Cockroach
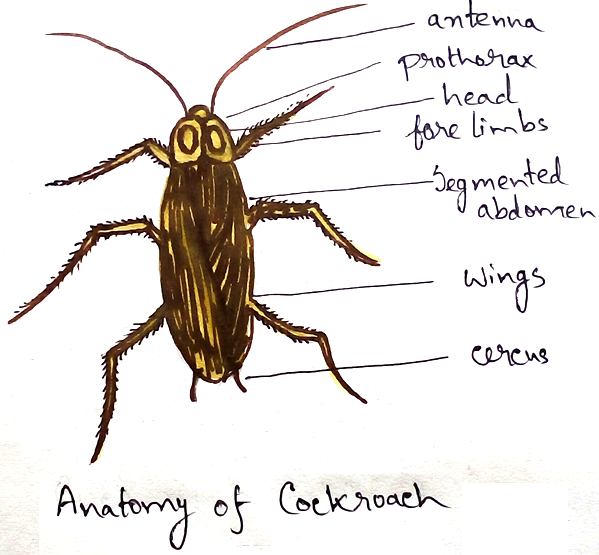
Morphology - Body of cockroach is dorsoventrally compressed and mathematically segmented. Entire body is divided into head, thorax and abdomen. Head contains pair of antennae, a pair of compound eyes and a pair of fenestrae. Thorax contains three segments. Each bears a pair of legs ,two pairs of wings (which is present on the thorax portion). Abdomen of consists of ten segments. Mouth part consists of labarum, maxillae, mandibles and hypo pharynx.
Body cavity - body cavity (haemocoel) is filled up with haemolymph.
Sensations – They have sensillae or receptor s, each of them has sensory cell, nerve fibres, a trichogen and a few hair membrane or tormogen cells. Different receptors are observed in their body. Different type of receptors are-
Thigmoreceptors – Antennae and bristles present on legs , cerci, body and maxillary palps.
Olfactory receptor - present mostly on antennae.
Gustatoreceptors – palps of maxillae and labium.
Thermoreceptors – Pads between first four tarsal segments of legs.
Auditory receptors - Air borne vibrations on anal cerci.
Photoreceptor - It is found in eyes.
Digestive system: Alimentary canal of digestive system consists of
1. Stomodaeum or fore gut – It is lined by cuticle internally consists of mouth, pharynx, crop and muscular gizzard.
2. Mesenteron or mid gut- Short tubular part lined by endoderm . At its anterior end there are eight blind glandular hepatic caeca which secrets enzyme that is required for digestion.
3. Protodaeum or hind gut- It consists of ileum, colon, rectum,anus. Malpighian tubules occur at the junction of midgut and hind gut. Internally it is lined by cuticle and the coiled secrets digestive enzymes. It is omnivorous by nature and appropriate digestive enzymes are secreted by salivary gland and hepatic caeca.
Respiratory system: It consists of a network of branched closed tubes called trachea and ten pairs of spiracles. Two spiracles are combined to form thoracic and eight spiracles combined to form abdomen. Trachea and it’s branches are supported by chitinous rings. The finer tracheoles are devoid of chitinous rings. This are partially filled with tissue fluid and help in carrying air to tissue directly.
Circulatory system: Circulatory system of
cockroach is open type (blood do not flow in blood vessels, it is carried in
haemocoel). This haemocoel can be divided into three chambers. The three
chambers are – upper pericardial sinus, middle perivsceral sinus and lower
perineural sinus. This chamber is divided into two perforated dorsal and
ventral diaphragms. Blood is called haemolymph. Haemolymph does not contain any
pigment so, it does not take part in respiration. It conducts food, excretory
materials and hormones. Heart of cockroach is elongated, tubular and pulsatile
organ which is composed of narrow anterior aorta and thirteen segmentally arranged
funnel shaped chambers , perforated by Ostia. Conical alary muscles that are twelve pairs in number are
attached to the dorsal diaphragm which causes straightening of the heart and
causes circulation of the blood. Heart beats or pulsation are 49 per minute.
Excretion - Excretory organ of the cockroach is malpighian tubules, which are present in groups of 6 to 8 at the junction of mesenteron and proctodaeum help in excretion( 60 to 150 in number). Uric acid is produced as excretory product. Excretory product is uptaken by the malpighian tubules from the hemolymph.
Nervous system: Nervous system is well developed and is consists of.
Cerebral or supra oesophageal ganglion which is known as brain . Which is formed due to union of six ganglia.
Sub oesophageal ganglia.
Paired circumstances oesophageal connectives.
Double ventral nerve chord with three thoracic and six abdominal compound segments ganglia (except in fifth abdominal ganglia).
Reproductive systems – Cockroaches are dimorphic animals (insects). That means sexes are separate with very clear sexual dimorphism.
Male reproductive system- Male reproductive parts are – testes, vasa deferentia, Utricularia gland, ejaculatory duct, plallic or conglobate gland, male gonapophysis.
Testes – There are two pairs of testes in fourth and sixth abdominal segments. Each testes consists of 30 -40 small vesicles which form sperms. This in the most important reproductive parts of male organism. It
Vasa deferentia – The two vasa deferentia open into ejaculatory duct and each testes leads into a bad deferens.
Mushrooms or utricular glands – It is large compound gland that is formed from long tubules or utricular majores by formation of inner layer of spermatophore, small tubules or utriculi brevivores for nourishing sperm and small bulb like seminal vesicles for storing sperm.
Ejaculatory duct- It is a muscular tube which is opened at the male genitalial pore on ninth sternum.
Phallic or Conglobate glands – Phallic duct is an accessory gland which opens, near the male genitalial pore by phallic duct.Secretion from this gland forms covering of spermatophore.
Male Gonapophysis- this is three chitinous plates called phallomeres. Phallomeres are situated around the male genitalial pore. These are called left phallomeres, right phallomeres and ventral phallomeres.
Female reproductive system - Main parts of the female reproductive systems are ovaries, oviduct, vagina, spermatheca, genital or brood pouch, colleterial glands, female gonapophysis.
Ovaries: In the 4th and 6th abdominal segments of every female Cockroaches contain a pair of ovaries. Each ovary contains 8 ovarioles.
Oviduct – Oviduct are short tube paired that help in carrying ova from ovaries.
Vagina: both of the oviduct fuse to form vagina that opens in female genital aperture on 8th sternum.
Spermatheca – Two of this are joined basally. Only the left is developed for storing sperm.
Genital or brood pouch –It is formed by 7th sternum and has openings of colleterial glands, spermathecae and gonophore. Gonapophysis are also occurred in it.
Colleterial glands - They are branched tubular glands. Both of them open into brood pouch which produces scleroprotein for ootheca.
Female gonapophysis: This are six chitinuous structures which form ovipositor or egg laying apparatus.
Copulation or fertilization or development – The sperms are transferred to spermatheca of female sixteen eggs are laid in two rows in the brood pouch. Sperms are shed over them. Fertilization occurs in brood pouch. The fertilized eggs are enclosed in purse –shaped ootheca. Nymphs emerge out of ootheca. They are alike parent except they are small and wingless. After gradual metamorphosis each gives rise to an adult cockroach.
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.