Physiological Effects of Plant Growth Regulators
Internal regulators of growth and development internal regulator of growth and development are genetic factors and growth regulator as these are important internal regulator. Best genetic factors are transmitted from one generation to another in the living organisms. The growth regulators are basically organic substances which are required for the growth and are called hormones they are produced in one part of organisms and are transferred to some other part where they play different physiological effects and regulate different activities. Hormones are connected with control of growth.
According to the role of hormones on the plant growth and development they can be divided into different categories these are auxins gibberellin cytokinin abscisic acid ethylene etc.
There are also different hormones which are developed artificially by the scientist and they are using in different purposes in plants like increase the production of the fruits and serials improvement of the quality of the fruits, only development of fruits enhances the synthesis of flower and increase its number and development.
Auxins:
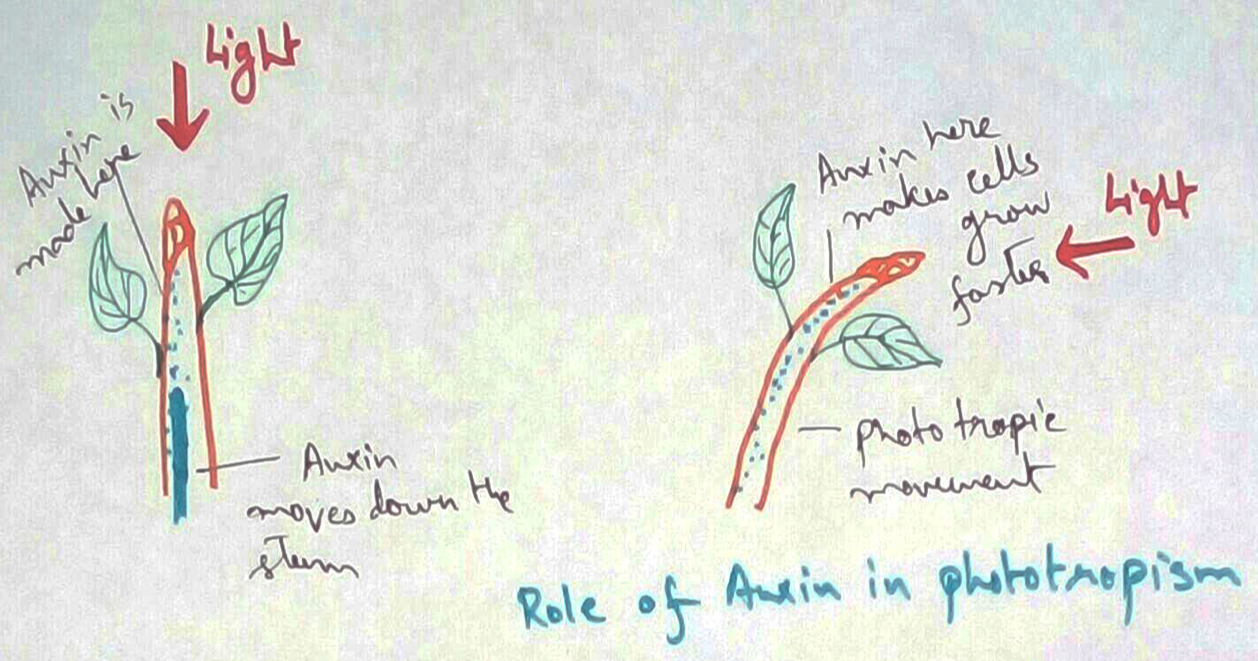
In 1881 diamond found that bending in 1881 diamond found that bending moment movement of collector of Canary grass was occurs due to exposure of tiff to unilateral light. Boyfriend jeans in INR 1910 and 1911 found that the chief producers are chemical which was letter named as auxins and in 1914 all removed collect and keep and replaced it asymmetrically to find the curvature. Auxin hormone was first collected by went in 1928 from coleoptile tip of a winner as he developed Avena curvature test for bioassay of auxin. Isolated 3 chemicals art of Sin A option B and real oxen real of sin is indole 3 acetic Acid or IAA which is synthesized mainly from tryptophan in shoot Apex and developing seeds. Auxin hormone is defined as mildly acidic growth hormone which having and unsaturated ring structure and are capable of promoting cell elongation specially of should segments in present in concentration of less than 100 PPM. Indole acetic acid is effective in stem elongation in concentration of 10 PPM root elongation has a concentration of .0001 PPM. Chemicals are auxin related Chemicals are Windows 3 acetaldehyde phenyl Acetic Acid 4 chloro indole acetic acid and Indore 3 acetonitrile. Natural auxin has the characteristics of Polar Transport from stem Apex to base and from there to root apex.
Role of auxins - Auxin is very important hormone which has major role in different plants life. They are-
1. Cell growth - Auxin hormone promote cell enlargement by loosening the cell wall microfibrils increases solubilization of carbohydrate reserve increased respiration increased membrane permeability and synthesis of all the new wall microfibrils.
2. Cambial activity - Auxin has the role in promotion of seasonal activity of cambium which is required for cell division and in grafting experiments this hormone is specially added to quick and the union of stock and scion.
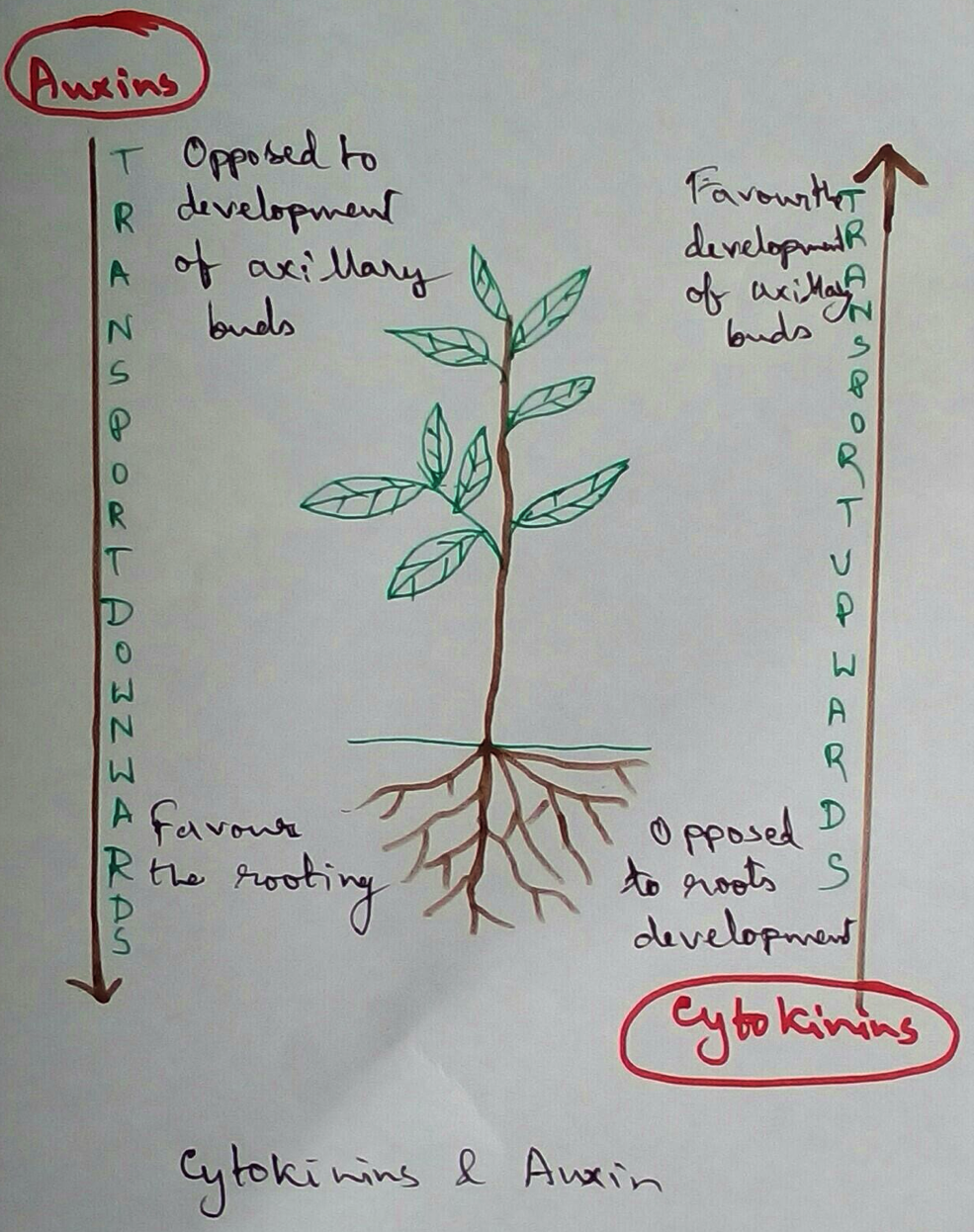
3. Apical dominance - Apical dominance of terminal bud is observed due to secretion of indole Acetic Acid by the plants and lateral buds do not grow if the decapitated shoot tip is provided with auxin.
4. Abscission - Option is observed to be inhibits abscission of leaves and fruits as abscission layer is produced when the oxygen content falls below a minimum level.
5. Tropic movements - Auxin also plays a major role in phototrophic and geotropic movement which are mediated through differential distribution of indole acetic acid.
6. Rooting - Rooting of stem cuttings is also promoted by dilute solution of indole butyric acid or naphthalene acetic acid.
7. Weedicides - 2, 4 D and 2, 4, 5 T are the two types of hormones that are used for killing broad leaved weeds which causes harm to the desirable crops where as 2, 2 dichloro propionic acid kills grasses.
8. Storage - Some types of certain auxins are used for prolonging the life of storage products like towards coms rhizomes example of this type of auxin is NAAM.
9. Pre harvesting fruit drop - Naphthalene acetic acid is associated with the stoppage of preharvest drop of fruits.
10. Feminishing effect - Some of auxins show of feminishing effect in some plants.
11. Tissue formation - Auxin hormones are useful in callus formation tissue formation and prevention and as well as promotion of flowering in plants.
12. Parthenocarpy - Auxin hormone can also be used for production of seedless fruits which are known as the process of parthenocarpy through the promotion and application on un pollinated pistills.
13. Healing - If injury occurs, in plants,this is affected through auxin induced division in the cells around the injured area does auxin was formerly named as traumatic acid or traumatin.
14. Prevention of lodging - Spraying of auxin hormone prevents lodging in crops live cereal and legumes
15. Nodule formation - In plants like legumes indole acetic acid is known to be stimulate nodule formation.
Gibberellins –
these are a major group of plant hormones after auxin, in 1926 kurosawa observed in a rice field in Japan that among the dwarf variety rice plant some of the plants become very tall due to the foolish seedling disease or bakanae disease that caused by a fungus called Gibberella fujikuroi. He observed that application of cell free extract of this type of fungus also caused internode elongation of the healthy rice plant.
In 1935 Yabuta name the substance as gibberellin after the name of the fungus.
In 1938 Yabuta and Tsumiki isolated two classes of gibberellin compounds known as gibberellin a and gibberellin b which was formerly a mixture of three active gibberellin compounds while the latter is a mixture of two active and one inactive compounds.
In 1950 Mission and store dollar in 1955 in USA isolated two classes of gibberellin compounds those are gibberellin A1 and gibberellins A2.
In 1955 Brian it all isolated and was able to purified gibberellin in UK and name this gibberellic acid.
Cross etal was able to give the structure of gibberellin and they showed that it had a jiban ring advertising newly form compounds can be synthesized which was denoted as GA1, GA2, GA3, GA4 etc and Ga3 was the most common form of the gibberellin, by this way they are able to identify more than 110 types of gibberellin from the fungus gibberella fujikuroi ,also contains 15 different types of gibberellin compounds.
Site of gibberellins production - In 1960 Wheeler obtained gibberellins from germinating seeds and germinated seedling, obtained from cotyledon matured seeds and leaves.
Chemical nature of gibberellin compounds are identified as acetic acid. In 1954 cross stated that the formula of gibberellic acid is GA3.
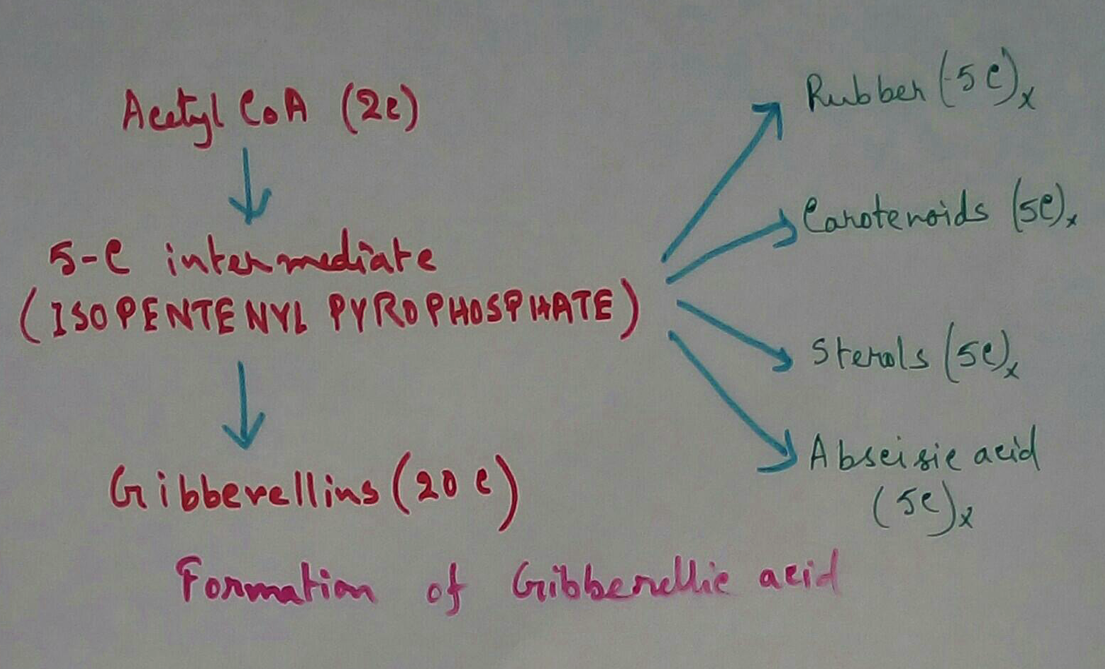
Synthesis of gibberellin - Synthesis of gibberellin generally occurs by the union of acetyl CoA and isopentenyl pyrophosphate. In 1954 Brian atal. was able to synthesise GA3 by the reaction of malonic acid with geranyl geraniol phosphate.
Mechanism of the action of gibberellin - Due to application of gibberellin on plants may cause hyper elongation each effect on the internodes of plants. This may increase the concentration of various hydrolytic and proteolytic enzymes inside the cell and may change its osmotic concentration by causing endosmosis and it is initiated elongation of cells. Gibberellins normally application occurs through of sin by altering its concentration inside the cell but it is transported to every direction in plants.
Role of gibberellins in the growth of seedlings - Role of this hormone can be brought about in three different ways by gibberellin they are followed-
1. Induction of seed germination is associated with the newly synthesis of Alpha amylase which act on the aleurone layer of the endosperm of cereal grains. As the starch is converted to simple soluble sugar which provides nourishment to the developing embryo and it also increases the osmotic concentration of the seed by facilitating entry of water by the process of endosmosis. Due to this ,the germination process of the seed is fastened.
2. Reduction of the inhibitory effect of light on stem growth-as we know that during a plant seedling is grown in light it becomes shorter and green but when it is grown in darkness it becomes long pale and thin. In which cases treatment of gibberellins promotes growth in the dark brown shade. It increases the process of protein breakdown weather its synthesis and why this way it promotes growth. Thus it can be concluded that presence of light can inhibits gibberellin and there by inhibits growth.
3. Elongation of internode by gibberellin- most important action of gibberellins is seedling growth and it can even induce growth in genetically different plants like pea and maize. From this it is included that the genetic dwarf plants are lack of the gene for gibberellins synthesis and due to external application of gibberellin removed by innovative reaction of natural is most innovative and for this why the growth of seedlings iare promoted.
Other functions of the gibberellin - Gibberellins also plays role in different purpose-
Breaking dormancy - Gibberellin hormone takes part in breaking of natural dormancy of seeds buds and underground structures.
Growth - Gibberellin hormone has a role in promotion of growth in both stems and leaves.
Bolting - The process of bolting or elongation of stems in rosette plants can be caused by gibberellins.
Parthenocarpy - This hormone can induce parthenocarpy in a different plants where there is production of fruits without seeds.
Maleness - This hormone stimulates maleness.
Fruit yield - Application of gibberellin hormone increases the number and size of fruits as heat effect is observed in case of grapes.
Malt - Due to increase production of males when gibberellins are provided to germinate Barley grains and it is possible due to greater production of Alpha amylase.
Sugar cane - Application of gibberellic acid increases sugar mills of sugarcane by promoting internodal length.
Overcoming genetic dormancy - Genetic draught plans like females show normal size in the presence of gibberellins has it stimulate the growth of internodes.
Substitution of cold treatment - Vernalization is essential to overcome the cold treatment but it can be substituted by the gibberellin hormone.
Cytokinin - Cytokinins are basic growth hormones which are mild and usually amino purine derivatives that promote cell division in plants. In 1955 Mila etal. discovered the first cytokinin through autoclaving Herring sperm DNA. The thing that produce due to autoclave was Kinetin and it 9 furfuryl amino purine.The first natural cytokinin was discovered in 1963 by letham et all and was zeatin. Almost 18 cytokinins have been already discovered among them dihydro zeatin IPA benzyl adenine etc are examples. IPA is ISO 2989 compound and are maximum found as constituents of tRNA s.
Synthesis of cytokinin - Synthesis of cytokinin occurs in roots and endosperm of seeds and also in coconut milk apple fruit extract which are rich in cytokinins.
Different experiments like bioassay is done through retention of chlorophyll by leaf disc and gain of weight of a tissue in culture.
Functions of cytokinin:
Cell division - This hormone is essential for cell divisions of cytokinesis by the formation of interfascicular cambium and also control by this hormone.
Cell growth - This hormone take part in cell elongation along with auxins and gibberellins.
Morphogenesis - In associated with auxins cytokinins control morphogenesis by development of buds on axis if cytokinin concentration is more than oxygen and roots are formed when oxygen content is more as they are in fault in lignification and plastid development.
Apical dominance - This hormone promote sprouting of lateral buds and overcome apical dominance of plants.
Prevention of senescence - This hormone causes retarded solutions which was discovered in 1967 by Richmond Lang effect by Richmond and lang.
Resistance - This hormone increases resistance to harmful temperature and diseases.
Dormancy - This hormone helps to overcome seed and other types of dormancy.
Phloem transport - It has a role in the transport system of phloem during the distribution of food that produce in the leaves.
Solutes - This hormone has a role in mobilisation of solids and other nutrients towards the route so that plant can easily uptake those things.
Shelf life - Cytokinin also has a role in increase shelf life of vegetables and cut flowers.
Fruits - This hormone is associated with the improvement and yield of good quality fruits.
Short day plants - This hormone promotes flowering in some short day plants like Lemna and wolffia.
Pomalin - Combination of cytokinin means 6 benzyl adenine and gibberellin Ga4 and Ga7 called pomalin that is particularly effective in increasing apple size.
Ethylene hormone - This is a gaseous plant hormone which is effective in concentration of point 0 .1 PPM to 10 PPM and it stimulates transfers growth but in Abids are the types of growth as well as normal functioning. The commercial product which profile ethylene is it a phone or 2 chloro ethyl phosphonic acid.
Functions of Ethylene:
Transverse growth - Transfer growth is promoted by easily but it inhibits longitudinal growth.
Senescence - Ethylene also associated with the promotion of senescence.
Abscission - This hormone promotes obsession of leaves flowers and fruits.
Flowering - Feeding of flower in its presence , in presence of this hormone rolling of petals in blossom flowers can be occur due to this hormone but it can also be used for promoting flowering in pineapple.
Dormancy – this break dormancy of different plant organs but not of lateral buds.
Feminishing effect - It has a feminishing effect on flowers.
Fruit ripening - this hormone is very essential for ripening of fruits artificially.
Epinasty - This hormone induces apinasty or downward bending of leaves.
Auxin and ethylene - Excessive auxin solutions stimulate production of ethylene, this hormone lowers the synthesis and transport of auxin.
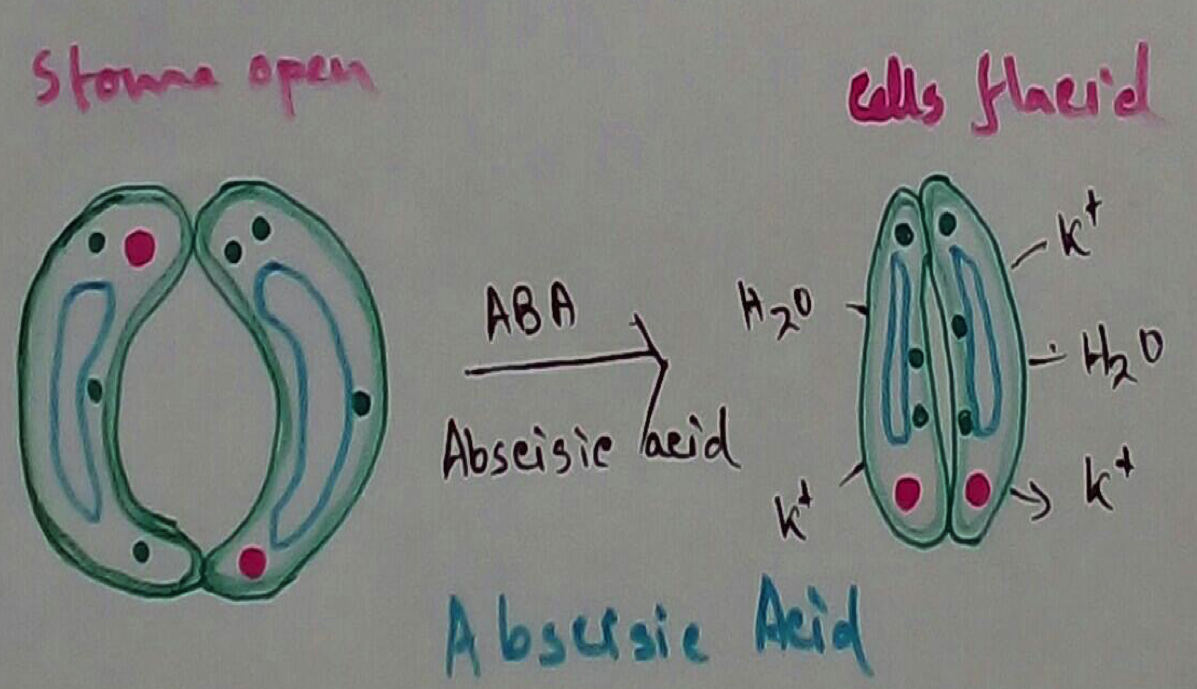
Abscisic acid - Abscisic hormone or acetic acid is also known as stress hormone or dormain. This hormone is an inhibitor which counteracts the influence of growth promoting hormones like auxins gibberellins and cytokinins it also induces dormancy and helps to overcome the condition of stress. In 1963 the hormone was discovered by Addicott etal. and it is commonly found inside the chloroplast either from mevalonic acid or xanthophyll like violoxanthin. Chemically acetic acid is dextrorotatory or cis- sesquiterpene.
Function of abscisic acid:
Control - Abscisic acid keeps growth under control by counteracting the effect of growth promoting hormones because of this abscisic acid is also popularly known as anti gibberellin hormone.
Dormancy - Dormancy is induces in buds, seeds and underground storage organs.
Leaf senescence - Leaves senescence is produced due to ageing in leaves by abscisic acid.
Abscission - This hormone is also associated with abscission of fruits and flowers.
Stomatal closure - This hormone has the role in the closing of stomata.
Hardiness - This promotes cold hardiness and inhibits growth of pathogens.
Flowering - This hormone promotes flowering in some short day plants.
Questions:
What is the effect of temperature on growth and development?
Temperature is a factor that can influence growth and development because minimum optimum and maximum temperature for plant growth are 2 degree centigrade 2 5 degree centigrade 20 degree centigrade to 30 degree centigrade and 40 degree centigrade to 50 degree centigrade. Both low and high temperature may cause injury to different parts of the plants has low temperature produces desiccation due to absorption of soil water chilling and freezing. On the other hand high temperature causes sunscald leave scotch heat cranker and desiccation.
From Physiological Effects of Plant Growth Regulators to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…







New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.