Bones and Muscles
Bones and muscles give our body a definite shape. Here we will learn about the different parts of our body and their postures.
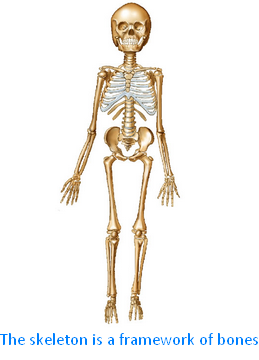
Bones: All parts of the body are held together by bones. Our bones together form the skeleton. Skeleton is the framework of bones in the body. The skeleton gives our body its shape.
When we born we had more than 300 bones.
Some of these will join together and when we are grown up we have 206 bones. So, there are 206 bones in our body. Thigh has the longest bone. Bones support and protect the soft inner body parts. The place where two or more bones meet is called a joint. We can bend our body at the joints like elbow joint.
|
Muscles:The soft parts below the skin are the muscles. Muscles are attached to the bones. Bones and muscles work together and help us to move, walk, run and cycle. Muscles become strong when we use them regularly. |
Let us learn how different exercise and body postures can make our body healthy and strong.
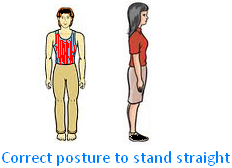
Postures:Posture is the position to hold our body when we stand, sit or move about.
|
How to stand? To stand in the correct posture we need to: (i) Stand erect with the back straight, chin in and chest out. (ii) Put the weight of our body evenly on the feet. |
|
How to sit? To sit in the correct posture we need to: (i) Sit up against the back of the chair with our back straight.
(ii) Keep our feet flat on the floor. (iii) Do not bend or stoop our body or shoulders. |
|
How to walk? To walk in the correct posture we need to: (i) Walk straight with our shoulders thrown back and head held high.
(ii) Swing our arms freely. |
A good posture gives proper shape to our body and keeps us healthy.
From Bones and Muscles to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…








New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.