The Earth’s Water
We will discuss about the Earth’s water. We know about three-fourths of the Earth’s surface is covered with water. It is present in oceans, seas, rivers, lakes and ponds. It is also present under the Earth’s surface as ground water. Water is very important for life. All living things need water to live.
Most of the water available on the Earth cannot be used by us for drinking. The water in seas and oceans is salty. At most places, the water in rivers and lakes is not clean enough to drink. It contains dirt and germs. It is said to be polluted water. Water gets polluted because wastes from our houses and factories are allowed to flow into rivers and lakes.
Polluted water has dirt and germs in it. Drinking polluted water can cause several diseases. Dirt and germs have to be removed to make the water fit for drinking. Water from a river or lake is pumped into the waterworks in the city. Here it is passed through filters to remove dirt.
Special substances such as bleaching powder are added to kill germs. The clean water is then pumped into our homes. Clean water is very precious. It should not be wasted.
From The Earth’s Water to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Respiratory Balance Sheet | TCA Cycle | ATP Consumption Process
Feb 18, 24 01:56 PM
The major component that produced during the photosynthesis is Glucose which is further metabolised by the different metabolic pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, TCA cycle and produces energy whic… -
Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation | ETC |Diagram
Feb 04, 24 01:57 PM
It is also called ETC. Electron transfer means the process where one electron relocates from one atom to the other atom. Definition of electron transport chain - The biological process where a chains… -
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle | Krebs Cycle | Steps | End Products |Diagram
Jan 28, 24 12:39 PM
This is a type of process which execute in a cyclical form and final common pathway for oxidation of Carbohydrates fat protein through which acetyl coenzyme a or acetyl CoA is completely oxidised to c… -
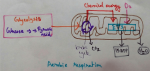
Aerobic Respiration | Definition of Aerobic Respiration | Glycolysis
Dec 15, 23 08:42 AM
This is a type of respiration where molecular free oxygen is used as the final acceptor and it is observed in cell. Site of Aerobic Respiration - Aerobic respiration is observed in most of the eukaryo… -
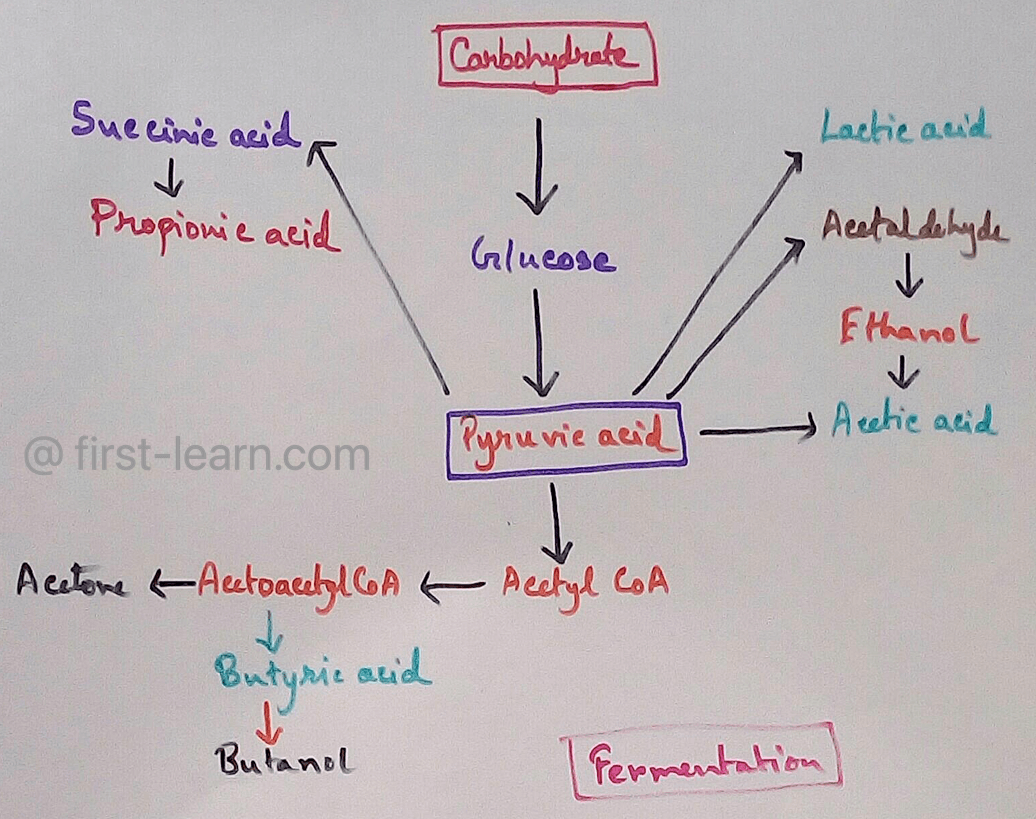
Fermentation | Definition | Types of Fermentation | Application
Nov 29, 23 10:27 PM
Definition of fermentation- It is a process that is energy yielding process of anaerobic oxidation of organic compounds which are carried out by the enzyme action of micro organisms where neither gase…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.