Chemiosmotic Hypothesis
Chemiosmotic Theory - Piter D. Mitchell proposed the chemiosmotic hypothesis in 1961 and this theory suggest essentiality that most adenosine triphosphate phosphate (ATP) cells comes from the electrochemical gradient across the inner membrane of mitochondriaby using energy that get from the NADH and FADH2 that formed by the breakdown of the glucose.
The chemiosmotic hypothesis suggest the actin of proton motive force causes ATP synthase to convert inorganic phosphate and phosphoryl ADP into ATP.
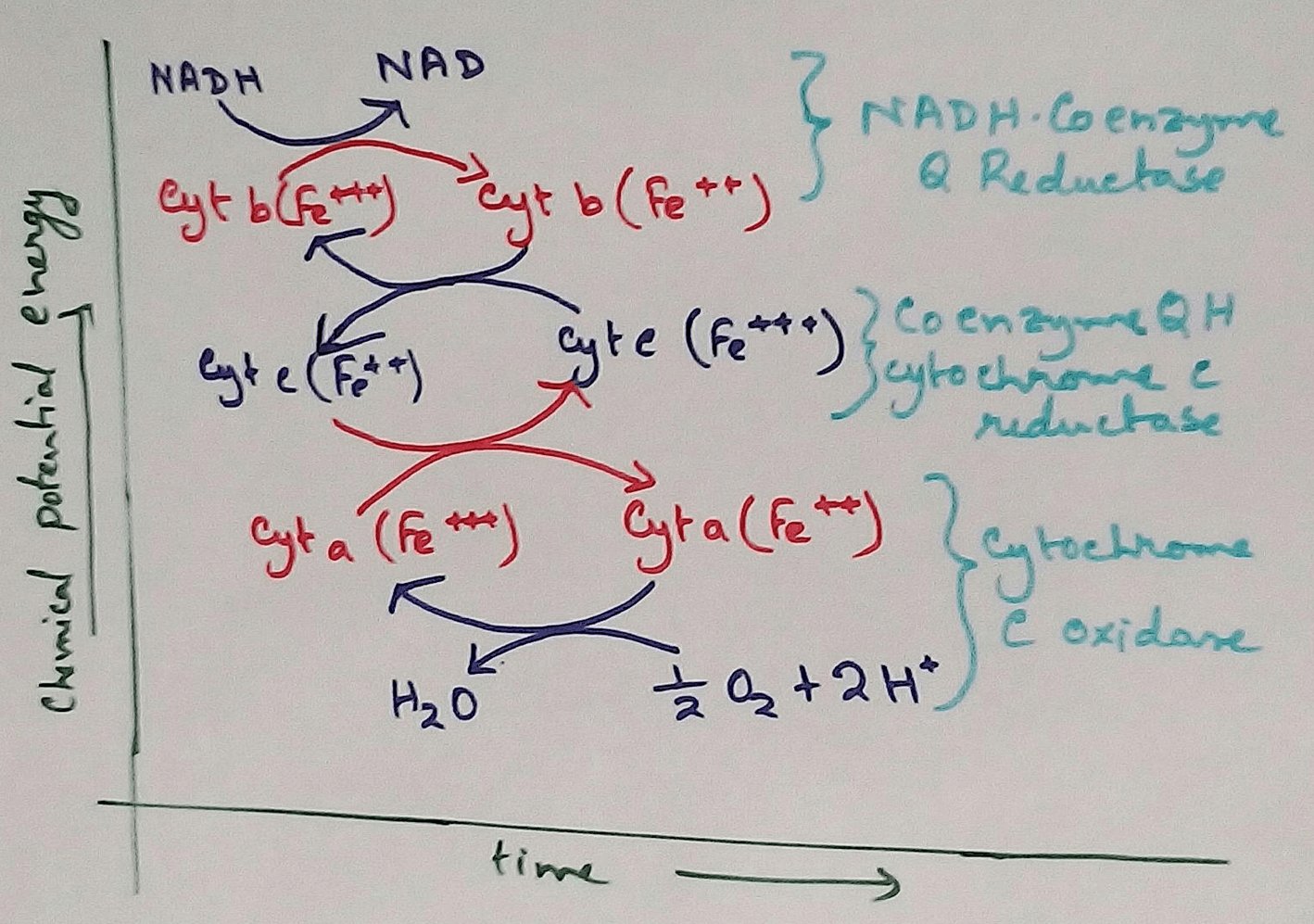
Molecules of glucose are metabolized to produce acetyi CoA which is an energy rich intermediate. Oxidation of acetyl coA in the mitochondrial matrix is coupled to the reduction of carrier protein are Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). These carrier proteins transport electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC) in the inner mitochondrial membrane and then the transport proteins transfer them to other transport proteins of the ETC.
The movement of ions in the inner mitochondrial membrane is caused by –
- Diffusion force which is caused by the concentration gradient as all particle diffuse from the higher concentration to the lower concentration.
- Electrochemical force which is caused by the cations electrical gradient like proton (H+) tends to diffuse down the electrical potential from the positive side of the membrane to the negative side. Whereas anions spontaneously diffuse to the opposite direction.
As lipid bi layer created obstruction to the ions to pass through them, thus energy is stored as the above two gradients to use for the transport of proton pump. Only some of the special protein like ion channels are created for the passage of ions and continuous flow of proton through the chemical energy bond of ATP.
Proton motive force is derived from the electrochemical gradient mentioned by the researchers which can be described Gibbs free energy.
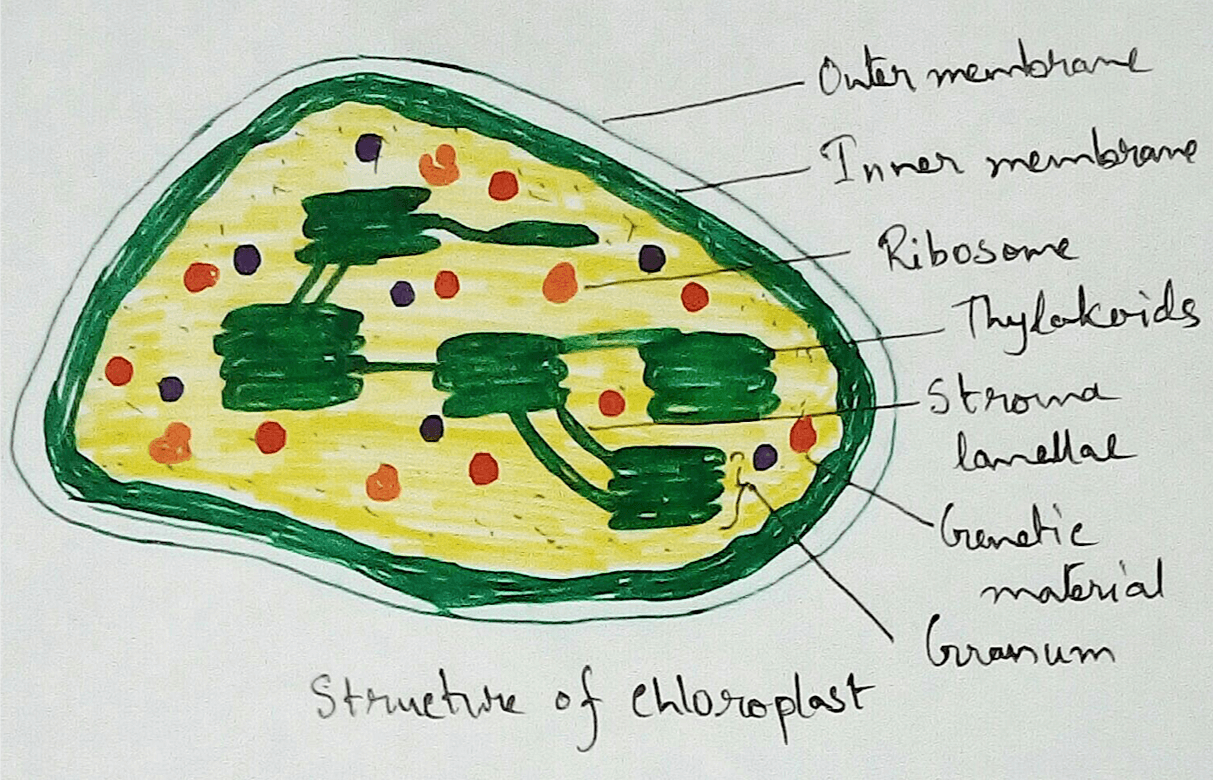
In Mitochondria - As we all know that the food we take that is metabolised by the respiratory different enzymes for the release of the energy from their food. Due to metabolism glucose is produced which undergo glycolysis reaction and converted into pyruvic acid. This pyruvic acid is then undergoes TCA cycle reaction where pyruvic acid under goes different types of reaction by combined with acetylCoA. These reaction produces NADH ,FADH, ATP etc. These energy molecules then transported to the inner mitochondrial membrane and enters the ETC cycle. There energy is released and electrons are transported as a result ATP molecules are created.
Chemiosmosis in Bacteria - Bacteria and archea are the microorganisms to create a chemiosmosis to generate ATP. Green -sulpher bacteria, cyanobacteria etc produces ATP by photophosphorylation. These bacteria creates a proton gradient by the photosynthetic electron transport chain. Non photosynthetic bacteria causes this by ATP synthase.
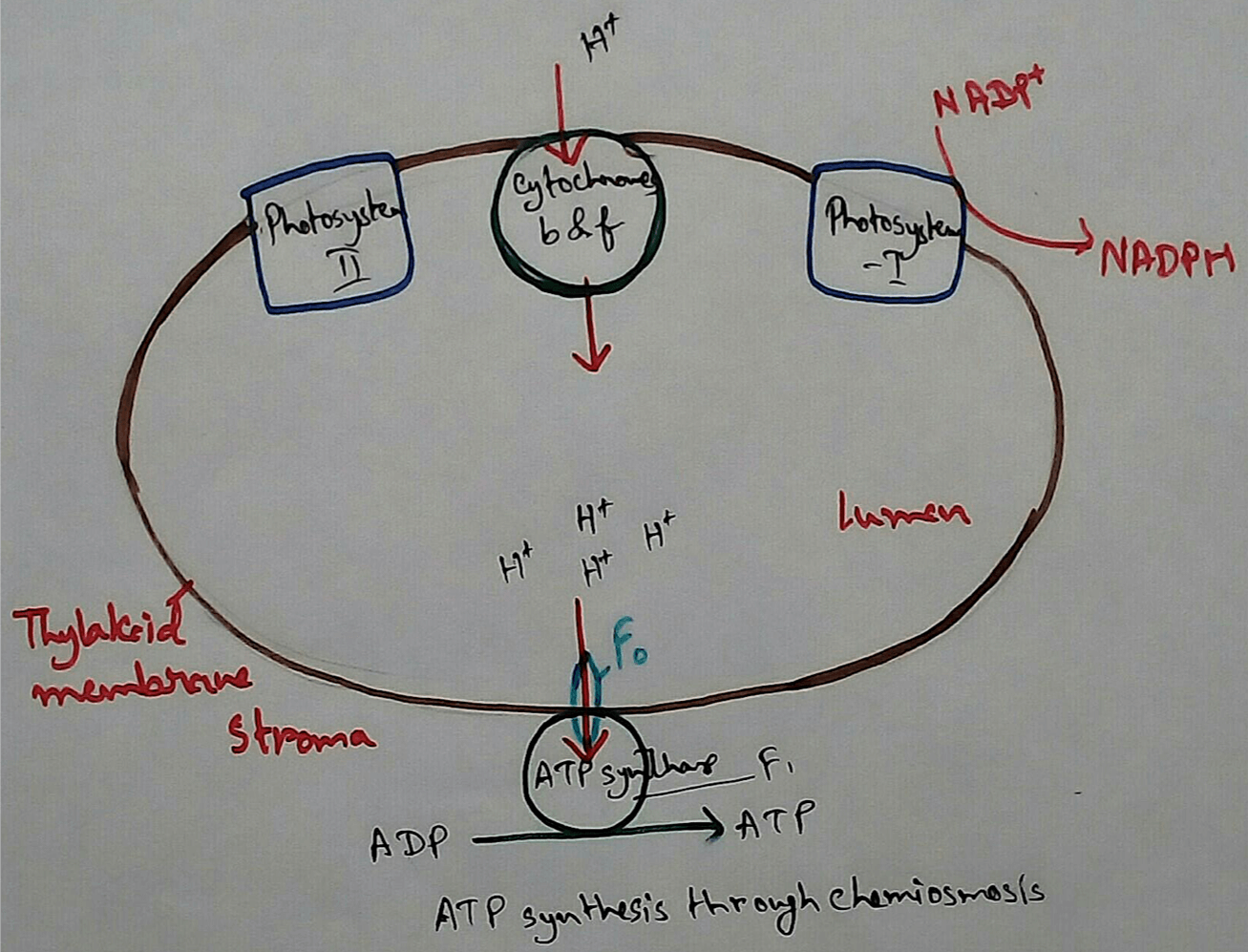
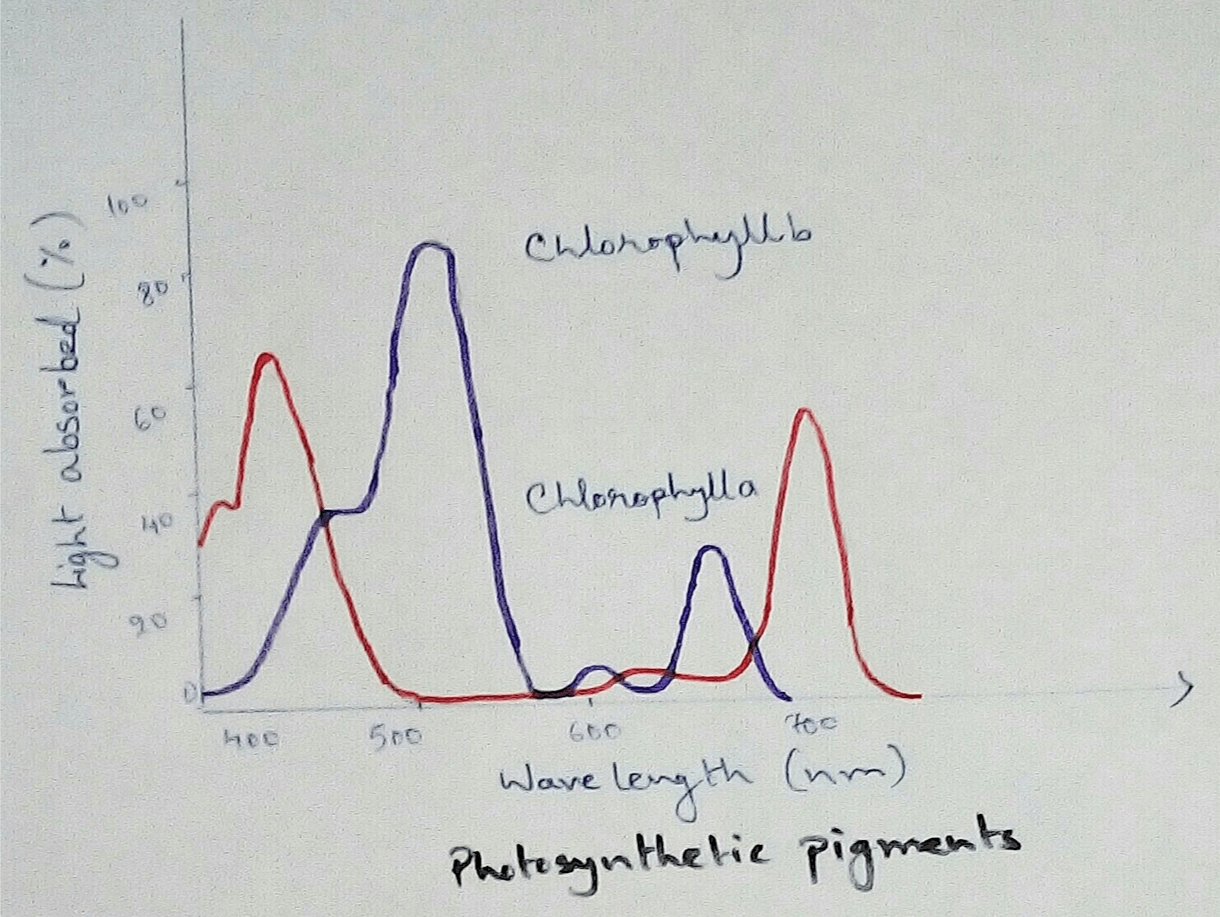
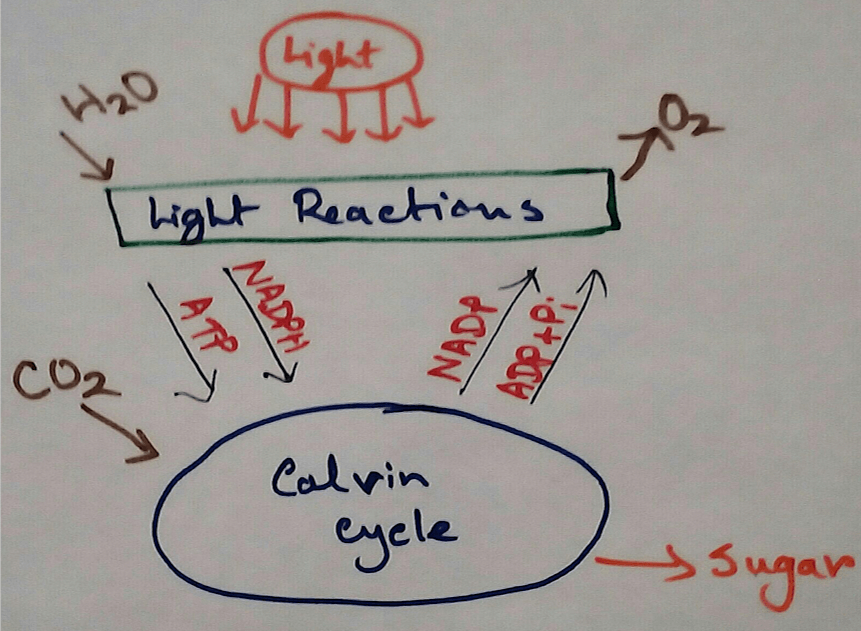
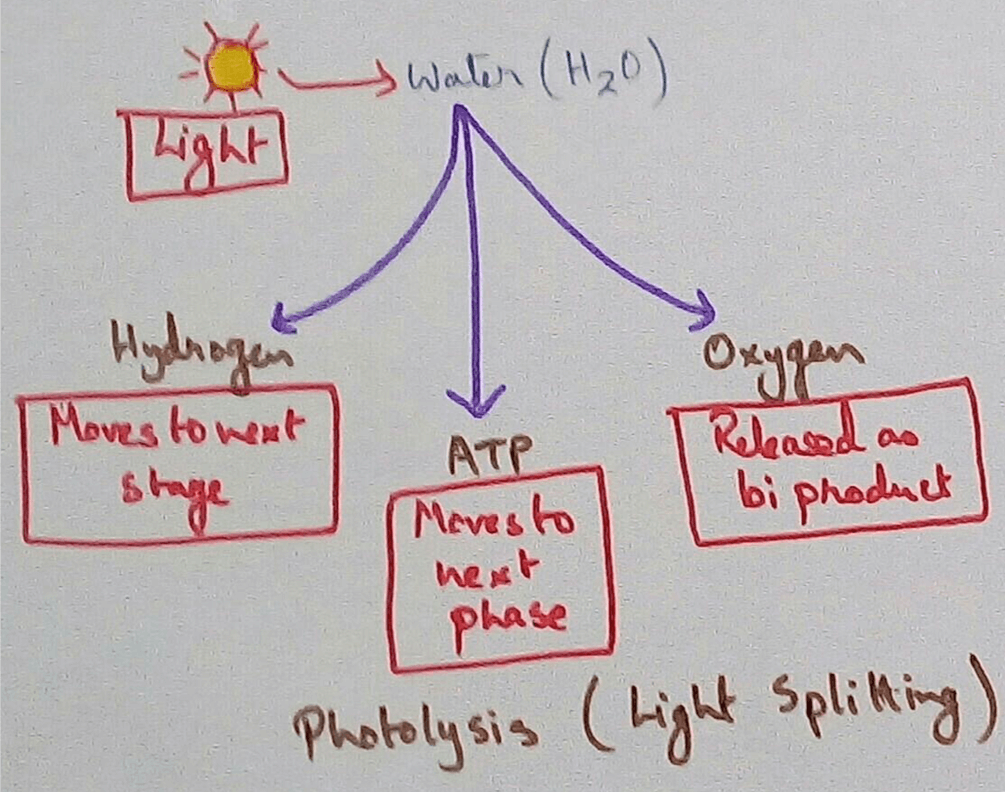
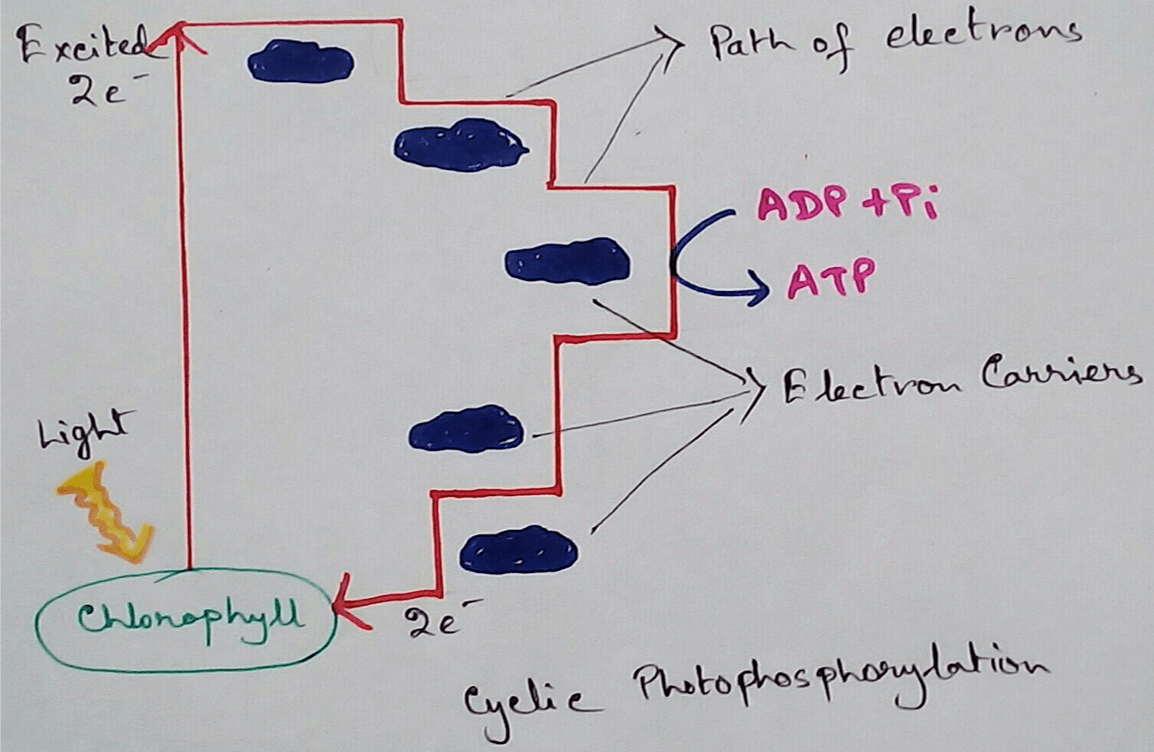
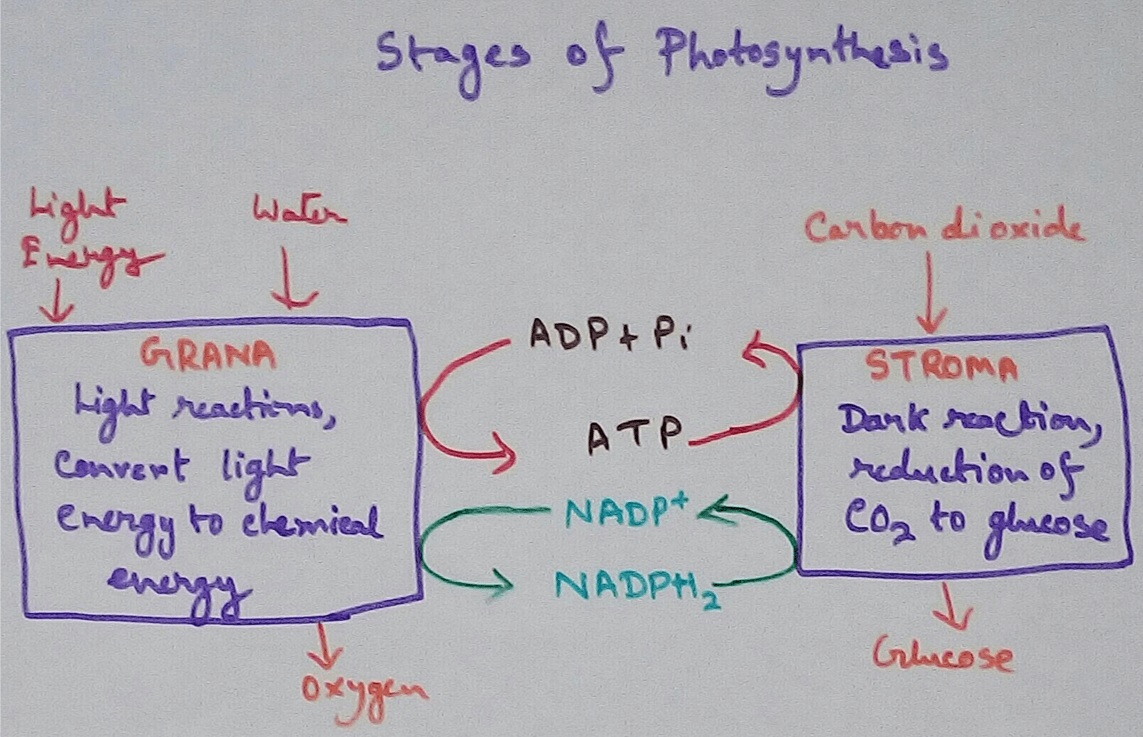
Chemiosmosis in Plants - In the light reaction of photosynthesis ATP is generated by the chemiosmosis process. The photons of sunlight are received by the antennae of photosystem 2 which excuse the electrons at the higher energy levels.
These electrons are then transported down the electron transport chain and causes proton to be actively pumped across the thylakoid membrane to the thylakoid lumen.
From Chemiosmotic Hypothesis to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.