First Learn Blog
This page will let you know our latest added and the updated pages to my website. Visiting this page will update you with what we have added recently.
Feb 03, 2026
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water.
Continue reading "Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants"
Jan 15, 2026
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood platelets.
Continue reading "Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils"
Nov 07, 2025
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means of pumping activity of heart. An adult human contains almost 5 litres
Continue reading "What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol"
Oct 28, 2025
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of this track specially very common for lungs.
Continue reading "Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema"
Oct 14, 2025
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like inspiratory area pneumotaxic area ,expiratory area, chemosensitive area.
Continue reading "Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |"
Oct 09, 2025
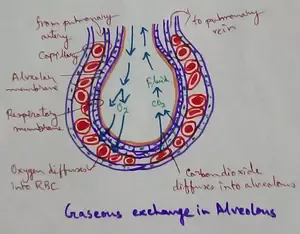
Explain Transport of Gases | External Respiration | Tissue Respiration
In humans gaseous exchange is completed in the following ways the steps are - External Respiration or Breathing - Breathing in false taking in of Oxygen and giving out of carbon dioxide in the body. Mechanism of breathing can be divided into two parts that is inspiration
Continue reading "Explain Transport of Gases | External Respiration | Tissue Respiration"
Sep 11, 2025
Kind and Number of Teeth | Location of Teeth in Mouth | Care of Teeth
Kind and Number of Teeth
Continue reading "Kind and Number of Teeth | Location of Teeth in Mouth | Care of Teeth"
Sep 10, 2025
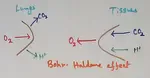
The Gaseous Exchange | Transport of Oxygen | Haldane Effect |
Oxygen carrying capacity of blood is 20 ml for 100m but 3% of dissolved in plasma and 97% of the oxygen combines with haemoglobin to form a loose reversible Complex called oxyhaemoglobin and is transported from one tissue to another via blood.
Continue reading "The Gaseous Exchange | Transport of Oxygen | Haldane Effect | "
Sep 10, 2025
Respiratory Volumes and Capacities | Tidal Volume | Dead Space
Explain respiratory volumes and capacities: Tidal Volume - Tidal volume is the volume of air inspired or expired in relaxed or resting position. Amount of tidal volume is about 500 m and it consists of 150 ml of Dead Space volume and 350 ml of alveolar volume.
Continue reading "Respiratory Volumes and Capacities | Tidal Volume | Dead Space"
Aug 17, 2025
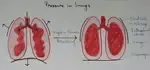
Mechanism of Breathing | Definition of Inspiration and Expiration
Breathing is the process which is accomplished in three states that is inspiration expiration and pause . Definition of inspiration - Entry of air into the lungs from outside during breathing is called inspiration
Continue reading "Mechanism of Breathing | Definition of Inspiration and Expiration"
Aug 04, 2025
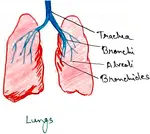
Human Respiratory System | External Nares | Nasal Cavity | Pharynx
Definition of respiration - This is the process of making energy available to organisms and their living cells through enzyme controlled catabolic breakdown of organic molecules. The organic materials that give energy during catabolism are called respiratory substrates.
Continue reading "Human Respiratory System | External Nares | Nasal Cavity | Pharynx"
Jul 16, 2025
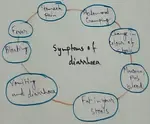
Disorders of Digestive System | Symptoms of Jaundice | Vomiting |
Jaundice- It is a disease that occurs due to Umesh discoloration of the skin due to deposition of bilirubin and biliverdin pigment. Jaundice can be offered according to the different position like prehepatic jaundice, intrahepatic jaundice and post hepatic jaundice.
Continue reading "Disorders of Digestive System | Symptoms of Jaundice | Vomiting | "
Jul 09, 2025
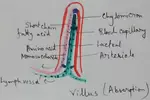
Absorption of Digested Products | Absorption of Water | Nephrons
Food and water is observed in different parts of the body and is distributed in different cells and tissues. Absorption of food is observed to be observed in the small intestine in the specific type of cell which is allotted for the absorption are called the villi
Continue reading "Absorption of Digested Products | Absorption of Water | Nephrons"
Jun 27, 2025
Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Biology
Eleventh grade biology has been designed in accordance with the recommended topics. We will cover all the topics in biology very exciting and interesting way.
Continue reading "Eleventh Grade | Eleventh Grade Science | Eleventh Grade Biology"
Jun 27, 2025
Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach
Before the digestion is start by the different enzymes secreted from the different digestive glands food must be turned and chut or mixed with saliva inside the mouth.
Continue reading "Explain Digestion of Food | Salivary Glands | Oesophagus | Stomach"
Jun 21, 2025
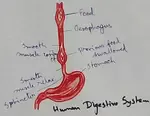
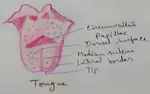
Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth
Digestive system is a system of alimentary canal and digestive glands. Alimentary canal- alimentary canal is a tube of variable diameter having muscular wall and glandular epithelial tissues which starts from a mouth and ends at anus. It is made up of mouth vestibule
Continue reading "Explain Human Digestive System | Mouth | Tongue | Pharynx | Teeth"
Jun 18, 2025
Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization |
Definition of vernalisation- The change of flowering habit due to the low temperature treatment is known as vernalisation. This is a physiological process which was denoted by Clipart in 1857 invite but later it was explained and named by Lysenko in 1928.
Continue reading "Vernalisation in Plants | Definition | Mechanism | Devernalization | "
Jun 15, 2025
The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates
What are the food that we should eat? Find out the names of ten food items in the word maze. Write the names in the correct column of the table given below. Food we get from plants Food we get from animals fish, egg, milk Why do we need food? All living things need food to
Continue reading "The Food We Eat | Food we Get from Plants and Animals | Carbohydrates"
Jun 10, 2025
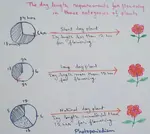
Photoperiodism Long Day and Short Day Plant |Definition of Phytochrome
Definition of photoperiodism- photoperiodism is a process where the response of a particular flowering plant to the effective day length with respect to flowering occurs. In 1920 and in 1922 Garner and Allard in a variety of soybean made some experiments for understandin
Continue reading "Photoperiodism Long Day and Short Day Plant |Definition of Phytochrome"
Jun 09, 2025
Physiological Effects of Plant Growth Regulators | Auxin, Gibberellins
Internal regulators of growth and development internal regulator of growth and development are genetic factors and growth regulator as these are important internal regulator. Best genetic factors are transmitted from one generation to another in the living organisms.
Continue reading "Physiological Effects of Plant Growth Regulators | Auxin, Gibberellins"
Apr 27, 2025
Characteristics of Plant Growth Regulators | Definition | Functions |
Definition of plant growth regulators- This are very small molecules synthesized from the cells of different parts which are associated with the plant cell growth. Growth in unicellular organism employees the increase in volume or increasing the number of organisms.
Continue reading "Characteristics of Plant Growth Regulators | Definition | Functions | "
Apr 22, 2025
Plants Development | Definition | Leaf Development | Factors Affecting
Definition of development- development is a biological process which can be defined as the process in which there is sequence of qualitative changes towards a higher or more Complex state.It consists of all the changes an organism have to undergo from the time of birth till
Continue reading "Plants Development | Definition | Leaf Development | Factors Affecting"
Apr 21, 2025
Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation | Definition
Cells from the root apical meristem and shoot apical meristem the camera that differentiate , mature to perform different functions. This process by which the cells undergo different major structural changes or few structural changes both in their protoplasm
Continue reading "Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation | Definition"
Feb 27, 2025
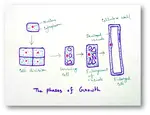
Explain about Growth in Plants |Definition of Growth & Differentiation
Growth is a permanent increase in length or volume of an organism that brought upon by an increase in its dimensions due to synthesis of new protoplasmic material.
Continue reading "Explain about Growth in Plants |Definition of Growth & Differentiation"
Dec 02, 2024
Definition of Respiratory Quotient | calculation | Application | Plant
Definition of respiration quotient- the ratio of the carbon-dioxide evolved to that of the oxygen consumed by a cell, tissue, plants or animals in a given time is called respiratory quotient. It is used for the basal metabolic rate in the living organisms when the BMR
Continue reading "Definition of Respiratory Quotient | calculation | Application | Plant"
Jun 06, 2024
Amphibolic Pathway | Definition | Examples | Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Definition of amphibolic pathway- Amphibolic pathway is a biochemical pathway where anabolism and catabolism are both combined together. Examples of amphibolic pathway- there are different biochemical reactions system as amphibolic pathway.
Continue reading "Amphibolic Pathway | Definition | Examples | Pentose Phosphate Pathway"
Feb 18, 2024
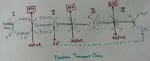
Respiratory Balance Sheet | TCA Cycle | ATP Consumption Process
The major component that produced during the photosynthesis is Glucose which is further metabolised by the different metabolic pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, TCA cycle and produces energy which is then utilise by the organism for their different physiological
Continue reading "Respiratory Balance Sheet | TCA Cycle | ATP Consumption Process"
Feb 04, 2024
Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation | ETC |Diagram
It is also called ETC. Electron transfer means the process where one electron relocates from one atom to the other atom. Definition of electron transport chain - The biological process where a chains of redox reaction take place as electrons are transferred from the
Continue reading "Electron Transport System and Oxidative Phosphorylation | ETC |Diagram"
Jan 28, 2024
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle | Krebs Cycle | Steps | End Products |Diagram
This is a type of process which execute in a cyclical form and final common pathway for oxidation of Carbohydrates fat protein through which acetyl coenzyme a or acetyl CoA is completely oxidised to carbon dioxide and ultimately water is known as tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Continue reading "Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle | Krebs Cycle | Steps | End Products |Diagram"
Dec 15, 2023
Aerobic Respiration | Definition of Aerobic Respiration | Glycolysis
This is a type of respiration where molecular free oxygen is used as the final acceptor and it is observed in cell. Site of Aerobic Respiration - Aerobic respiration is observed in most of the eukaryotic cells that starting from unicellular organisms to those found in higher
Continue reading "Aerobic Respiration | Definition of Aerobic Respiration | Glycolysis"
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…















New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.