Types of Plant Tissues
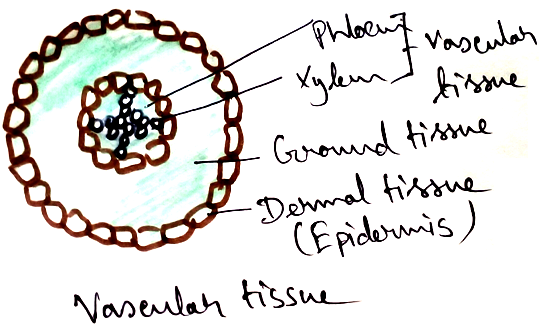
Three different types of tissues- epidermal tissues, ground tissue and vascular tissues.
Three main different types of tissue are follows-
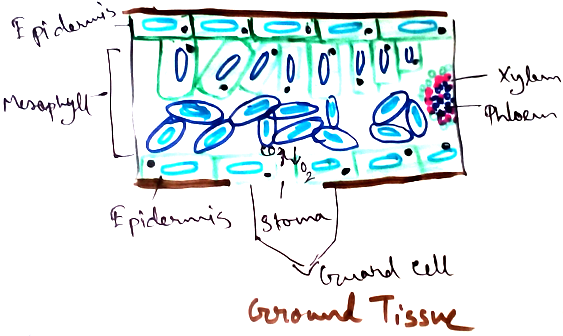
Epidermal tissue - It is composed of closely packed cells which have thick walls. It is the outer most covering of the young plants, roots, stems and leaves. Secretion of waxy coatings are observed in the stem and leaves. It is called cuticle that helps the plant to retain water and prevent it from drying. This part also contain stomata which associated with exchange of gases required during photosynthesis and respiration in plants.
Ground tissue - Maximum part of the plants are made up of ground tissue. It is of three types –parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma. Main functions of the ground tissue are – synthesize food, act as food storage, provide mechanical support to the plant.
Parenchyma - These cells arethin walled , spherical or oval with intracellular spaces and a large vacuoles in their cytoplasm. Function is to synthesize and store food. It is of three types- chlorenchyma (contain chloroplasts, aerenchyma (contains air and help in floating),
Collenchyma- These cells are elongated ,oval and absence of intracellular spaces. Cell walls are thickened chiefly at the corners and provide mechanical strength to the plants.
Sclerenchyma – These cells are thick walled,closely packed and absence of intracellular spaces. Associated with the mechanical strength of the plant. It can be of two types-
1. Fibres- these are elongated with pointed ends and produces different natural fibres- cotton , jute.
2. Sclereids- this cells are small , oval irregular in shape and possesses extremely thick lignified walls with pits. It is observed in the seed coat and pulp of the fruits.
Vascular tissues - Vascular tissues are made up of mainly xylem and phloem.
Both xylem and phloem ae called complex tissue because they are made up of different kinds of cells are work together to perform the functions. Xylem is the tissue that associated with water transport. Phloem is the tissue that is associated with transport of food. Thus they are known as conducting tissue.
Xylem - Xylem is mainly made up of dead cells and only one cell is living in this that is xylem parenchyma. Xylem is made up of tracheids, trachea or vessels, xylem fibers (all of them are dead). Tracheids and vessels are long , hollow and cylindrical in structure. It’s main function is to conduct water and dissolved minerals from roots to the leaves. Tracheids contain tapering end whereas vessels have cells placed in a direction so that end on end remain attached and their partition wall dissolved away between them. As a result it forms a pipe line structure that enhanced the ascent of sap (upward movement of sap through xylem).
Phloem - Phloem is associated with conducting the dissolving food particles to different parts of the plant. This tissues are made up of mainly living cells that are –sieve tubes, companion cells, sieve plates (all are living) and only one dead tissue that is phloem fibers. Boundaries of the tissues are dissolved to form a continuous path for food transport.
From Types of Plant Tissues to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.