Kingdom Fungi
Alexopoulos in 1952 defined Fungi as -“nucleated, achlorophyllous organisms, which typically reproduce asexually and sexually and whose usually filamentous, branched somatic structures are surrounded by the walls containing cellulose or chitin or both”.
Characteristics of Fungi:
- Fungi grow on humus soil (mushrooms), on tree trunk (polyporus), on dung ( ascobollus), symbiotically with algae (lichen), symbiosis with plant root (mycorrhiza).
- Unicellular (yeasts), multicellular or dimorphic (Candida albicans).
- Fungi are eukaryotic, cell wall consist of chitin or cellulose only lack of any plastid.
- Body of fungus consist of microscopic threads or filamentous structure called hyphae. It is a web of hyphae called mycelium.
- Hyphae are associated to form personating structure of two types- one is rhyzomorphs (root like and subterranean)and another is sclerotia (consist of fruit body)
- Lomasome is a convulated complex of membranous outgrowth of plasma lemma that lies below the cell wall.
- Nuclei undergo intranuclear spindle formation.
Mode of Nutrition in Fungi:
Fungi do not contain any chlorophyll, so they cannot make their own food. For nutrition they are saprophytic in nature. They have some species types of enzymes in their body. They grow on dead plants and animals and collect their food by making lyses of the dead tissues.
Reproduction in Fungi:
In Fungi three types of reproduction can be seen.
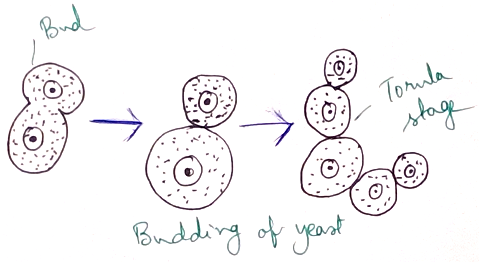
Vegetative reproduction- Vegetative reproduction of Fungi can proceed by budding, fragmentation, fission, rhizomorphs, sclerotia.
Asexual reproduction – Accomplished by means of spores. They are Conidia, oidia, chlamydospore, endospores, basidiospore, uredospore, ascospores, pycniospores, teleutospore.
Sexual reproduction- It occurs by fusion of egg and motile male gamete. It is of 3 type- isogamy, anisogamy, oogamy.
Economic importance
Useful Role of Fungi are Follows:
1. In industry mushrooms are cultivated as their nutritional value is very high. Mushrooms are rich in vitamin and minerals (especially vitamin B). It is also rich in protein and uses by the people those who are no vegetarian for their protein supplement.
2. Yeasts are used in bread making industry because they give out carbon dioxide and made the item spongy.
3. Yeast is also used in fermentation industry for making wine as it turns glucose into ethyl alcohol.
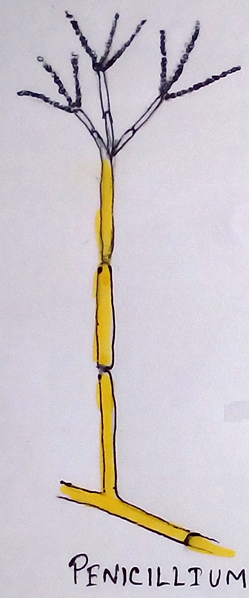
4. Penicillium is enriched in high quality of protein, fat, minerals (calcium, phosphorus), vitamin A, vitamin B which adds flavour to the cheese.
5. Aspergillus produces citric acid, Gallic acid which is used in chemical industry.
6. Penicillin was the first antibiotic that discovered from Penicillium notatum.
7. Beside these fungi are also used for synthesis of different vitamin, protein, fats, and enzymes.
Questions and Answers on Kingdom Fungi:
1. What is the black powder we see on stale bread?
The black powder is the spores of moulds, (like Rhizopus), that fall on it and germinate to form mycelium, when a piece of bread is kept in a warm place.
2. List five important steps for cultivation of mushrooms.
I. Compositing
II. Spawning
III. Casing
IV. Cropping and Harvesting
V. Preservation.
3. What do you mean by fermentation?
It is a type of anaerobic respiration done by yeast and other microorganisms where glucose is converted into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
4. Name one harmful fungi.
Phytopthythora infestans-late blight of potato.
From Kingdom Fungi to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…







New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.