Root and its Types
Root is generally non green (do not contains chlorophyll) underground, positively geotrophic (grow towards the gravity), positively hydrotrophic (grow towards the source of water), negatively phototropic (grow opposite to the source of light) part of plants. Roots do not contain any nodes, internodes, leaves, lowers and fruits. Buds are absent except when roots take part in vegetative propagation. This type of example can be seen in Ipomoea batatas,Dalbergia, Populous, Dahlia etc.
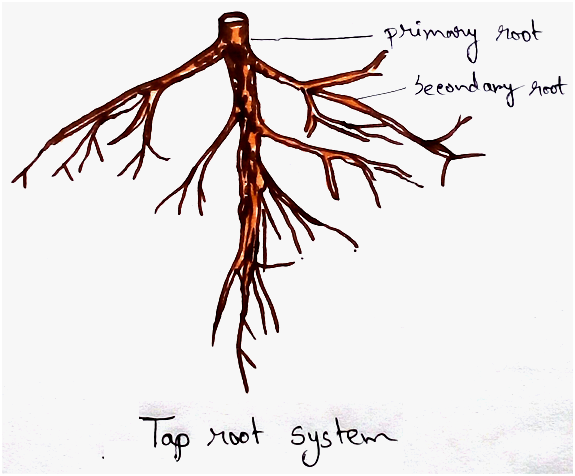
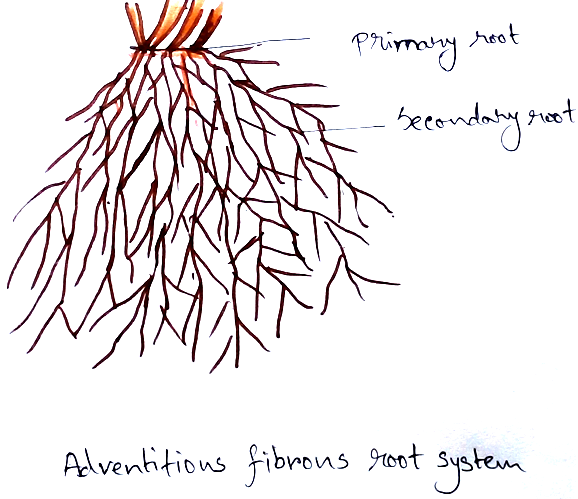
Structure of root- Root consists of root cap, root hairs which are fine thread like (in subapical region). Root branches are endogenous in origin (developing from the pericycle in between two protoxylem points).
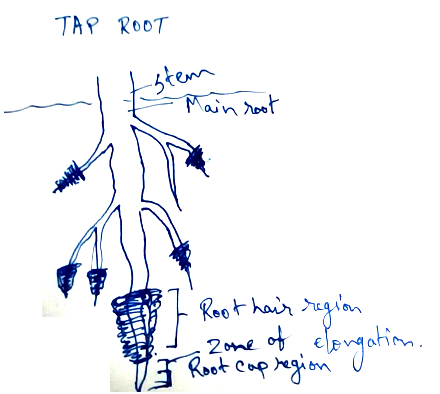
Parts of the roots - In a typical root, there are five distinctive zones starting from apex to the base.
These parts are follows: -
1. Root cap - It is a cap like covering over the tip of the root which gives protection against friction and weir and tear from soil particles. Root cap also help in graviperception. In different situations root caps are modified to give protection. In aquatic plants root pockets are observed instead of root cap because they are nonrenewable and act as balancers. Multiple root cap is observed in the aerial root of different plants. Example is Pandanus.
2. Growing point of root - It is found in the long region of meristematic cells which is almost 1 mm long. This growing part produces new cells for root cap and basal part.
3. Zone of elongation - It is behind the tip which is 4-8 mm long. As it is responsible for the elongation of root so, cells of this area elongated rapidly.
4. Root hair zone - This area is a cell maturation zone. Thus, xylem and phloem differentiated here. The region is 1-6 cm long. For increasing absorptive area outer cell give rise to tubular root hairs.
5. Zone of mature cells - Bulk of root is made of it.
Primary Functions of Root:
1. It helps the plant body to remain fixed with the soil.
2. One of the essential thing is water for plants and dissolved nutrients are transported with the help of root.
3. Water and dissolved minerals make a continuous water column through root by xylem and help in uptake by the plant.
4. Roots prevent soil erosionas it holds the loose soil tight.
5. Only source of nitrogenous salt are absorbed by the root which is very essential for plants.
Special functions of roots:
Root acts as - store house of food for plants, reproductive organ, pillar for plant, supportive part of plant, climbers etc.
Root system – A complex of one type of roots and their branches is called root system. They are of two types –
1. Tap root system - It is a complex of roots formed by tap root and different types of branches borne by it. E.g. mango, peepal.
2. Adventitious root system – It is a complexed formed by roots that develop from the parts of the plant other than primary root or its branches.
It can develop from any part of the plant.
From What is Living? to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.