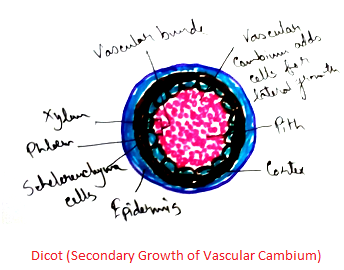
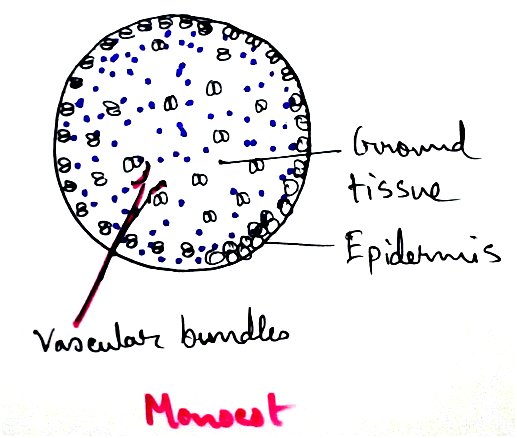
Secondary Growth of Vascular Cambium
Secondary growth of vascular cambium can be observed in dicot root and secondary growth of stem.
Dicot Root - Secondary growth is observed in vascular cambium and phellogen. It is formed secondarily from conjunctive parenchyma and part of pericycle lying opposite the protocol email points. As initially vascular cambiums are wavy and later it becomes circular. It is derived from pericycle from primary vascular rays. In some other places it forms secondary xylem on the inner side and secondary phloem on the outside. Secondary vascular rays occur at places. Primary vascular rays are muliseriate in the beginning and is uniseriate on later.
Secondary phloem does not persist as the previous phloem get crushed then the new secondary phloem becomes operational. Secondary xylem (primary xylem) are persist. Annual rings are absent because there is little seasonal variation in soil temperature.
Secondary Growth of Stem - Secondary growth of stem is occurred due to vascular cambium and phellogen. Vascular cambium is formed by strips of fascicular cambium (primary meristems) and interfascicular cambium formed by differentiation of medulary ray cells. Vascular cambium is of two types division- anticlinal and periclinal. Anticlinal vascular cambium increases circumference of vascular cambiums (at right angles to surface) and periclinal divisions produce xylem, phloem and vascular rays. Vascular cambium contains two types of cells, ray initials and fusiform initial produces outside secondary phloem and inner secondary xylem. Phloem is not persistent as soon as the older one crushed new one becomes functional. Secondary xylem is persistence. It grows with age and increase the girth of stem. In temperate area spring wood is wider with large, lightly coloured xylem and in autumn wood has smaller, darker and narrower xylem. It produces annual growth ring which help in determining the age of plants.
From Secondary Growth of Vascular Cambium to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.