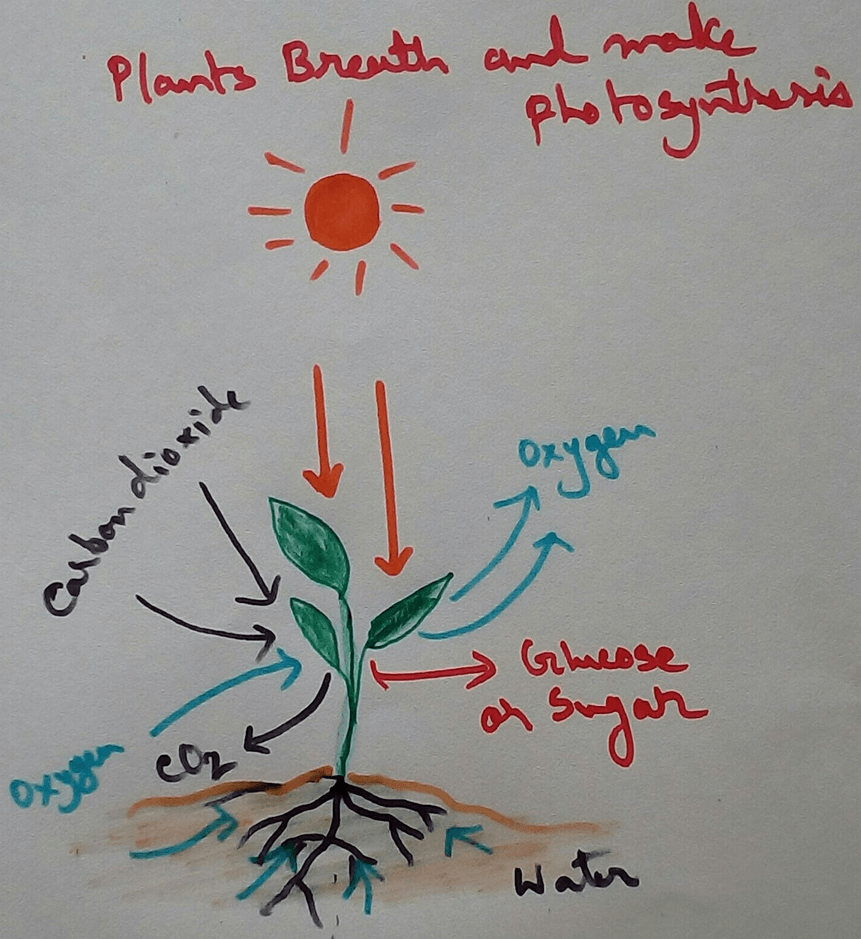
Do Plants Breathe?
Green plants contain stomata in some cases mainly in Dicot leaves stomata are observed in the downloads layer of the leaf and in monocot stomata are observed on the both side of the leaf. Stomata contains a stomatal pore which opens and close according to the difference in concentration gradient of potassium ions and turgidity. This opening and closing of stomata is also created by the activity of guard cell. Opening and closing of stomata helps to enter the water vapour carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into the green leaves for making food by the process of photosynthesis and also help to release oxygen to the environment which produce during photosynthesis by the green plants as byproduct.
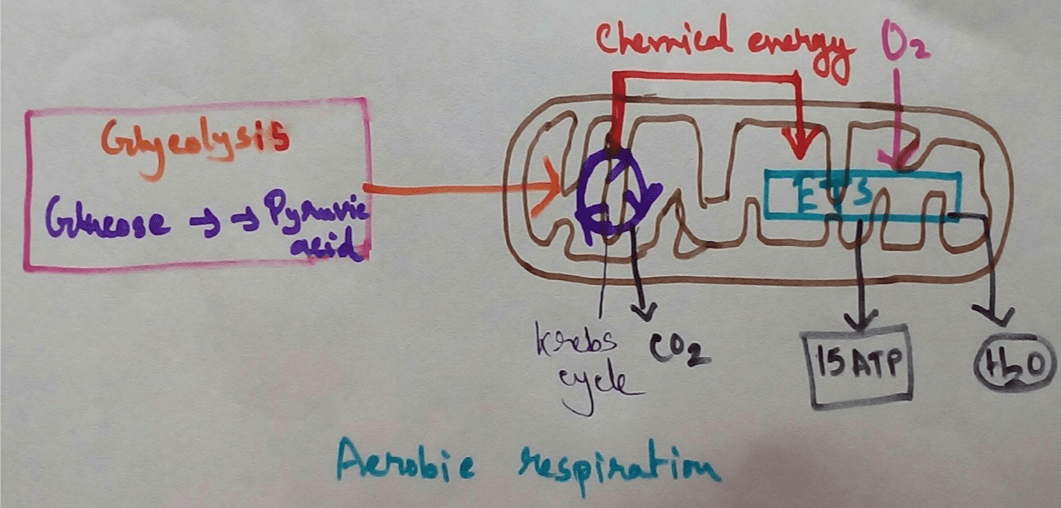
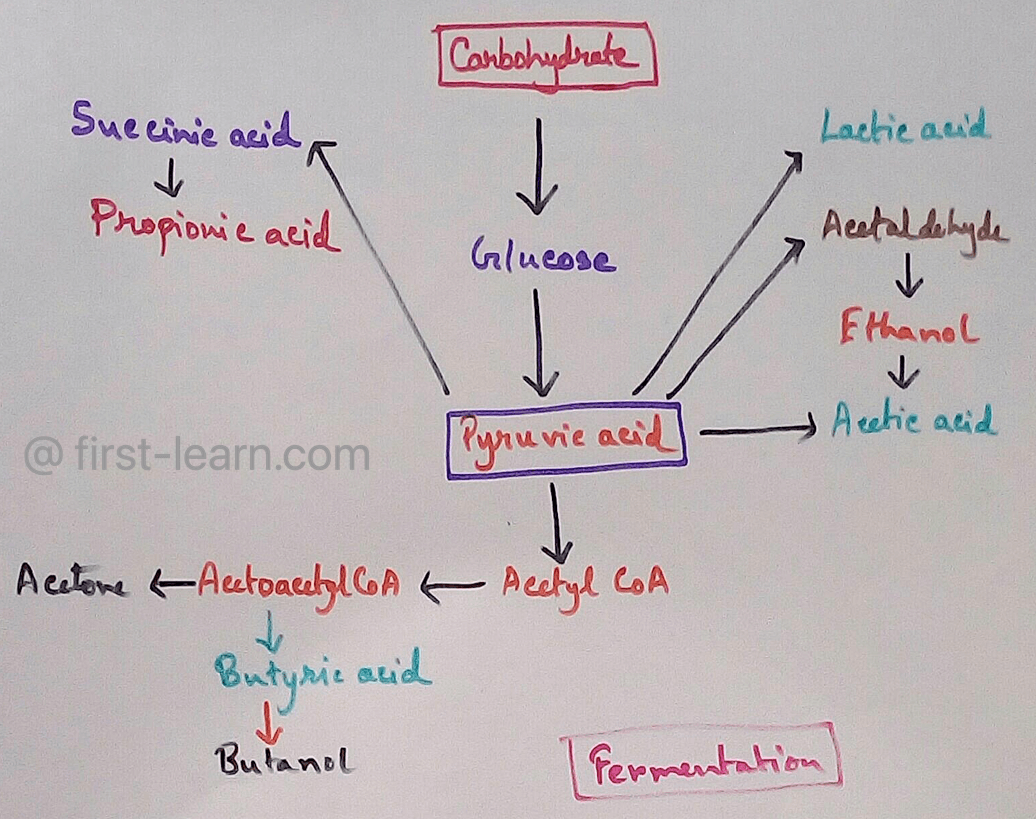
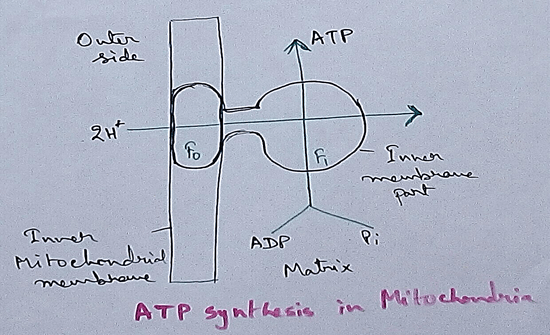
Respiration in Plants - The physiological activity called respiration which is observed in living organisms for the release of energy that is stored in food into the usable form of energy is also observed in plants. Plants also produce glucose by the process of photosynthesis and day after accident during respiration which used as fuel to release the chemical energy that is stored in the food to the usable form of energy for different physiological purpose. Respiration in plants occurs throughout the day and night when oxygen is taken from the environment and carbon dioxide is released to the environment but during daytime in the presence of Sunlight photosynthesis only take place for Carbon dioxide is obtained from the environment and oxygen is released. When there is a time for the same rate of uptake of Oxygen and release of oxygen is same in the environment it is called compensation point.
Breathing Organs in Plants - Plants do not contain any specific breathing organ by which oxygen can be after came and carbon dioxide can be released even it does not contain any respiratory muscles which help to expand and contract during the breathing.
Breathing in Terrestrial Plants - in Terrestrial plants stomata are present in both side of the leaves for case of monocot and dicot in the lower surface stomata are obtained which are able to exchange the gas within the atmosphere. Desert plans leaves are converted to thorn as they do not contain huge amount of water and their number of stomata is also in shunkan condition.
Breathing in Aquatic Plants - In aquatic plants stomata are present on the upper surface of the leaf so that floating plants can accept carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release oxygen to the year but in case of the submerged plants where there interbody is underwater there is some specific types of sales throughout their body which are able to exchange Oxygen and Carbon dioxide within water and extract those gases from their dissolved form.
Breathing in Aerial Plants - Aerial plants have aerial roots which and able to collect carbon dioxide from the air and release Oxygen and the water vapour can be released by this to the environment.
Mangrove trees have special type of route which are called pneumatophore that grows against the gravity and unable to participate for the exchange of gas.
From Do Plants Breathe? to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.