Animals that Lay Eggs
Many animals do not reproduce their young ones directly. The mother animals lay eggs.
They also hatch the eggs. After a certain period, their young ones come out of the eggs. Such animals are called egg-laying animals. Fish, snakes, turtles, frogs, birds etc. are egg-laying animals.
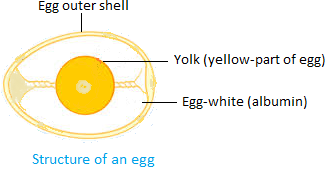
The egg consists of a hard protective outer shell. Inside the shell in
the centre is a yellow portion called the yolk. It contains the
developing baby called the embryo. It also contains food for the embryo.
Surrounding the yolk is a white portion called the albumin. It protects
the embryo and provides water to it.
The eggs are hatched by the
concerning animals. The egg (yolk) takes the shape of the animal in a
few days due to proper hatching. The young one comes out at the end of
the hatching period.
The following are some of the egg-laying animals:
|
(i) Mostly birds built nests to lay their eggs. Father and mother birds hatch the eggs. The female bird lays the eggs. After the eggs are laid, one of the parent birds usually the mother sits on the eggs to keep them warm. The baby birds start growing inside the eggs. After a few weeks when the baby birds are fully developed they break open the shell and the baby birds come out. At that time it has no fur on its body. It grows after some time. The parent birds take care of the new born and feed it till it gets fit enough to look after itself and begins to fly. |
Note: Eggs of an ostrich are the biggest ones in the word.
|
(ii) Crocodiles dig shallow pits in sandy river banks to lay their eggs. Their eggs also have shells but not very hard. They are tough and leathery. The mother covers the eggs with sand and guards them. The eggs are hatched by the warmth of the sun. When the babies hatch it digs away the sand and sets them free. As they come out, the mother keeps them in a special pouch at the bottom of her mouth. |
|
(iii) Tortoises and turtles dig holes in the sand and lay their eggs in it. They cover them and leave them alone to hatch. The young ones find their way out and crawl to the nearest water. |
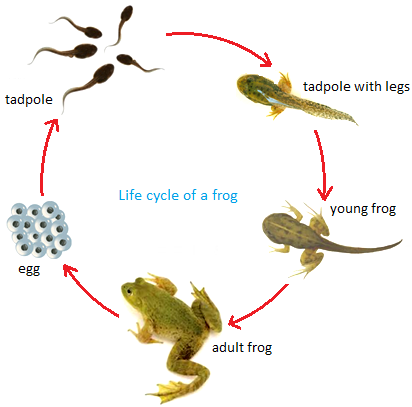
(iv) Frogs: A female frog lays hundreds of eggs at a time in water i.e. in a lake or a pond.
Their eggs are protected by a thick jelly-like substance. When the eggs hatch tiny tadpoles comes out. They swim in the water and look like fishes. After a few weeks the tadpoles start to grow legs. Their tails becomes shorter and shorter and finally disappear. After sometimes these tadpoles grow into adult frogs.
(v) Fishes lay eggs in water. They lay thousands of eggs at one time. The egg of a fish is hatched into a fry and the fry changes into an adult fish. But many of the eggs and baby fishes are eaten by other fishes.
(vi) Snakes and turtles lay eggs on the ground.
Nearly all animals protect their young ones and take care of them. This is called parental care. But there are some other animals too that do not take care of their young ones. They only lay eggs in a safe place and leave them to their fate. Animals like snakes, lizards, frogs etc. belong to this category.
From Animals that Lay Eggs to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…









New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.