Kingdom Animalia
Animal kingdom classify into chordata and nonchordate.
Characteristics of nonchordates are-
1. They do not have no to chord throughout their life.
2. Non chordata are lack of nerve chord
3. They don’t have closed circular system.
4. Maximum of them is lack of trophoblastic layer. Annelid develop true coelomate.
5. Non chordata can be divided into –
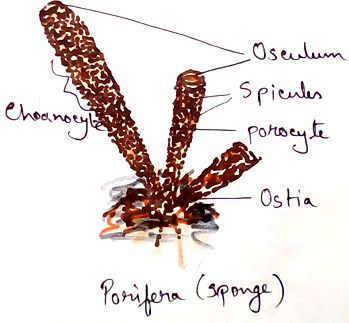
Poriferan
1. They are fixed under the ocean.
2. Their body contains many pores called Ostia and osculum
3. Their body surface has many pores by which transport of food, water,gas by diffusion.
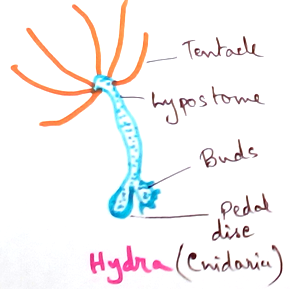
Cnidaria
1. Animals are radially symmetrical.
2. Diplomatic means two layer and first canal system observed.
3. Shows tissue grade of organisation.
4. All of them are aquatic. Some of them are free floating (jellyfish) and some of them are attached to the ocean floor (Hydra).
5. Cnidoblast cell or stinging cells present.
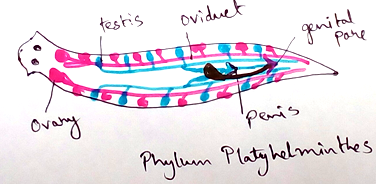
Platyhelminthes
1. Animals are flat bilaterally symmetrical with no body cavity (acoelomates)
2. Most of them are parasites and contain hook and sucker to remind attached with other animals.
3. Only one opening or mouth is present.
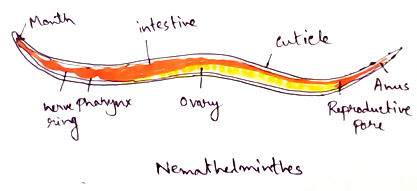
Nematoda
1. They are bilaterally symmetrical and the body is unsegmented
2. long and cylindrical
3. respiratory and circulatory systems are absent.
4. Ascaris or roundworm
Annelid
1. Segmented and bilaterally symmetrical.
2. They have true coelomate.
3. Digestive, circulatory, excretory system are well developed.
4. Earth worm is an example.
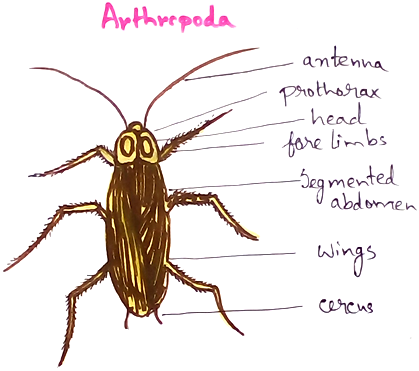
Arthropods
1. It is the largest phylum about 75%.
2. They have segmented body, jointed legs, compound eyes
3. Exoskeleton is covered by chitin.
4. They undergo moulting (shedding and regrowing) of exoskeleton.
5. They are divided into Insecta, Myriapod, Arachnida, crustaceans.
Mollusca
1. Body is soft and unsegmented.
2. It is enclosed in calcareous shell.
3. Contains muscular feet called mantle.
Echinodermata
1.The adults are radially symmetrical.
2. Whereas larvae has bilateral symmetrical.
3. They have water vascular system and tube feet.
4. Starfish, sea cucumber, sea lily.
Characteristics of Chordata
1. They have notochord.
2. They have nerve chord.
3. Gill slits in the pharynx.
4. Body is bilaterally symmetrical, trophoblastic, coelomate.
5. Closed circulatory system.
6. Chordata are divided into subphyla.
Chordata are divided into following:
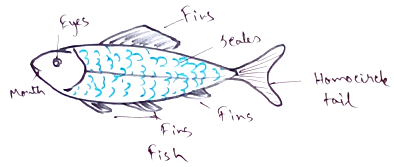
I. Pisces
1. They are cold blooded and aquatic.
2. Body is covered with scales.
3. Heart is two chambered.
4. Fishes are two types cartilaginous (shark, dogfish) and bony fish (carps).
II. Amphibians (frog, toad)
1. They live on land and in water (two phases of life is observed- aquatic and terrestrial)
2. Cold blooded
3. Moist skin without scales
4.Three chambered
III. Reptilia (lizard,snake)
1. They are the first terrestrial vertebrates.
2. They are cold blooded and skin is covered with rough scales.
3. Two pairs of limbs.
IV. Aves (crow, parrot)
1. Warm blooded means they can regulate their body temperature and bipeded.
2. They can fly as the forelimbs are modified into wings.
3. Four chambered heart.
V. Mammalia (cow, dog ,man etc.)
1. Most evolved animals.
2. Females contain mammary gland and give direct birth to the young ones.
3. Warm blooded animals.
4. Four chambered heart.
5. Neck contains seven vertebrae.
Questions and answers on Kingdom Animalia:
1. Bat and birds both can fly. But bats are not bird why?
Bat is a mammal as it give direct birth to the baby and have mammary glands whereas birds lay eggs and body is covered with feathers.
2. Are crocodile and frog belong to same category?
No, crocodile belong to reptiles and frog belong to amphibians class.
From Kingdom Animalia to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.