Kind and Number of Teeth
Kind and number of teeth
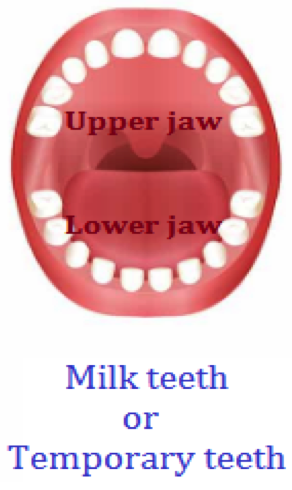
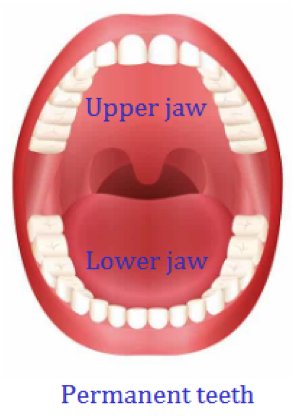
Location of teeth in mouth
Parts of teeth
Care of teeth and gums
Regular check-up of teeth
Importance of dental care
Role of food in development of healthy teeth and gums
Why do we need teeth?
Try saying, 'thirty-three thirsty thieves,' without letting your tongue touch your teeth. Is it easy to talk without using your teeth?
Are all your teeth of the same shape? Are they soft or hard?
What is the colour of your gums? Why are they important?
Teeth are present in our mouth. They help us to chew food, talk, eat, smile, sing, etc.
Sets Of Teeth:
The pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth are together called the jaws. The lower movable jaw is called the mandible and the upper fixed jaw is called the maxilla. The jaws contain teeth.
A baby is born without any teeth. Teeth start growing in babies when they are around six months old. By the time they are two or three years old, children get a set of 20 teeth, 10 teeth in each jaw. This set is called milk teeth or temporary teeth. It is called temporary teeth because the teeth in this set start to fall by the time the child is six years old.
As the milk teeth fall, they are slowly replaced by new permanent teeth. The permanent teeth are the second set of teeth. There are 32 teeth in the permanent set, 16 teeth in each jaw.
What are the differences between milk Teeth and permanent teeth?
Differences between Milk Teeth and Permanent Teeth
|
S. No |
Milk Teeth |
Permanent Teeth |
|
1. |
This set has 20 temporary teeth. |
This set has 32 permanent teeth. |
|
2. |
This is the first set |
This is the second set. |
|
3. |
This set has smaller teeth. |
This set has bigger teeth. |
|
4. |
There are no pre-molars in this set. |
There are 8 pre-molars in this set. |
|
5. |
There are 8 molars in this set. |
There are 12 molars in this set. |
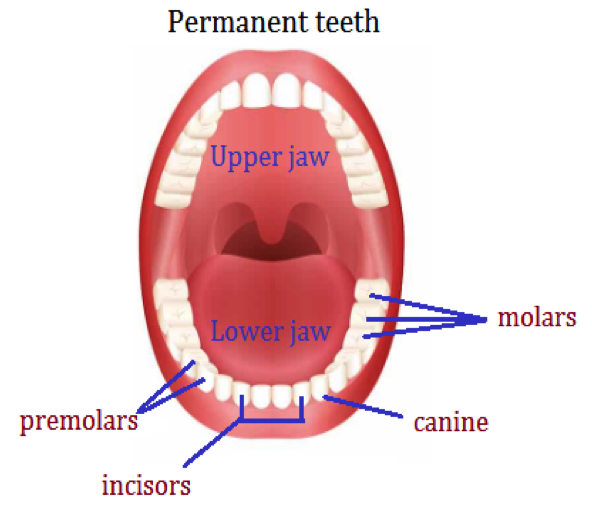
Types Of Permanent Teeth:
We have four types of permanent teeth. They are of different shapes and perform different functions. The front 8 (4 in each jaw) teeth are called incisors. On either side of the incisors, 4 canines (2 in each jaw) are present. The pre-molars lie next to the canines followed by the molars.
The table below summarises all the details about the different types of teeth.
|
Types of Teeth |
Number of Teeth |
Shape of Teeth |
Use of Teeth |
|
8 (Four in each jaw) |
Sharp, flat and chisel-shaped |
Cutting and biting of food | |
|
4 (Two in each jaw) |
Sharp and pointed |
Tearing of food | |
|
8 (Four in each jaw) |
Flat and broad |
Tearing and crushing of food | |
|
12 (six in each jaw) |
Flat and broad (bigger in size than premolars) |
Grinding, tearing and crushing of food |
The last molar on both sides of each jaw is called wisdom tooth. They are 4 in number. These grow later in life usually between the ages of 17 and 25.
Do you remember losing any of your teeth? How many teeth have you lost till date? Did you get any teeth in place of the lost ones? Share your experiences in the class and listen to your classmates experiences.
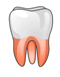
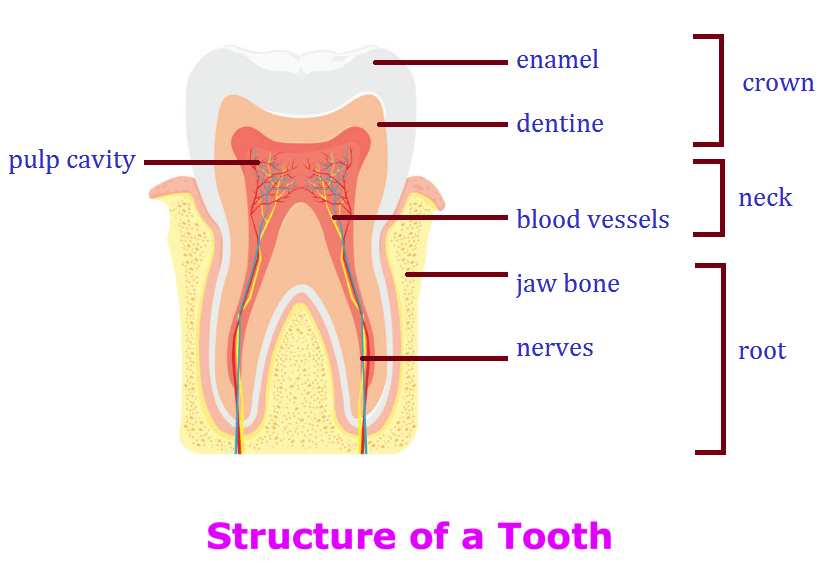
Structure of Tooth:
Each tooth is made up of three parts - crown, neck and root.
The part of the tooth which is visible to us is called the crown. It is covered with a hard translucent substance called enamel. The part of the tooth covered by gums is called the neck. The part of the tooth which goes inside the jaw bone is called the root. The root is covered by a hard substance cementum that binds the root firmly to the gums and the jawbone.
Each tooth has three layers. The outer layer of the tooth is called the enamel. It is the hardest substance in our body. The part below the enamel is the dentine.
Inside the tooth, in the centre, is the soft part of the tooth called the pulp cavity. It has blood vessels and nerves in it. Blood vessels carry blood that is rich in nutrients and oxygen to the tooth. The nerves send and receive messages from the brain.
Note:
Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body. It consists of large amounts of minerals.
From Kind and Number of Teeth to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.