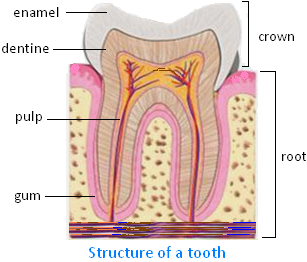
Structure of a Tooth
We will discuss here about the structure of a tooth.
The part of the tooth that we can see above the gum is covered with enamel and is known as the crown. The surface of the crown is made of the hardest substance in our body, which is known as the enamel. It is very difficult to scratch on the surface of this layer (i.e. enamel).
Beneath the enamel is the dentine. The dentine is not so hard. Inside the dentine is a soft portion, which has blood vessels and nerves. It is known as the pulp.
The part of the tooth that is inside the gums is known as the root of the tooth. It holds the tooth firmly in place, just like the root of a plant.
So, teeth consist of the crown, whose surface is covered with hard enamel, the dentine and the pulp.
From Structure of a Tooth to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like… -
Explain Transport of Gases | External Respiration | Tissue Respiration
Oct 09, 25 11:35 PM
In humans gaseous exchange is completed in the following ways the steps are - External Respiration or Breathing - Breathing in false taking in of Oxygen and giving out of carbon dioxide in the body. M… -
Kind and Number of Teeth | Location of Teeth in Mouth | Care of Teeth
Sep 11, 25 12:52 AM
Kind and Number of Teeth




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.