Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation
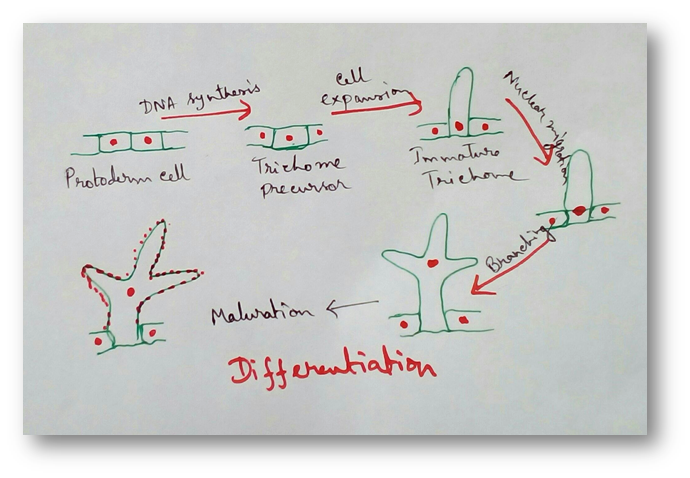
Differentiation - Cells from the root apical meristem and shoot apical meristem the camera that differentiate , mature to perform different functions. This process by which the cells undergo different major structural changes or few structural changes both in their protoplasm and in the plasma membrane are called differentiation.
The cells those are involved in this process are called differentiated cells.
It can be defined by example where a trachery element of the cells loose it’s protoplasm and developes it’s lignocellulosic secondary wall which is best suitable for the water to carry the long distance even under extreme tensed condition.
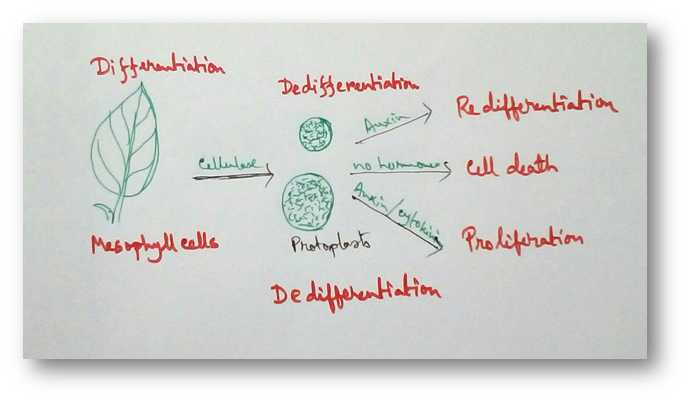
Dedifferentiation - In case of plants living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under some certain condition. Sum of some events bestowed the capacity to divide once again and termed as dedifferentiation. A dedifferentiating tissue can act as meristems.
Examples are cork cambium, interfascicular vascular cambium, wound meristems.
Redifferentiation - Product of the dedifferentiating tissues that loose the ability to divide is known as redifferentiation- tissue or redifferentiated cells. This process is known as redifferentiation.
We know that growth in plants are open and even growth in plants are also open. Stem, root, phloem fibres, xylem fibres etc are developed from same origin but they have different maturation. Final structure of the cell or tissue during maturity arising from the same meristems is ditermined by the location of the cell within.
This can be explained by the example-cells that positioned distal to root apical meristem differentiated as root cap cell and this are pushed to periphery as mature epidermis.
From Differentiation, Dedifferentiation and Redifferentiation to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.