Division of a Decimal by a Whole Number
This topic would discuss about division of decimal by a whole number. As in multiplication of decimal number we have done the multiplication ignoring the decimal point same as that in division also we will do the division ignoring the decimal point and when we reach the tenths place that is first place in the fractional part of the decimal number we will place the decimal point.
Steps of division of a decimal by a whole number:
Step I: First divide the decimal by the whole number ignoring the decimal point
Step II: Then on reaching the tenths place that is the first place in the fractional part of the whole number place the decimal point
There is another trick in division of a decimal is that then the digits in the dividend is no more but the division is not complete then we need to add zeros at each step till the division is complete.
Here are few examples to illustrated division of decimal by a whole number:
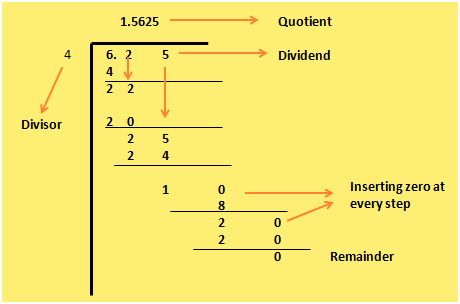
1. 6.25 ÷ 4
Solution:
Explanation:
Here 6.25 is divided by 4 (ignoring the decimal point) and the remainder is 1. Now put the decimal point in the quotient after division of 6 by 4 that is after 1 in the quotient the decimal point is placed. But in decimal division we cannot leave any remainder at the end and the rule is that at each step (after there are no more digits in dividend) one zero is added. Hence with the remainder 1 a zero is added to make it 10 Now 4 multiplied by 2 is 8 again a remainder 2 hence another is zero placed with 2 making it 20. Now 4 multiplied by 5 is 20 with no remainder.
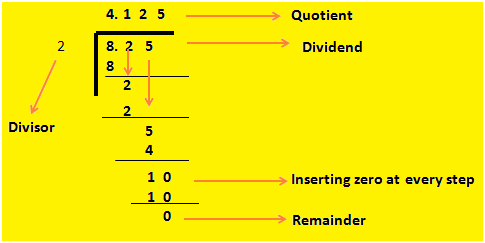
2. 8.25 ÷ 2
Solution:
Here in this sum we have to divide 8.25 by 2 (ignoring the decimal point) and the remainder is 1. Place the decimal point in the quotient after dividing 8 by 2 that is 4. Now we can see that on dividing 8.25 by 2 we get a remainder 1 but we cannot leave remainder in case of division of decimal. So, a zero is placed with the remainder 1 to make it 10. Then 2 multiplied by 5 is 10.
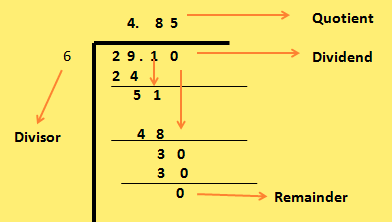
3. Divide 29.10 by 6
Explanation:
Here 29.10 is divided by 6 ignoring the decimal point. Then in the quotient the decimal is placed after dividing 29 by 4 that is after the first digit. On dividing 29.10 by 6 there is no remainder hence we need not put any extra zero at any step to complete the division.
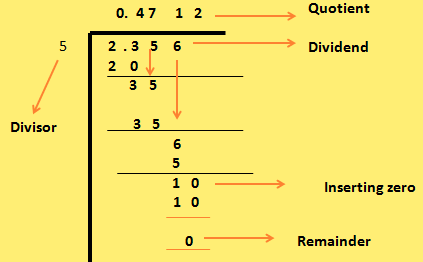
4. Divide 2.356 by 5
Explanation:
Here 2 cannot be dividend by 5 as 2 is less than 5 hence we need to consider 23. As 2 cannot be divided by 5 hence we need to put 0 in the quotient and then place the decimal point and continue the division. At the last step we would get a remainder 1 and in decimal division we know we cannot leave remainder hence a zero is placed with 1 to make it 10. Then 5 multiplied by 2 is zero.
From Division of a Decimal by a Whole Number to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.