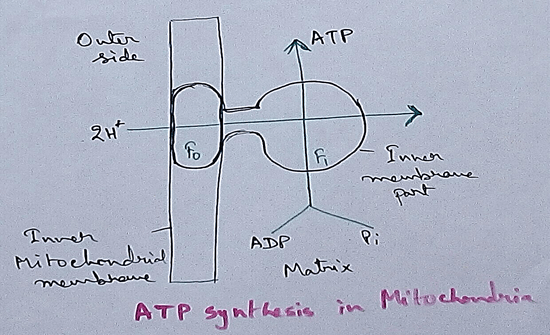
Respiratory Balance Sheet
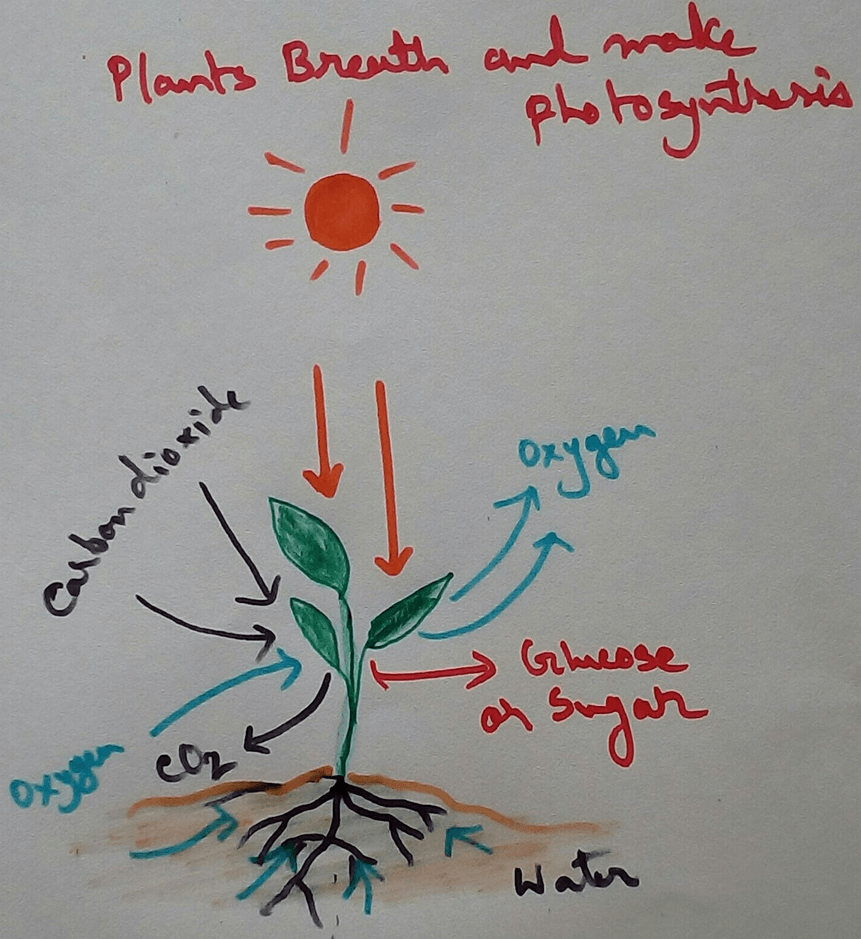
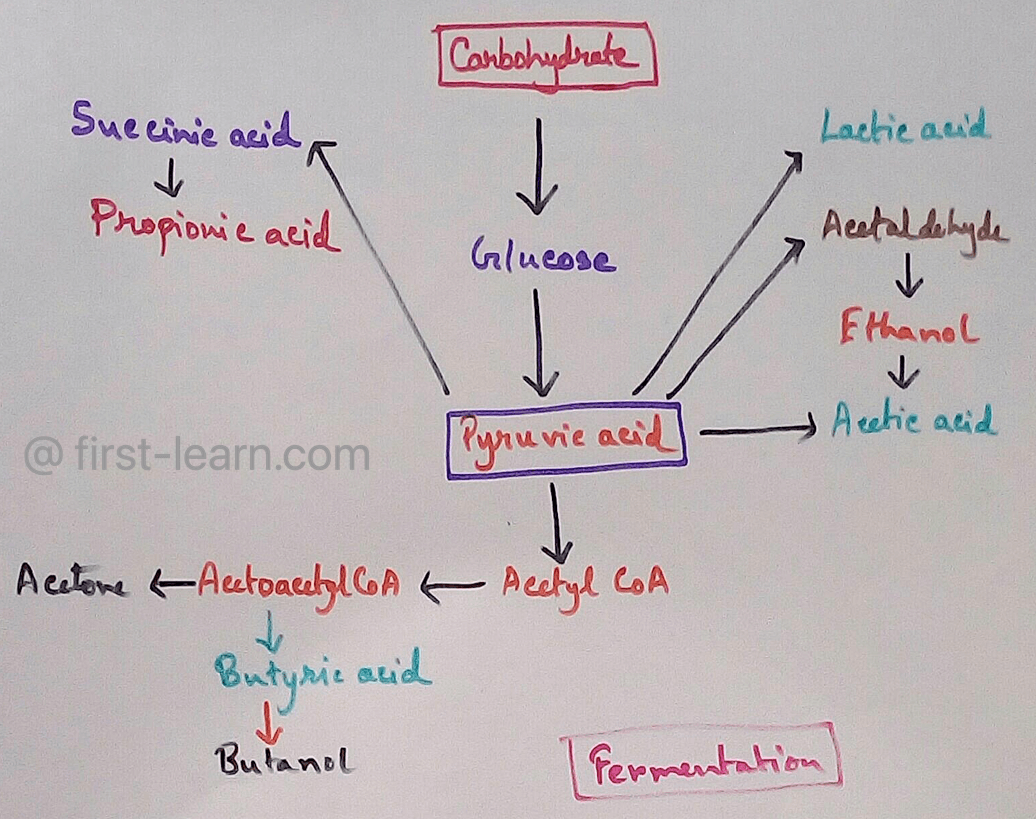
The major component that produced during the photosynthesis is Glucose which is further metabolised by the different metabolic pathways like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, TCA cycle and produces energy which is then utilise by the organism for their different physiological activities.
On account of consumption and production of ATP water molecules carbon dioxide molecule and oxygen molecule incomplete aerobic oxidation of one molecule of glucose through the various processes like glycolysis tricarboxylic acid cycle or electron transport chain or electron transport system is describe below:
In the process of glycolysis the first step is conversion of glucose to glucose 6 phosphate by the addition of inorganic phosphate molecular to glucose which is produced due to the breaking down of ATP molecules. Thus this is an ATP consumption process.
Fructose 6 phosphate is then converted to Fructose 1 6 bisphosphate where again another molecule of inorganic phosphate is attached to the fruit of 6 phosphate and one molecule of ATP is consumed as it degraded to give inorganic phosphate.
Next two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate is converted to 13 diverse for glyceric Acid and produces NADPH2 free then undergoes in the ecosystem and give rise to six molecules of ATP.
Another energy producing state is conversion of two molecules of 1, 3 di phosphoglyceric acid into 3 phosphoglyceric acid where two molecules of ATP are produced as each ATP molecule is formed from each conversion.
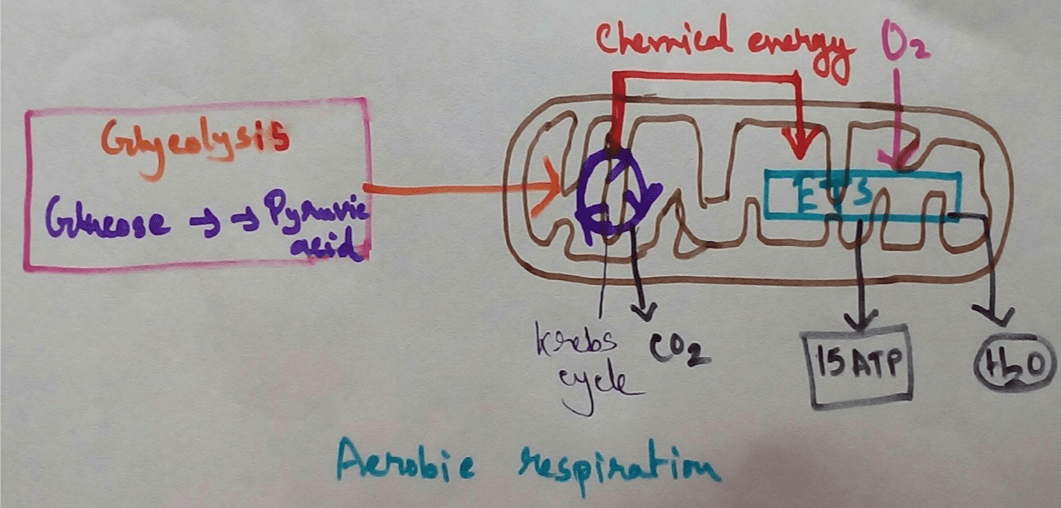
Next two phosphoenolpyruvic acid is converted to into two molecules of pyruvic acid. In this step of glycolysis ATP molecules are produced from every step. As a result total 8 molecules of ATP are produced during the conversion of glucose into pyruvic acid before entering into the TCA cycle.
Oxidative Decarboxylation of Pyruvic Acid - During oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid, pyruvic acid molecule is converted to acetyl CoA, NADPH2 is produced which will pass through the ETS cycle and produces three molecules of ATP from each NADPH2. As two molecules of pyruvic acid are produced during glycolysis, thus two molecules of NADPH2 are produced during oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid which ultimately give rise to the six molecules of ATP via ETS cycles.
TCA cycle - in TCA cycle are
tricarboxylic acid cycle energy molecules are produced in different reactions
which are described below-
Isocitrate acid is converted into Alpha ketoglutaric acid that produces NADPH2. Ultimately three molecules of ATP are produced by ETS cycle. Alpha ketoglutaric acid is converted into succinyl CoA where again two molecules of NADPH2 are produced during this reaction which pass into the ETS cycle and produces six molecules of ATP. Next succinyl CoA is converted to succinic acid that produces two molecules of ATP. Succinic acid is again converted to fumaric acid that produces two molecules of FADH2 that ultimately producers 4 molecules of ATP. During the conversion of maleic acid into Oxalic acetic acid six molecules of ATP are produced. Thus total 24 molecules of ATP.
Total 8 + 6 + 24 = 38 molecules of ATP.
From Respiratory Balance Sheet Acid Cycle to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.