Tissue and Their Two Main Groups
A collection of cells with structural and functional similarities working together to perform a specific function is calledtissue. Plant tissues are mainly of two types . One is meristematic and another is permanent.
Functions of tissues:
Meristematic tissues or meristem are actively dividing cells which undergo repeated division to form a mass of new cells. The Greek word ‘meristos’ means divisible.
Characteristics features of meristem
Meristem are a collection of cells that are capable of active cells division and there by adding new cells to plant body. These are actually localised embryonic tissues of plant body.
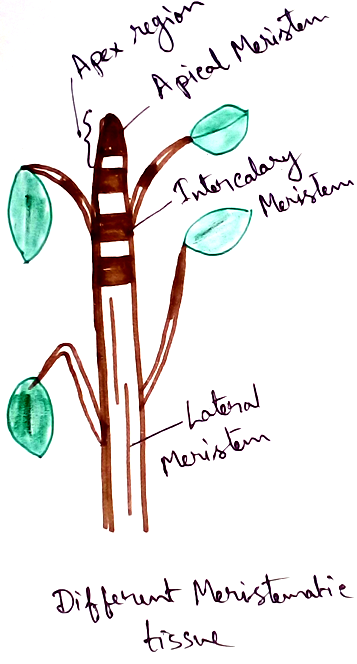
According to the location of meristem these are of three types:
Apical meristem - This type of meristem are found at the growing tips of stems and roots. This thing give increase in height of plant, specially at the tip of roots and shoots.
Lateral meristem - This tissue is responsible for lateral increase in diameter and is present on the lateral sides of stems. Cork cambium is present within the vascular tissue. Lateral meristem causes thickness of the girth causes secondary growth.
Intercalary meristem – Intercalary meristems are present at the base of the node ,along with internodes and on the leaf base of monocots. This meristems are responsible for the development of branches around the node region.
Permanent tissues - Characteristics features of permanent tissue.
Simple tissues are consist of dermal and ground tissues.
Dermal tissues consists of cells having thick wall and are closely packed. Examples –it is found in the outer most covering of young parts of plant, roots, stems, leaves which is called epidermis. In some stems and leaves epidermis produce formed stomata for gaseous exchange.
Most part of the plant are made up of ground tissues which synthesize food, act as food storage also provide mechanical strength to the plants. It is of three types-
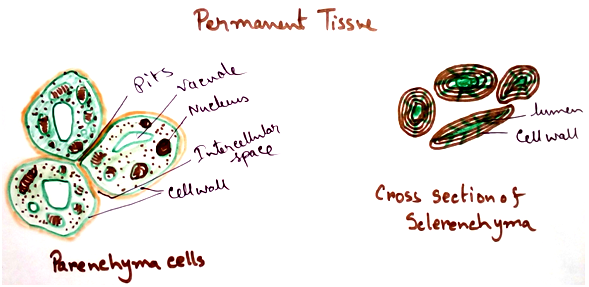
Parenchyma - Found in almost all parts of the body. Main function is to synthesize and store food. Chlorenchyma, aerenchyma etc are different types of parenchyma.
Collenchyma – It is found beneath the epidermis ,unevenly thickened walland provide mechanical strength to the plant body.
Sclerenchyma - This tissue provide mechanical support to the body. This is of two types- fibres and sclereids. These cells exhibit elastic properties. Fibres developed from meristematic cell and sclereids develop from parenchyma- cell.
Complex tissues are composed of mainly vascular bundles.Tissues those are made up of different types of tissue are called complex tissue. Two types of vascular bundles are xylem and phloem.
Xylem are mainly made up of dead cell (except xylem parenchyma), responsible for water transport through the vessel.
Phloem are mainly made up of living cell (except phloem fibre), responsible for transport of food throughout the plants body .
From Tissue and Their Two Main Groups to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.