Fabaceae Family
Characteristics features of fabaceae:
1. Plants of this family are herbs, shrubs, vines or climbing by twining or tendrils .
2. Root contains root nodules that have nitrogen fixing bacteria (rhizobium) and frequently non protein amino acids are found.
3. Leaves are mostly pinnatus and are spirally arranged, pulvinas of leaf and individual leafletsare well developed.
4. Leaf axis and leaflets usually showing sleep movements.
5. Stipules which are present are sometimes large or are represented by spines.
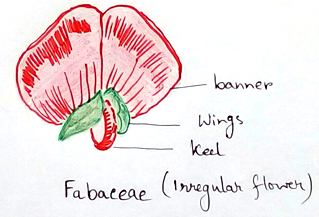
6. Flowers are usually bisexual, petals are regular or irregular cup shaped hypanthium. Petals are generally five in number.
7. Sepals are usually five in number, free or more commonly connate when a tube with usually valvate lobes or often bilabiate.
8. Irregular petals are – Adaxial small and lying within its laterals in I or large (standard) and outside them (resupinate occasionally) in III.
9. This is imbricate or basally connate, regular and usually valvate.
10. Androecium is with one to numerous stamens but usually ten, hidden by perianth to long- exerted and sometimes showy filaments distinct or connate.
11. If connate is monodelphous or diadelphous , pollen grains are tricolporate, tricolpate or triporate.
12. Gynoecium of one carpel, distinct, usually elongate and with a short gynophore.
13. Ovary is superior with parietal (marginal) placentation.
14. Ovules are anatropous to campylotropous.
15. Fruits are usually legumes.
16. Seeds are hard exotextal, embryo straight to curved with no or less endosperm.
Diagnostic features of the subfamilies of Fabaceae:
They can be divided into three subfamilies –
Mimosoideae – They are shrubs to trees and sometimes occasionally herbs. Leaves are bipinnately compound and the flowers are actinomorphic. Corolla is not radially valvate. Stamens can be minimum ten and maximum upto infinity. Pollen are monads, tetrads or polyads. Seeds are with U- shaped line.
Caesalpinioideae – Plants of this subfamily is trees to shrubs. Occasionally herbs. Leaves are usually pinnately or bipinnately compound. Flowers are more or less distinctly zygomorphic. The upper petals (standard), positioned within the adjacent lateral (wing) petals. Corolla is usually bilateral imbricate and usually showy. Pollen grains are monads stamen are ten in number. Seeds are without Using shaped line.
Papilionoideae – They are herbs, shrubs and. Leaves are pinnately compound to trifoliate occasionally unifoliate. Flowers are more or less zygomorphic – the upper petal (standard) positioned outside the lateral (wing ) petals. Corolla is bilateral vexillary and is showy. Stamens are ten or 9+1. Pollen is monads. Seeds are without U-shaped line.
Economic importance of fabaceae family:
Timber yielding plant – Indian blackwood, Sheesham, Iron wood, Siris, Australian blackwood.
Oil yielding plant - Soybean oil, ground but oil is extracted from some plants of the family.
Dye yielding plant - Dyes like indigo and haematoxylin is also derived from the plants.
Pulses yielding: Lentil, Masur, green gram, pea, chick pea, black gram, urd, mung, pigeon pea, arhar etc. are derived from the plants which are belong to this family.
Medicinal importance - Senna alata uses for skin diseases and vermifuge. Castamospermum australeis monitoring as the probable vaccine for AIDS. Glycyrrhiza glabra used as cough mixture.
From Fabaceae Family to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.