Frogs
Structure and Morphology -
Frogs are the classes of tetra pods which are placed at the first category of vertebrates. According to some scientist it is appeared during the Carboniferous era. These are included in amphibian’s category as their one phase of life is dependent on water and the other phase is on land. The larval stage of the toad means tadpoles are dependent on water as they contain gills for the breathing and also contains tails for swimming. On the other hand when it grows up, tails are abolished and they breathe through lungs and skin due to lack of their gills.
Their body is suitable for camouflage means changes their body color with the color of environment.
Structure of frog:
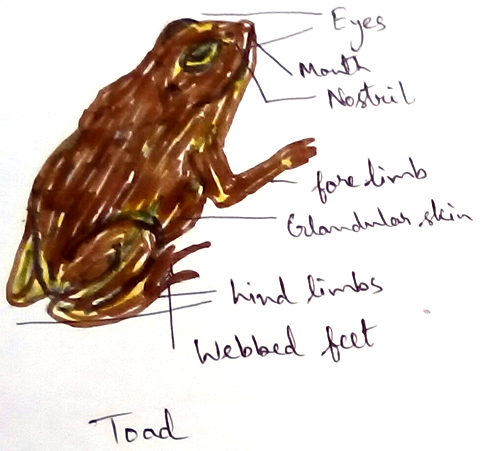
Shape- its body is divided into head and trunk. Head is triangular in shape contains a conical portion called snout. It has one pair of nostrils, one pair of tympanic membrane, one pair of vocal sac.
Limbs -
It contains two pairs of limbs. In the front portion of the trunk contains one
pairs of limb. Front limb is made up of upper arm, lower arm and menus. This
portion contains three digits in each hand without thumb. Though male frog
contains a special portion which is known as copulatory organ to grip the
female during breeding. This portion become increase during the breeding season
in male toad. Rainy season is the appropriate time for their breeding.
The hind limbs are also two in numbers. They contains three parts . Hands portion contain four digits which are also connected by thin membrane that helps in swimming. These are called webbed feet.
Skin - upper surface of the skin contains many glands which is associated with secretion. Among them there are mucous glands, parotid glands, submucous gland.
Tympanic membrane - These are present just behind the two eyes. This can feel the vibration of the sound wave. So, they are act as the auditory organs.
Nostrils - Frogs contain one pair of nostrils in front of the mouth. There are another pair of internal nostrils just above the buccopharengeal cavity.
Teeth – Teeth of frogs are premaxilary, maxillary. They are all of same kind thus and are changed in different times as the older one replaced by the new one. It is remain embedded in the jaw. Frog takes insects, crustaceans, larva etc as their food.They take the food then chew, masticated and then enter it into the oesophagus.
Eye - Eye contains three layer of membrane. Last two membranes are involved for proper vision from opaque to translucent. The third membrane is associated with the protection of the eyes from mud, dust, etc. This is also called nictinating membrane.
Vocal sac- It is a balloon like structure which is able to produce sound. It is bigger in case of male frog . Male frog sounds loudly to attract female frog during mating in rainy season. It Is situated just beneath the lower jaw.
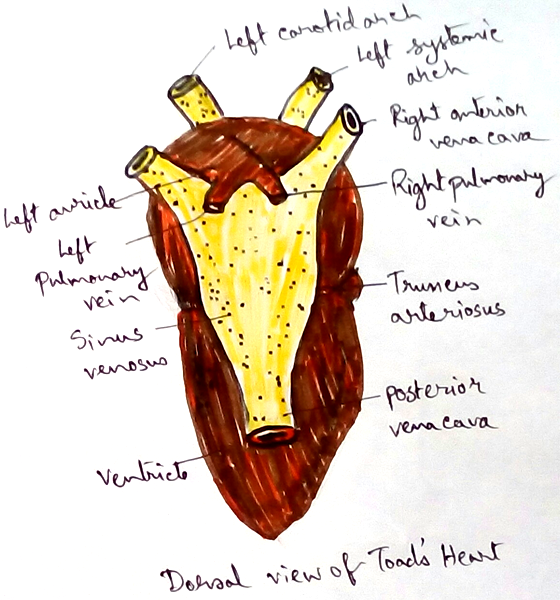
Heart- Frogs have three chambered heart. So there are mixing of pure and impure blood takes place. It contains two auricles and one ventricle.
Some physiological activities -
Systems in the body - It has alimentary system, circulatory system, reproductive system, respiratory system.
Alimentary system- this system consists of mouth, oesophagus, stomach, intestine, pancreas, liver etc. Their tongue is remain attached in the front portion and free at the back. When any organisms come in front of the frog it takes out the tongue and put it in the prey.As a result the sticky portion of the tongue stuck on it and they insert the tongue. Alimentary canal ends in the cloacal aparture.
Respiratory system - They have three types of respiration. These are –
Cutaneous respiration- Frogs skin is made up of thin layer of cells and contains large amount of blood vessels network. These networks of the skin helps in the gaseous exchange between body of frog and environment. When the frog is in water it’s body became moist and the oxygen can dissolved in the skin and enter the body. When the skin is dry mucous continuously secreted from the body and keep the body moist which help the oxygen to dissolve and enter into the body.
During hybernation and aestivation frogs remain inactive and respiration is occur through cutaneous .
Buccal respiration- Buccal respiration is observed in frog. It happens through buccopharengeal cavity.
Pulmonary respiration- pulmonary respiration takes place with the help of lungs. In this type of respiration oxygen enter the body through the nostrils and lungs took part in gaseous exchange for respiration. Frog does not contain diaphragm or rib cages. So respiration occurs by decreasing the lungs and pressure
Body temperature and hibernation- Frogs are belong to amphibians category as their blood is cold blooded. They donot have any mechanism to control their body temperature. So they go to hibernation during winter season. That time they remain inactive without taking food and breathing is done through skin.
They can also do aestivation during summer. Due to high temperature they are not able to cope up with the environment and under goes aestivation.
Excretory system - Excretory system of frog is made up of ureter, kidney, bladder and exit into cloaca. Excretory substance of the frogs body is filtered by kidney, then it is removed from the body. Urine is transferred from kidney to the bladder via urethra and then released from the body by cloaca. Urethra is a tube like structure that connects kidney to the bladder.
Reproduction - In frogs male and female are separated body.In case of frogs sexual reproduction takes place.Female frog lay eggs in the water and male frog release the sperm in water.External fertilization takes place as the mating of sperm and ovum takes place outside their body in water.In this time both male and female frog placed in a specific posture to make sure that the sperm transfer takes place in proper way and it fertilized the egg. After fertilization larva is developed from the egg and give birth to the tadpoles. From tadpoles due to morphogenesis adult toad appears.
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.