energy cannot be produced, it may only be transformed from one form to other.
In general, energy can be divided into seven forms. They are heat, light, sound, magnetic, electrical, mechanical, and chemical. But now we will discuss about the few forms of energy (i.e. solar energy, electrical energy and magnetic energy) and their usage.
Recent Articles
-
Respiratory Balance Sheet | TCA Cycle | ATP Consumption Process
Feb 18, 24 01:56 PM
The major component that produced during the photosynthesis is Glucose which is further metabolised by the different metabolic pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, TCA cycle and produces energy whic… -
Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation | ETC |Diagram
Feb 04, 24 01:57 PM
It is also called ETC. Electron transfer means the process where one electron relocates from one atom to the other atom. Definition of electron transport chain - The biological process where a chains… -
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle | Krebs Cycle | Steps | End Products |Diagram
Jan 28, 24 12:39 PM
This is a type of process which execute in a cyclical form and final common pathway for oxidation of Carbohydrates fat protein through which acetyl coenzyme a or acetyl CoA is completely oxidised to c… -
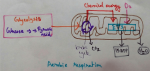
Aerobic Respiration | Definition of Aerobic Respiration | Glycolysis
Dec 15, 23 08:42 AM
This is a type of respiration where molecular free oxygen is used as the final acceptor and it is observed in cell. Site of Aerobic Respiration - Aerobic respiration is observed in most of the eukaryo… -
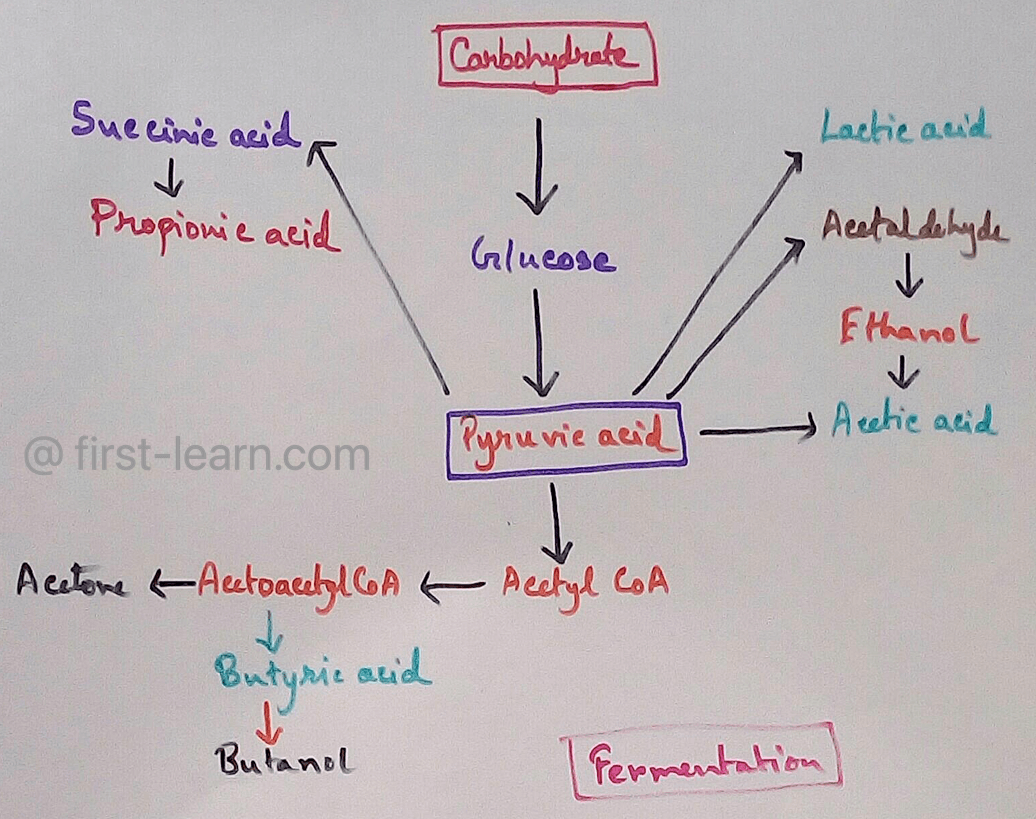
Fermentation | Definition | Types of Fermentation | Application
Nov 29, 23 10:27 PM
Definition of fermentation- It is a process that is energy yielding process of anaerobic oxidation of organic compounds which are carried out by the enzyme action of micro organisms where neither gase…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.