Measurement of Volume
We will discuss here about the methods of measurement of volume of a substance. Liquid substances do not have any specific shape. It takes the shape of the container in which it is kept. So we cannot measure liquid with a measuring tape or a scale. But we can measure the volume of a liquid very easily.
We know the volume of a substance is the space occupied by it. The unit used for measuring the volume of a liquid is liter (I). We use this unit to measure volume of milk, water, etc. To measure the volume of smaller quantity of liquid like medicines, chemical substances, etc., we use milliliter (ml). It is a very small unit of volume. One thousand milliliters make a liter.
Liquid occupies the space in any container it is kept. So we can measure the volume of a liquid with the help of a graduated container. It is called a measuring cylinder. It is a glass jar with a flat base having equal diameter all along its length. The wall of the cylinder is graduated in milliliter.
To measure
the volume of a liquid we have to pour the liquid within the measuring cylinder
and observe the upper surface of the liquid perpendicularly. The mark in the
graduation that coincides with the top level of the liquid, indicates its
volume in milliliter. With different measuring cylinders we can measure liquid
from 50 ml to 500 ml.
To measure volume of petrol, kerosene, etc., typical cone shaped measuring containers are used. Such containers are of different sizes and are used to measure different quantities of liquid. The size of the containers may vary from 500 ml to 5 liters.
From Measurement of Volume to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Respiratory Balance Sheet | TCA Cycle | ATP Consumption Process
Feb 18, 24 01:56 PM
The major component that produced during the photosynthesis is Glucose which is further metabolised by the different metabolic pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, TCA cycle and produces energy whic… -
Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation | ETC |Diagram
Feb 04, 24 01:57 PM
It is also called ETC. Electron transfer means the process where one electron relocates from one atom to the other atom. Definition of electron transport chain - The biological process where a chains… -
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle | Krebs Cycle | Steps | End Products |Diagram
Jan 28, 24 12:39 PM
This is a type of process which execute in a cyclical form and final common pathway for oxidation of Carbohydrates fat protein through which acetyl coenzyme a or acetyl CoA is completely oxidised to c… -
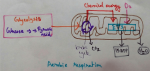
Aerobic Respiration | Definition of Aerobic Respiration | Glycolysis
Dec 15, 23 08:42 AM
This is a type of respiration where molecular free oxygen is used as the final acceptor and it is observed in cell. Site of Aerobic Respiration - Aerobic respiration is observed in most of the eukaryo… -
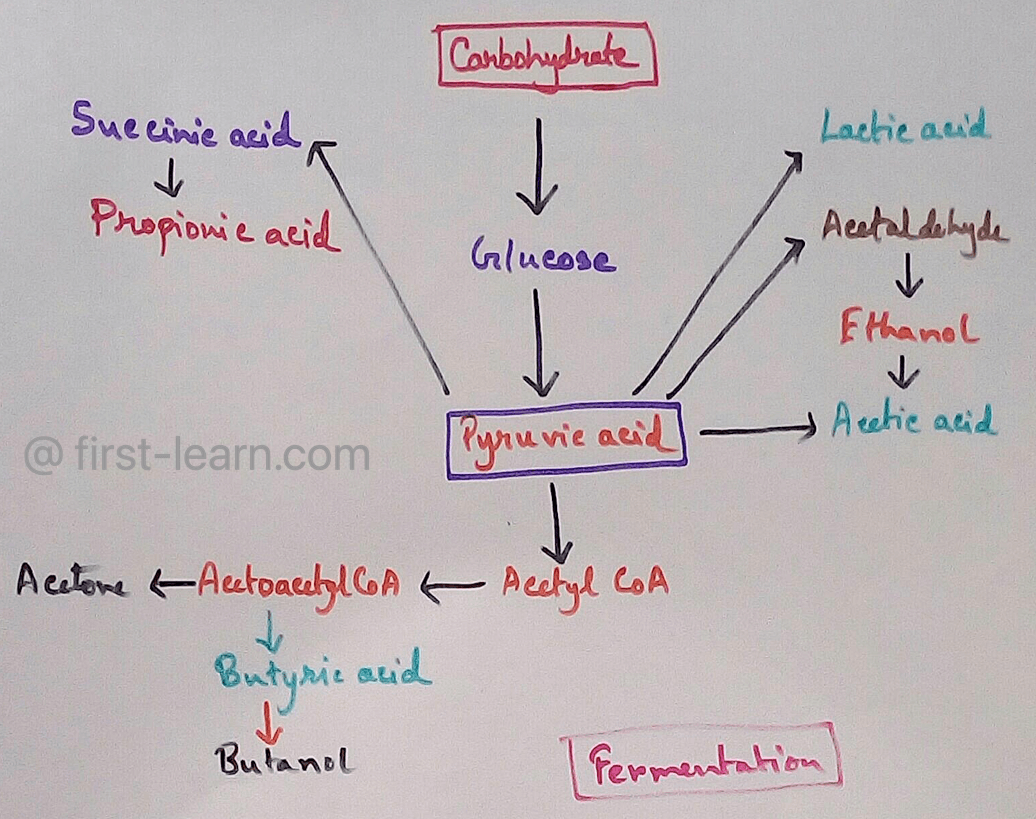
Fermentation | Definition | Types of Fermentation | Application
Nov 29, 23 10:27 PM
Definition of fermentation- It is a process that is energy yielding process of anaerobic oxidation of organic compounds which are carried out by the enzyme action of micro organisms where neither gase…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.