Angiosperms
The plant group that shared possession of flower like reproductive characters are called anthophytes. The group consider anthophytes are Bennettiales, gametophytes and angiosperms. About 2,35000 angiosperms are discovered. Among them 65,000 are monocot and 1,65,000 are eudicot species.
Characteristics of angiosperms:
1. Formation of flowers with closed carpels.
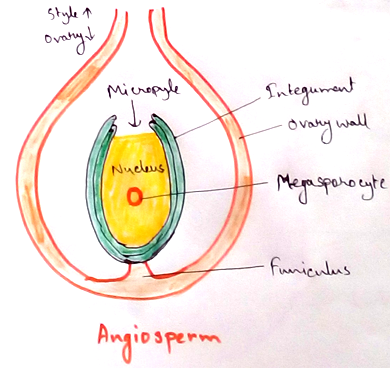
2. Double fertilization leading to endosperm formation.Macrosporophylls becomes modified into stamens while megasporophyls have produced carpel with stigmatised surface for receiving pollen grains.
3. A three nucleate micro gametophyte and an eight nucleated megagametophyte.
4. Stamens contain two pairs of pollen sacs. Female gametophyte is called embryo sac.It is 8 nucleate and 7 celled where archegonium is absent.
5. The presence of sieve tubes and companion cells in the phloem.
6. Angiosperms are divided into two – monocot and dicots due to presence of their umber of cotyledons.
Basic characteristics of monocots are:
(i) Plants with single cotyledons.
(ii) Radical aborting early in growth with the development adventitious root system.
(iii) Vascular bundles are complex andrarely showing secondary growth.
(iv) Leaves with parallel venation.
(v) Flowers are 3 merous.
(vi) Pollen grains usually monosulcate.
(vii) Sieve cell plastid with several cuneate protein crystals.
(viii) Pollens are monoaperturate.
(ix) Monocots are different types. They are:
1. Orchidaceae – Largest family of this category which contain flowering plants.
2. Poaceae – About half of the as many species are made up of true grass. Economically they are important because it includes grain (rice, bamboo, wheat, maize etc) which have economic importance.
3. Arecaceae - Some crops and palms are included in this category.
4. Musaceae - This include banana, plantain, ginger etc.
5. Zingiberaceae – This also contain some products like turmeric and cardamom.
6. Asparagaceae – Asparagus included in this category.
7. Bromiliaceae – Pine apples belong to this category.
8. Cyperaceae – Water chestnut are included in this category.
9. Amaryllidaceae - This category includes leeks, onion, garlic etc which have economic importance.
Basic characteristics of dicotyledon are:
1. Plants with two cotyledons are called dicotyledon plants
2. Radical, giving rise to mature root system and not aborting.
3. Vascular bundles in ring and often showing secondary growth.
4. Leaves with reticulate venation pattern.
5. Flowers four or five merous.
6. Pollen grains predominantly tricolpate or modifications there of.
Dicotyledon can be divided into different category. They are:
1. Eudicoits - It is monophyletic group having tricolpate pollen.
2. Magniliids - It represents families of dicotyledon including Magnoliales, Laurales and Illiciales.
3. Amborella – Molecular phylogenetic put it as sister of other flowering plants as it hasdifferent types of xylem than other plants.
4. Nymphaeales - It is aquatic, rhizomatous herbs, with laticifers, placentation parietal and seeds are usually operculate.
5. Austrobaileyales - Woody vines mostly found in tropical and temperate zone.
6. Chloranthales – They are fragrant herbs or shrubs which have the medicinal properties.
7. Ceratophyllum - It is unique among angiosperms. As it passes in life cycle completely underwater. This interesting feature indicates its primitive ness.
Question and answers on Angiosperms:
Which is the largest angiosperm of the world?
Some species of Eucalyptus may reach up to 100 meters in height with trunks near 20 meter in girth.
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.