Human Respiratory System
Definition of respiration - This is the process of making energy available to organisms and their living cells through enzyme controlled catabolic breakdown of organic molecules. The organic materials that give energy during catabolism are called respiratory substrates.
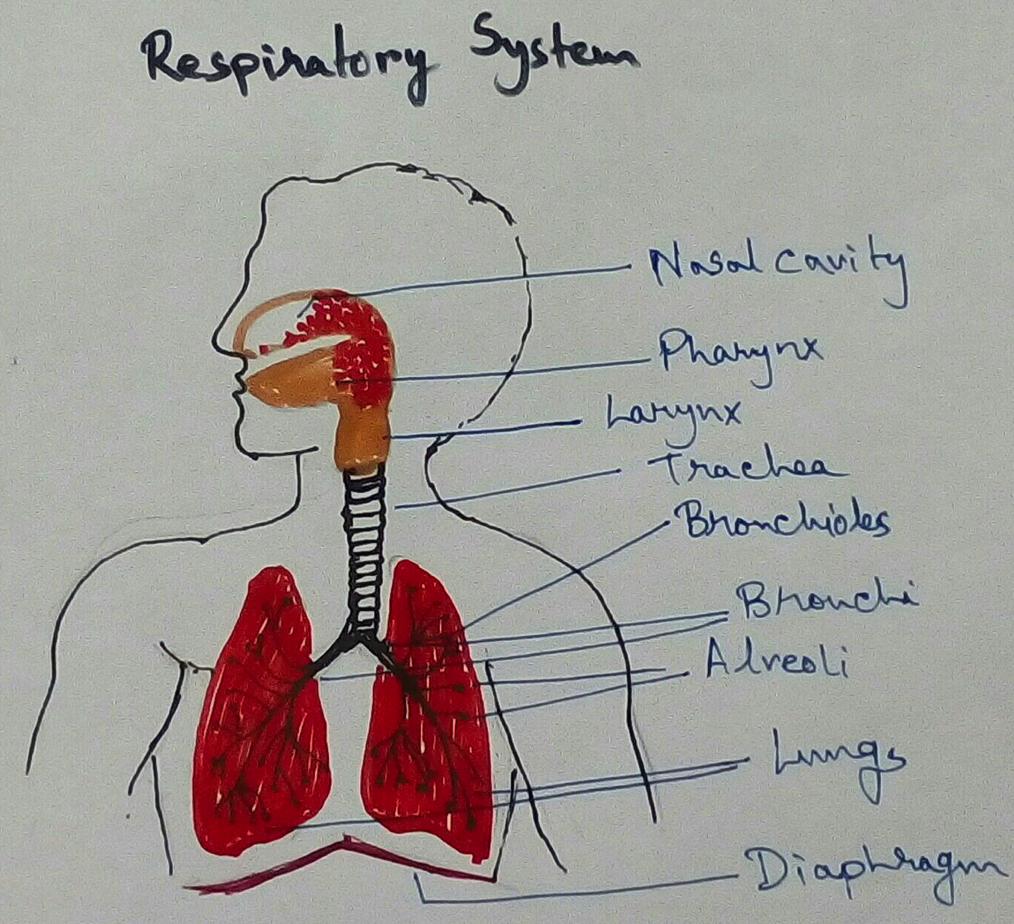
Mammalian respiratory system is consist of a respiratory tract a pair of lungs and structures those are involved in ventilation. Respiratory tract consists of external nasal cavity internal nares, naso pharynx, larynx trachea, bronchi and bronchioles within the system.
External Nares - External nares are a pair of slit like openings present on the lower end of nose.
Nasal Cavity - Nasal cavity is present between pivot and cranium as it is divisible into two nasal chambers by a nasal septum. Each nasal chamber is made up of three parts one is vestibule which is lower small part just above the external nose that is lined by skin and beard hair as well as oil glands. This here help in filtering out dust particles from in coming here within this part. Second is conditional which is the respiratory region and is the middle part of nasal chamber consists of three Bony projections called Nestle or turbinates superior middle and inferior and some sinuses that is maxillary, frontal, sphenoid and ethmoid. The specific part is reddish pink in colour due to abandon blood capillaries that is present in this portion. This is covered by ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with mucus producing cells and serous that is water secreting glands. This inhaled air is most want and clean by wrapping the dust and germ particles. The third is olfactory regions which is situated at the upper part of national chamber and superior nasal Comcast brown in colour. These are covered by olfactory epithelium which part is sensation of smell.
Internal Nares - Internal nares that also called choanae where the two nasal Chambers of internal pierce through internal near or choanae.
Pharynx- pharynx are situated at the base of the skull and has a lining of ciliated stratified squamous epithelium. Nasopharynx are lead to oropharynx or common pathway for the respiratory and digestive system. Oropharynx are passes into laropharynx which contains epiglottis and that passes into larynx.
Larynx - Larynx are also called voice box which opens into laryngo sharing through athlete like glottis which can be avoided by in string intrinsic muscles. Glottis can also be closed by a muscular cartilaginous flap called epiglottis and larynx has C shaped thyroid cartilage on sides and in front where it can be felt as Adam's Apple triangular arytenoid cartilage is on back. Adding like cricoid cartilage and the BA of nodular cartilages of Santorini Where are Parent of are it cartilages.
Trachea- trachea is the windpipe of the respiratory system which is 10 cm - 12 cm long. Its diameter is from 2 cm to 3 cm and it arises from layer and passes of the middle of Thorax. Trachea is supported by 16 to 20 C shaped incomplete cartilaginous C rings and lined by ciliated pseudostratified mucous epithelium.
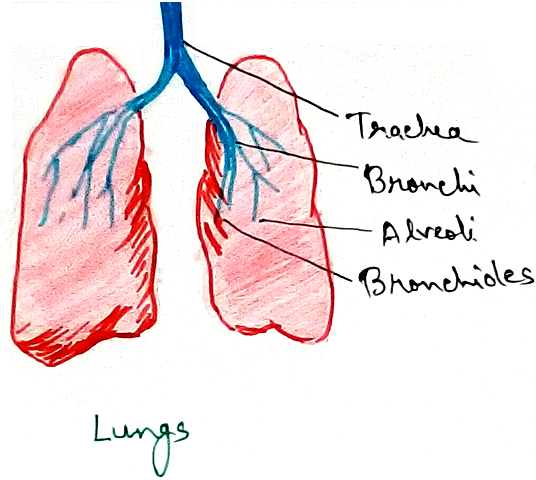
Bronchi - Bronchi of the respiratory system are divided into right bronchi and left primary bronchi. Left bronchus is about 5 cm long and right bronchus is only 2.5 cm long but right bronchus almost directly enters the right lung. Inside the long the primary bronchus are divided into secondary bronchi then the secondary bronchi is segmented into segmental bronchi and then into bronchioles. All the bronchi are lined by ciliated and mucus secreting pseudostratified epithelium and supported by incomplete cartilaginous rings. Bronchioles are divided into terminal bronchioles respiratory bronchioles alveolar sacs and alveoli. Mucus secreting cells are absent in the terminal bronchioles and the branches of epithelium is ciliated in broncos and terminal bronchioles. Non ciliated in respiratory bronchioles and their branches of the terminal bronchioles are observed.
If there is an infection of right lung and it is more common due to the entry of right bronchus directly into the right lung.
Lungs - Lungs are appeared of spongy elastic in a stick of pink is to slate grey colour air inside the thoracic cavity and a small space called mediastinum lies in between the two lamps specially due to concavity called cardiac notch of left lung. It includes the heart and its long is covered by a plural membrane made up of an outer parietal pleura and inner visceral pleura. There is a narrow plural cavity of diameter .02 mm occurs between this and it contains plural fluid which allows frictionless sliding of pleura during inspiration and expiration. Protection and moisture meaning of lungs are provided by this fluid where is pleurisy is painful infection which involve inflammation of pleura and over production of pleural fluid.
Left lung is slightly narrower and longer than the right lung where is right lungs has three lobes right superior right middle and right inferior. Left lung contain two lobes left superior and left inferior which contains a cardiac notch in anteromedial region for accommodating heart. Each lunglobe is internally segmented and the segments are divided into lobules which receives a terminal bronchioles. A respiratory bronchioles gives rise to 2-11 alveoducts where, each of which in in and alveolar sac or infundibulum. Infundibulum has a number of small pouch called alveoli and the number of alveoli in human pulmonary system is 300 to 400 million with surface area of 100 m square. Each of the alveolus is falling Adderall in outline with a thin wall made of non ciliated squamous epithelium with a few cubicle cells that secrete a of protein surfactant to prevent collapse and sticking alveolar walls during expiration where is blood capillaries offer on the surface of alveoli for gaseous exchange.
Diaphragm - Diaphragm is a membranous musculotendinous partition between Thorax and abdomen but normally it is conflict with convexity towards thorax. Phrenic muscles are attached to the diaphragm two leaves and vertebral column and contraction of muscles strengthen the diaphragm to increase thoracic cavity.
Intercostal Muscle - Intercostal muscles are of two sets -one is external intercostal muscle for normal inspiration and expiration and the other is internal intercostal muscle for forceful expiration.
Abdominal Muscles - Relaxation of abdominal muscles allows compression of abdominal organs in there from straightens and contraction possesses the abdominal viscera against diaphragm from to bulge it more upwardly for expiration.
From Disorders of Digestive System to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.