Formed Elements of Blood
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45% of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood platelets.
Erythrocytes - Erythrocytes are also called red blood corpuscles or RBCs feature by concave or oval elleptical flat in camel and Lama. It is a nucleus colour cells of diameter 7 micrometre 28 micrometre. RBC count is 6.5 million per millimetre cube in children and 5 to 5.5 million per metre cube in adult males and 4.5 to 5 million palmitic you or microlitre in adult females. Excess presence of red blood cells is known as polycythemia and their average life span is 120 days. Plasma membrane is permeable to water of RBC glucose urea Oxygen and Carbon dioxide but it is impermeable to Sodium and potassium ion. Sodium is abundant in plasma where is Potassium is abundant inside the erythrocyte. Mitochondria are absent in any three sides and the erythrocyte contain 30% to 35% hemoglobin for transport of oxygen. Hemoglobin is a pigment which is reddish in colour and it contains iron or haem group and the globin protein group. Main function of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen from one cell to another and the optimum content of hemoglobin is 15 gram per 100 ml in human males and 13 to 14 gram per 200 ml in human females. Hemoglobin is observed in some vertebrates but some invertebrates have bluishcopper containing pigment calledhaemocyanin and greenish iron containing pigment called chlorocruonin. Haemocyanin is present in molar and some arthropods whereas kholo chlorine is present in some annelids. Mature erythrocytes do not have membrane bound cell organelles and are functionally prokaryotic in nature.
ESR - ESR is called erythrocytes sedimentation rate and value of ESR is 3 mm per hour to 5 mm per hour for normal males and 7 mm per hour to 12 mm per hour for normal females. Higher is the rate in of infection indicates and specially involving change in albumin globulin ratio live TB.
Pale yellow colour of Plasma is occur due to presence of bilirubin or decomposition product of haem part of haemoglobin. Normally it is observed to be passed down to leave her for disposal in while and part of it is excreted in urine. If the bill of inheritance then it causes jaundice and the plasma then becomes yellow also in lipemia or excess fat greyish or greasy plasma is occur.
Hemoglobin hemoglobin pigment of erythrocyte that contains 29 into 10 to the power minus 12 gram hemoglobin and roughly hundred million molecules. Hemoglobin is artist Rama which contain four polypeptides in case of adults 2 Alpha Chain and 2 Beta chain is present whereas in foetus there is 2 Alpha Chain and 2gama chain is present. Alpha chain contains 141 amino acid Residue, beta chain contains 146 amino acids and ironporphyrins group or haem group is attached to each chain. Iron is present in ferric state as each haem groupcarry one oxygen. Carbon dioxide also binds to hemoglobin but in global part and oxyhaemoglobin is more acidic as compared to deoxyhemoglobin.
Leukocytes - White blood corpuscles or white blood cells are colourless nucleated amoeboid cells where its normal count is 5000 to 8000 millimetre cube or microlitre of blood. Higher value of leukocytes indicate infection where is very high value may occur in leukaemia all leukocytes or blood cancer. No value infolink acid deficiency is called leukopenia and leukocytes are broadly divided into granulocytes due to granules or polymorphonuclear leukocytes due to lobed nucleus. Agranulocytes are the type of leukocytes where there is absence of granules and granulocytes are found in red bone marrow from large cells called megakaryocytes. Agranulocytes are the type of leukocytes where there is absence of granules and granulocytes are formed in red bone marrow from large cells called megakaryocytes.
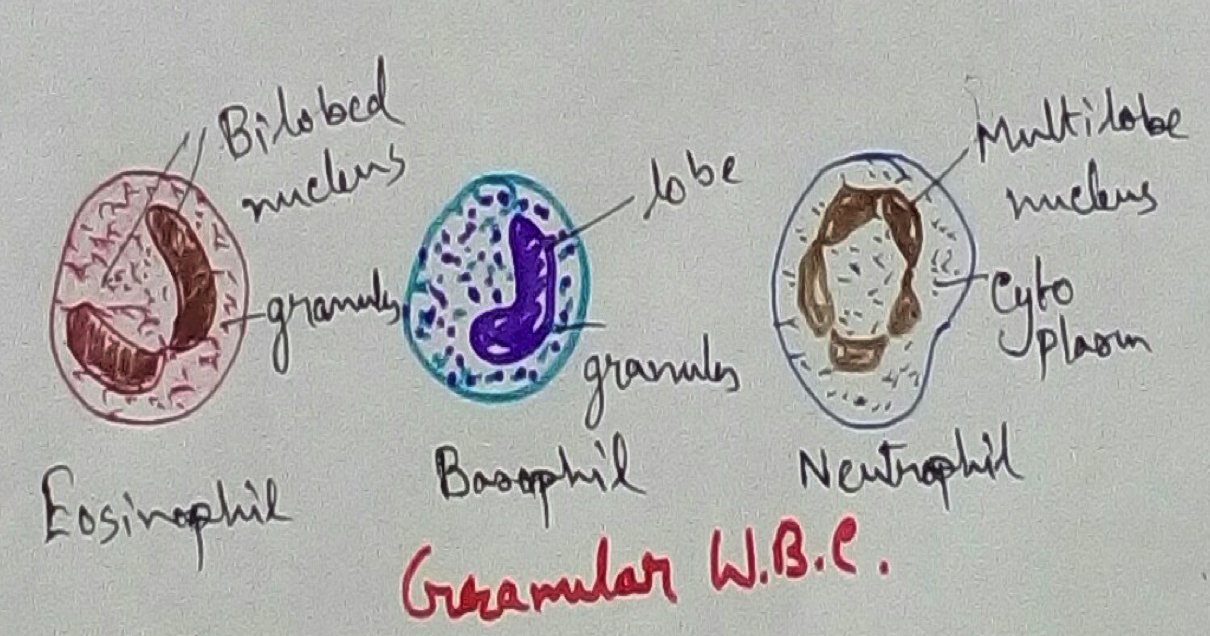
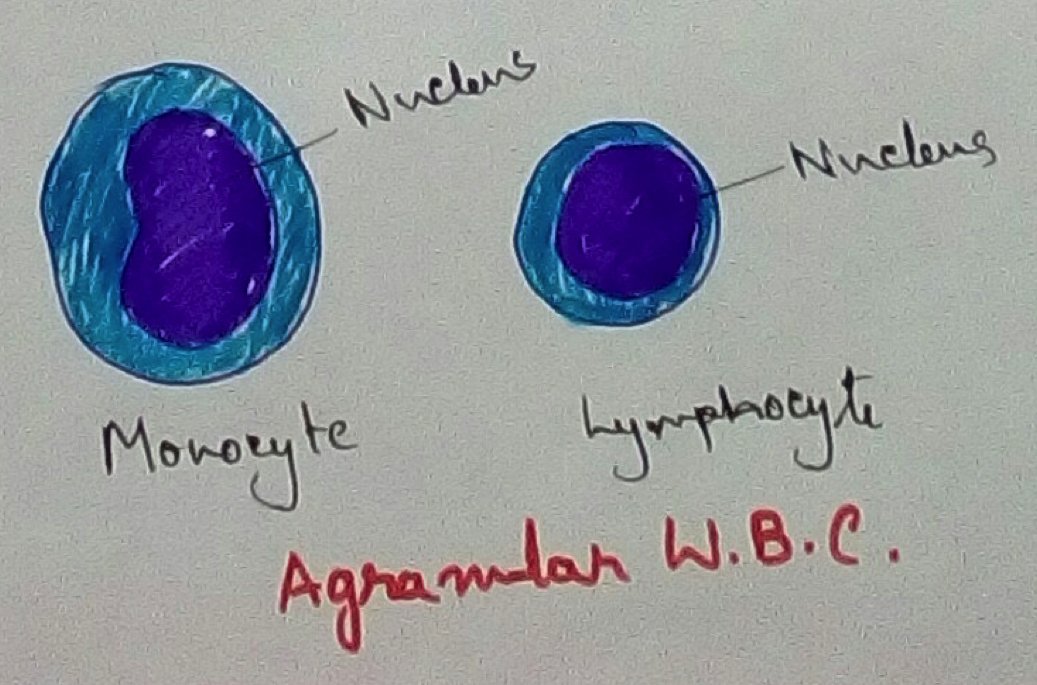
Types of White Blood Corpuscles - White blood cell can be divided into two types granulocytes and agranulocytes according to the presence of the granules within it. Granulocytes are of three types there are neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. Agranulocytes of to type that is Lymphocytes and monocytes. Lymphocytes and monocytes have phagocytic activity for the following material that entered the body. Eosinophils secrets histamine which is anti allergic in nature. Where is lymphocyte produces antibody against antigen within the serum. The process of formation of monocytes and Lymphocytes is called leukopoiesis and the ratio between the RBC and WBC is 600:1.
Neutrophils - Neutrophils at the most abundant and they officeyes 50% to 75% of the total blood cell where their lifespan is from 10 hours to 12 hours.These are stained with neutral guys and nucleus are many lot they also have phagocytic activity. Their size is from 9 micrometre to 12 micrometre.
Basophils - Granules are fewer and courses and staying with basic dyes such as methylene blue and they are generally 3 lobed nucleus. Size of basophils and 10 micrometre to 15 micrometre and their life span is from 9 months to 18 months. Basophils release histamine heparin and serotonin and it occupies. 75% of the total blood count.
Eosinophils- you can a filter also called acid of use because granules stained with acidic dyes and its size ranges from 10 micrometre to 14 micrometre who's lifespan are few days.
Monocytes - Monocytes at largest leukocytes where size is 12 micrometre to 20 micrometre and life span is variable from a few days to several days. Nucleus are being shipped and it has phagocytic nature It occupies 3% to 8% of the total blood.
Lymphocytes - Lymphocytes are large nucleus with scanty cytoplasm where it produces antibodies about 20% to 45% of its total. Size of lymphocyte is 7 to 8 micrometre and 10- 15micrometer. Lifespan of B lymphocyte is 3 to 7 days and maybe to several years.
Blood Platelets - Blood platelets are also called thrombocytes as they are non nucleated biconvex rounded or oval small cells whose diameter is 2 micrometre to 3 micrometre and is actually represents in fragments of megakaryocytes of bone marrow. Number of blood platelets is. 15 Million per micrometre cube to .45 million par micrometre cube. Lifespan of the blood platelets are 7 days to 10 days and they take part in blood coagulation through release of platelet factors in certain forms of haemophilia blood platelets do not Birds 2 release platelet factors but they reduce number of platelets which is called thrombocytopenia.When platelet count below 50000 permillimetre cubethen it produces hemorrhagic disorder called purpura. On exposure blood platelets birds and their release growth factors platelet factors thromboplastin and threatening feature required for blood clotting ,constriction of blood vessels and healing.
From Formed Elements of Blood to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.