Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Photosynthesis Definition - Photosynthesis is a physiological process in which green plants make their own food in presence of sunlight, water collected by the roots, carbon dioxide from the air and produces oxygen which is released into the air.
Photosynthesis in green plants takes place in the organelles called chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are special type of organelles which is a specialized type of compartments in the plant cells and algal cells.
Location and the Shape of Chloroplasts - As algae are able to make photosynthesis they also contains chlorophyll which are of different shapes like – ribbon like, oval, round etc. Next comes bryophytes after algae where chloroplast are observed. Pteridophytes also contains chloroplast essential for photosynthesis. Next we can come to gymnosperms that do not contain flowers and contains naked seeds are also contain chloroplast. Angiosperms are the most advanced plants those are able to make photosynthesis. Thus photosystem is observed from the unicellular algae to the multicellular green plants. Only organisms that belongs to plant kingdom are able to do photosynthesis.
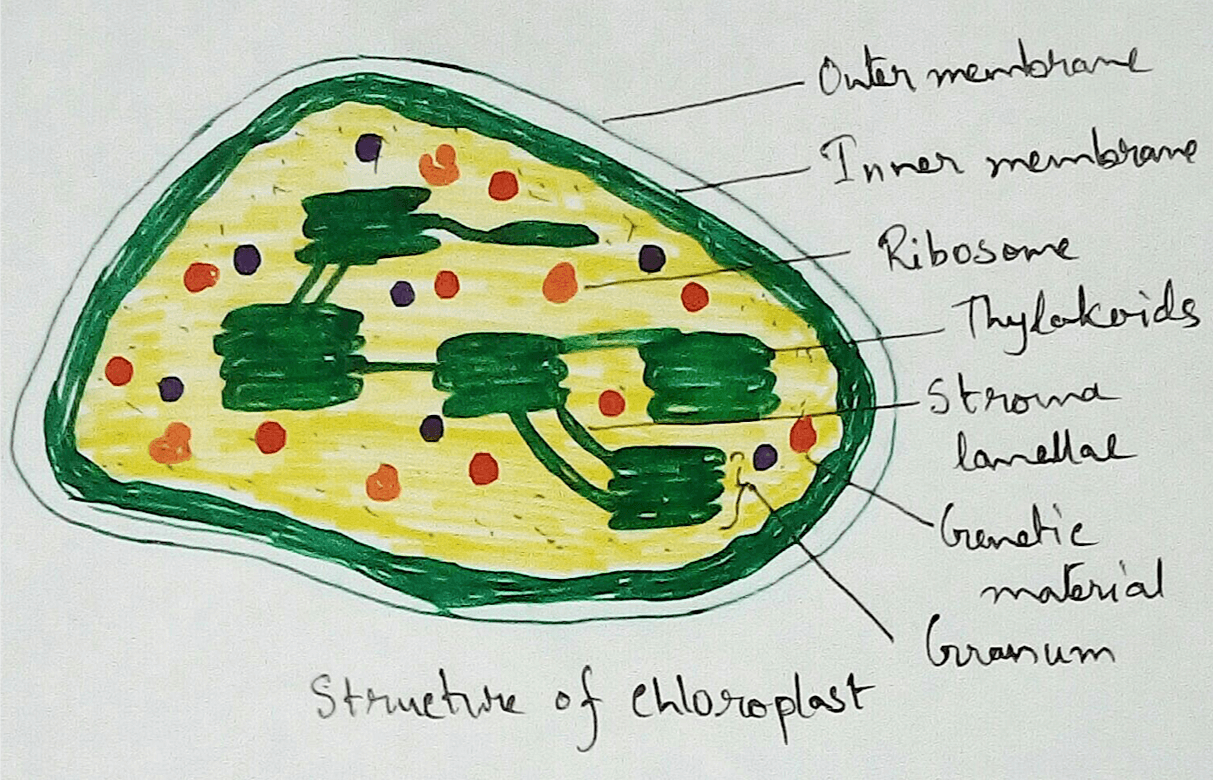
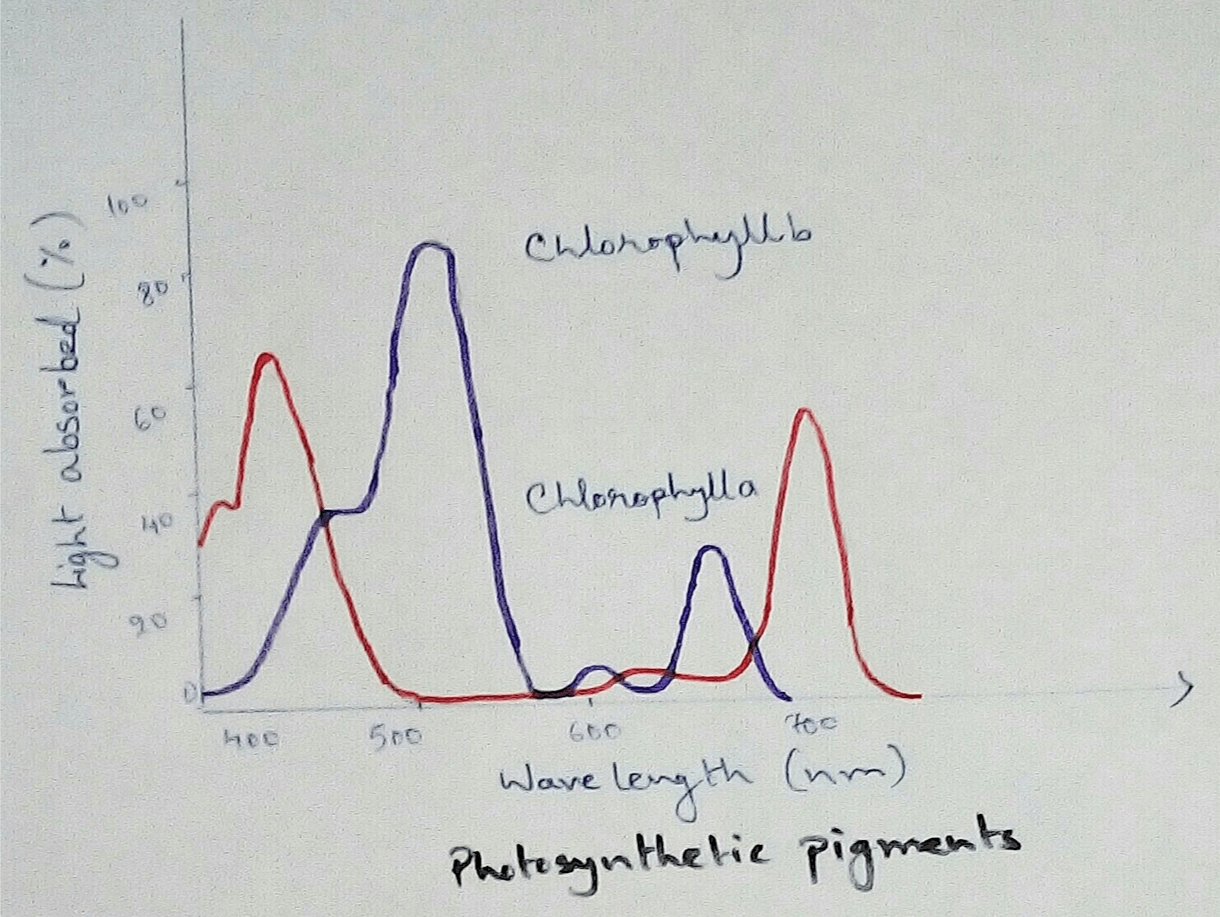
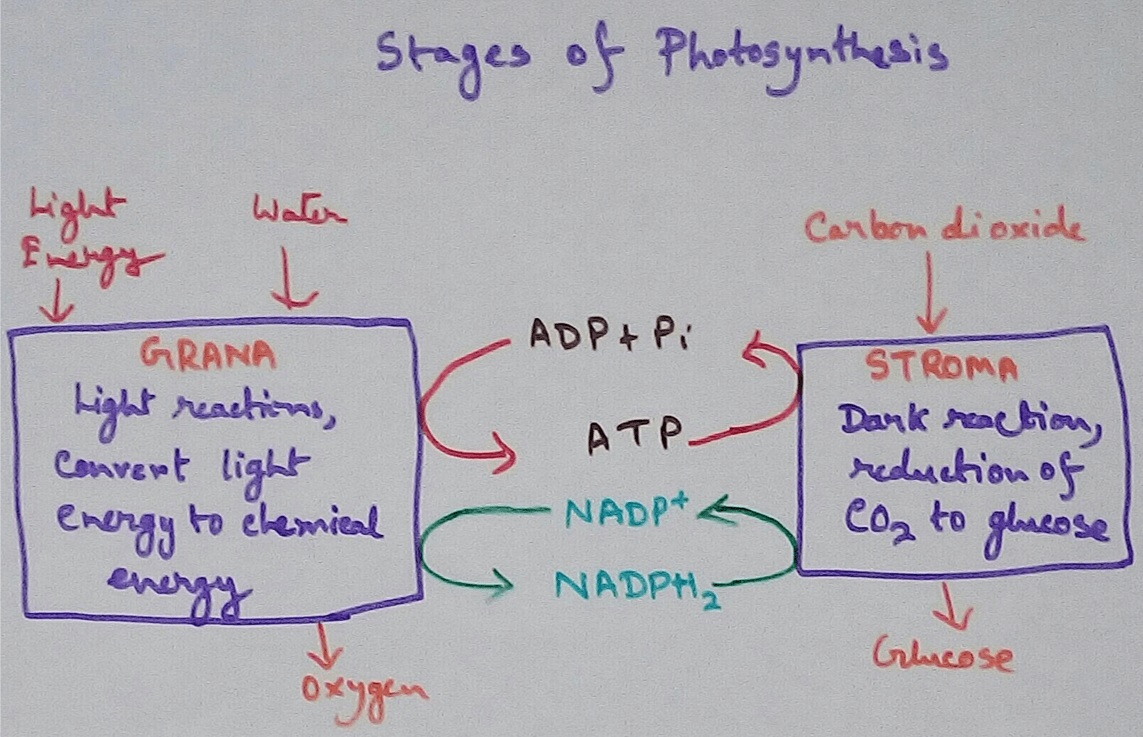
Structure of Chloroplasts - Chloroplasts are oval or spherical in shape . They are membrane bound organelles which are found to be circulated into the cell cytoplasm. According to some scientist it is believed that chloroplasts were separate individual cyanobacteria many years ago, then it was engulfed by the eukaryotic cells and from then they are taken as individual organelles or chloroplasts. It contains different types of proteins and enzymes which are used for the different physiological reactions. Chloroplasts contain a chlorophyll pigments which absorbed all the colour lights and reflects the green colour. Thus it seems to be green in colour. Every chloroplasts has three membrane system. These are outer membrane, inner membrane of chloroplasts and thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts. Chloroplasts contains a jelly like matrix inside the inner membrane, this matrix is called stroma and thylakoid floats on it. Thylakoids are made up of dish like substances and are interconnected with each other by the lamella.
Genes of Chloroplasts - Chloroplasts have its own set of genome. They can be 120000 to 170000 base pair long. They contains single stranded circular DNA.
Function of the Chloroplasts – Chloroplasts have some types of functions. These are-
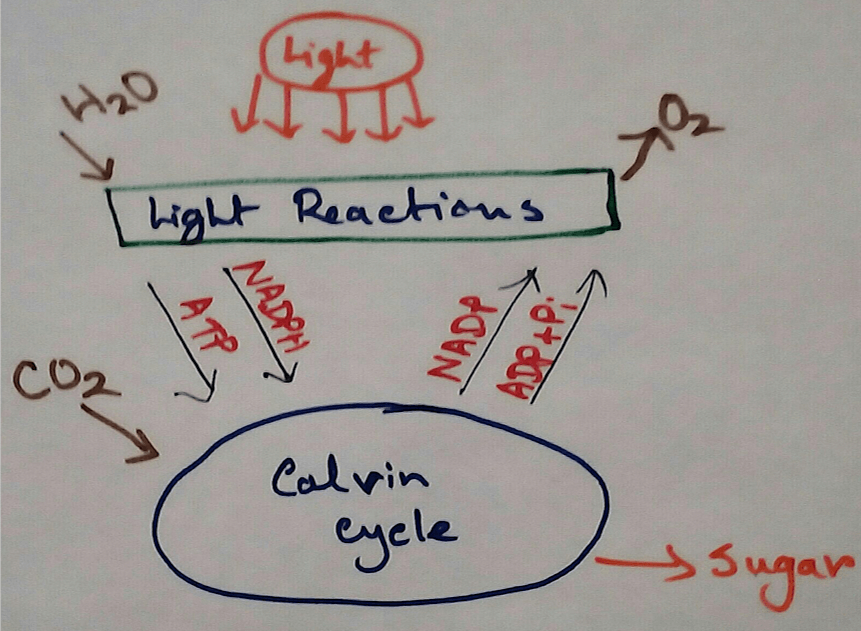
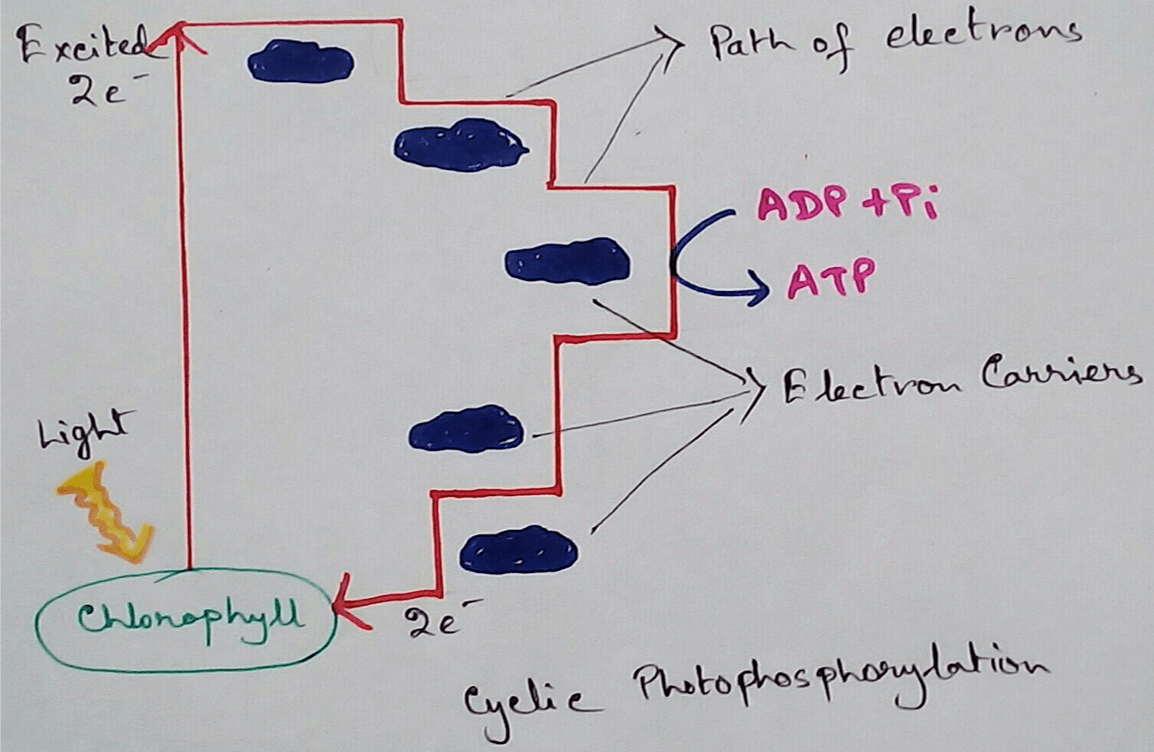
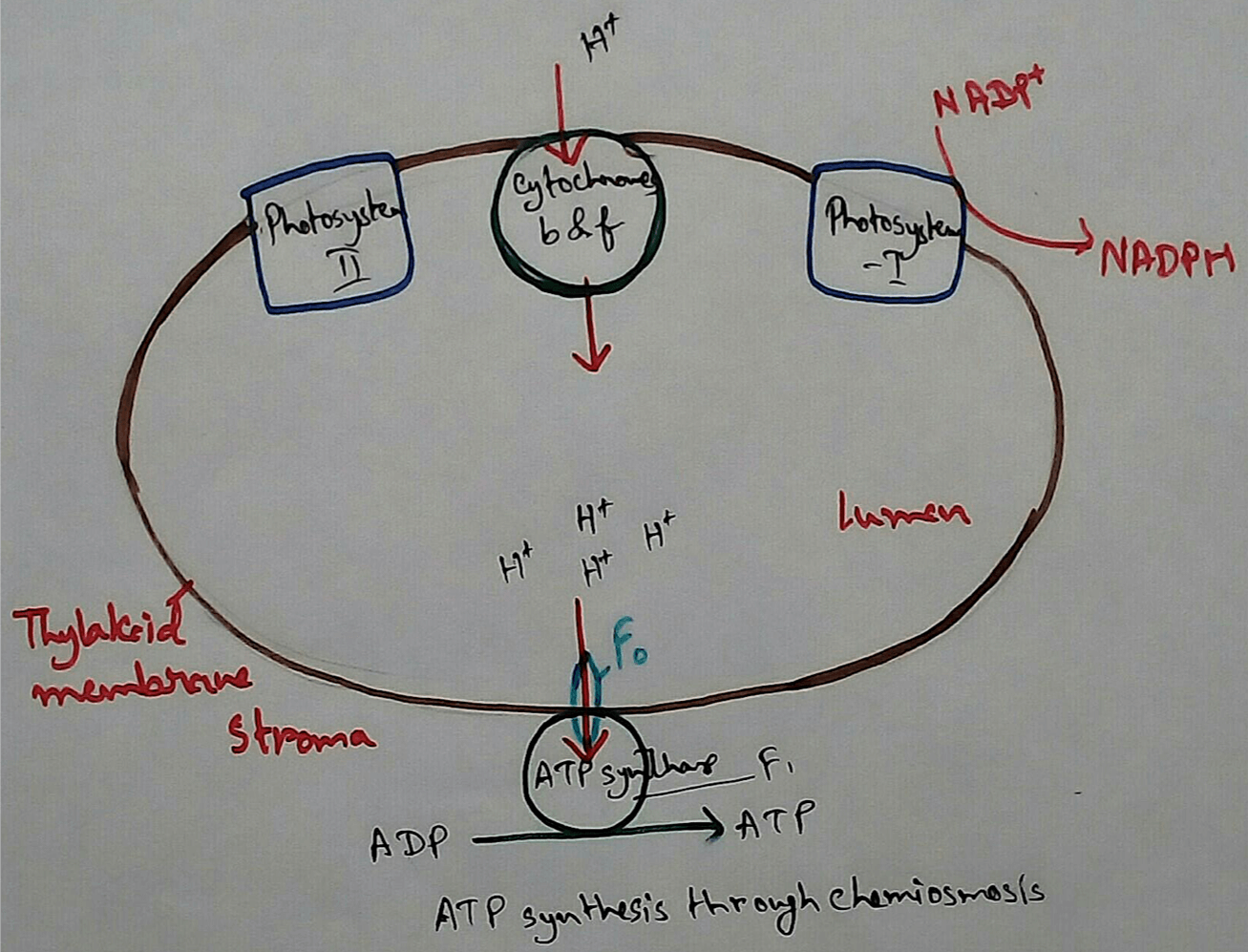
1. Trap the Sunlight - Chloroplasts are the organelles which can trade the sunlight from the sun that is the only source of the energy on the earth. This energy is then transported to the different levels of the consumers and used for their physiological activities. It produces energy stored molecules like ATP and NADPH.
2. Produces Food for Green Plants - Photosynthesis is the process find in green plants that can help green plants to produce their own food.
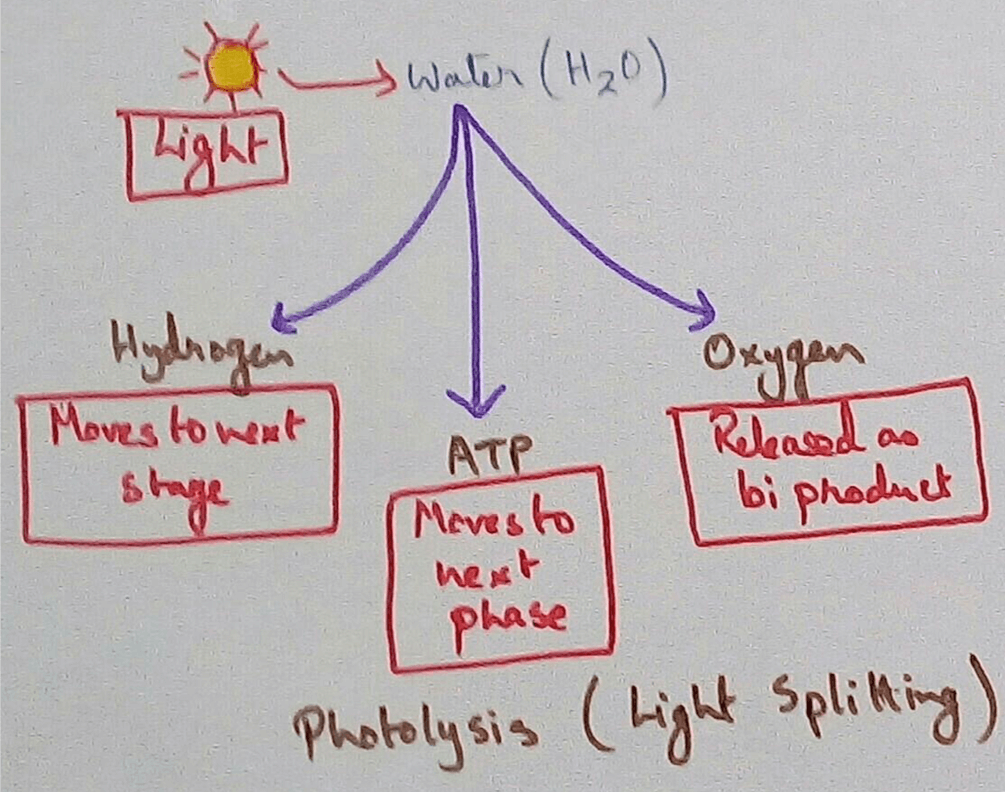
3. Produces Oxygen as a Product of Photosynthesis - Green plants produces oxygen as a result of photosynthetic reaction. Here water is oxidised to form oxygen. This is the only natural source on the earth for the production of oxygen.
4. Others Functions - Chloroplasts are associated with some other functions like fatty acids synthesis, amino acid synthesis, immune response etc.
From Metabolism of Nitrogen to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…
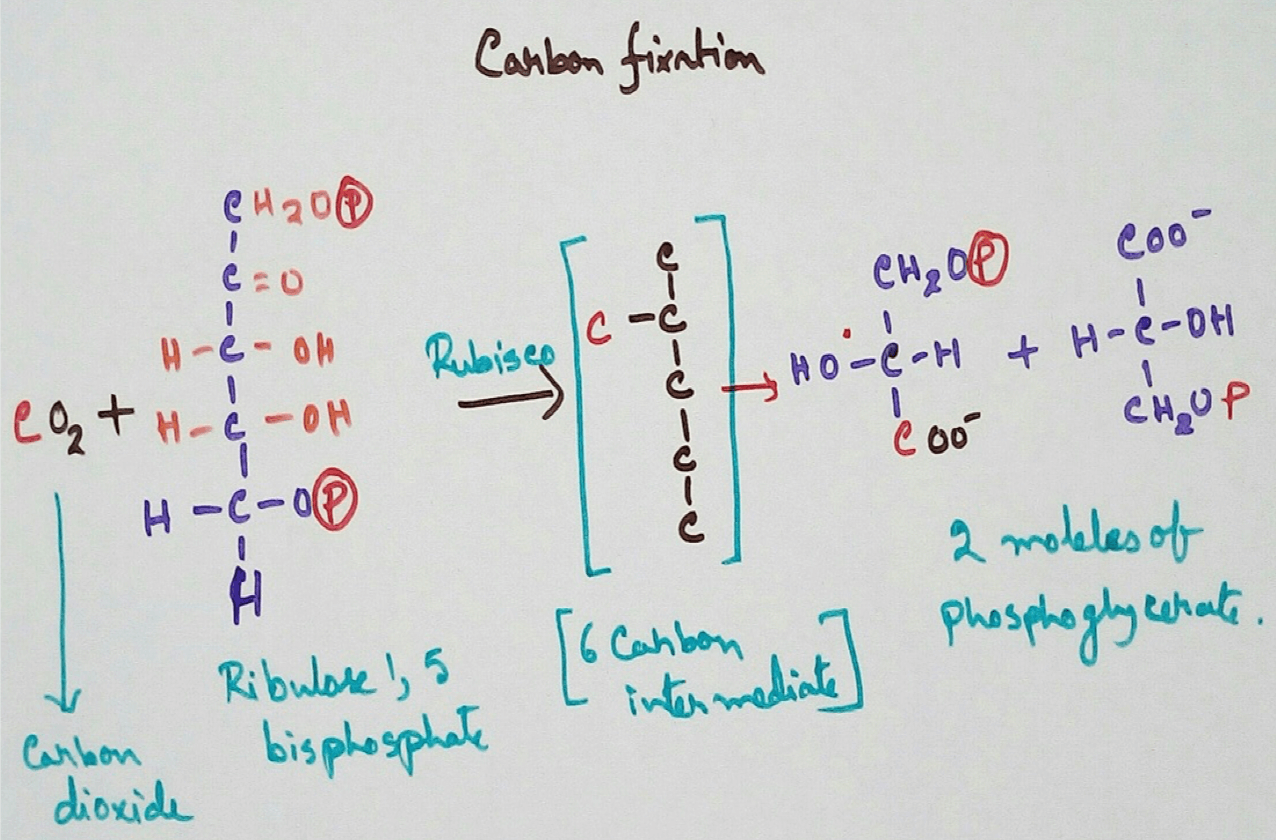
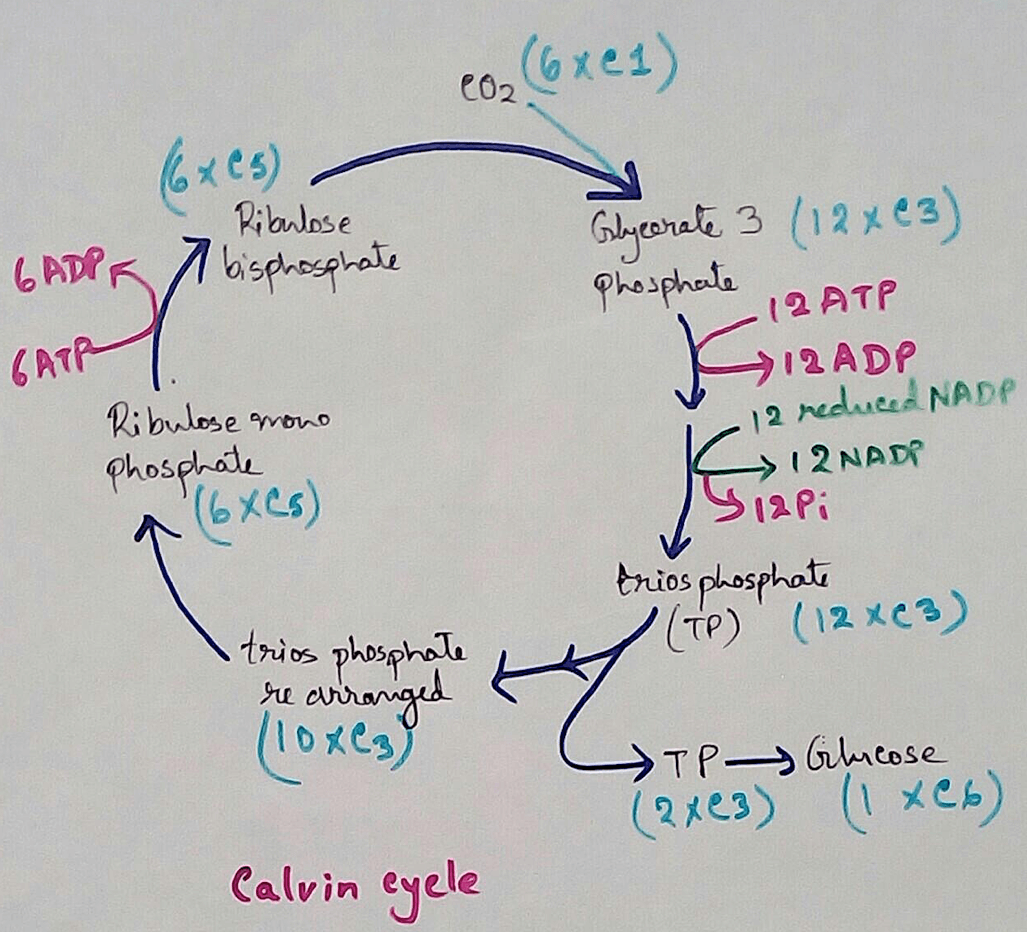
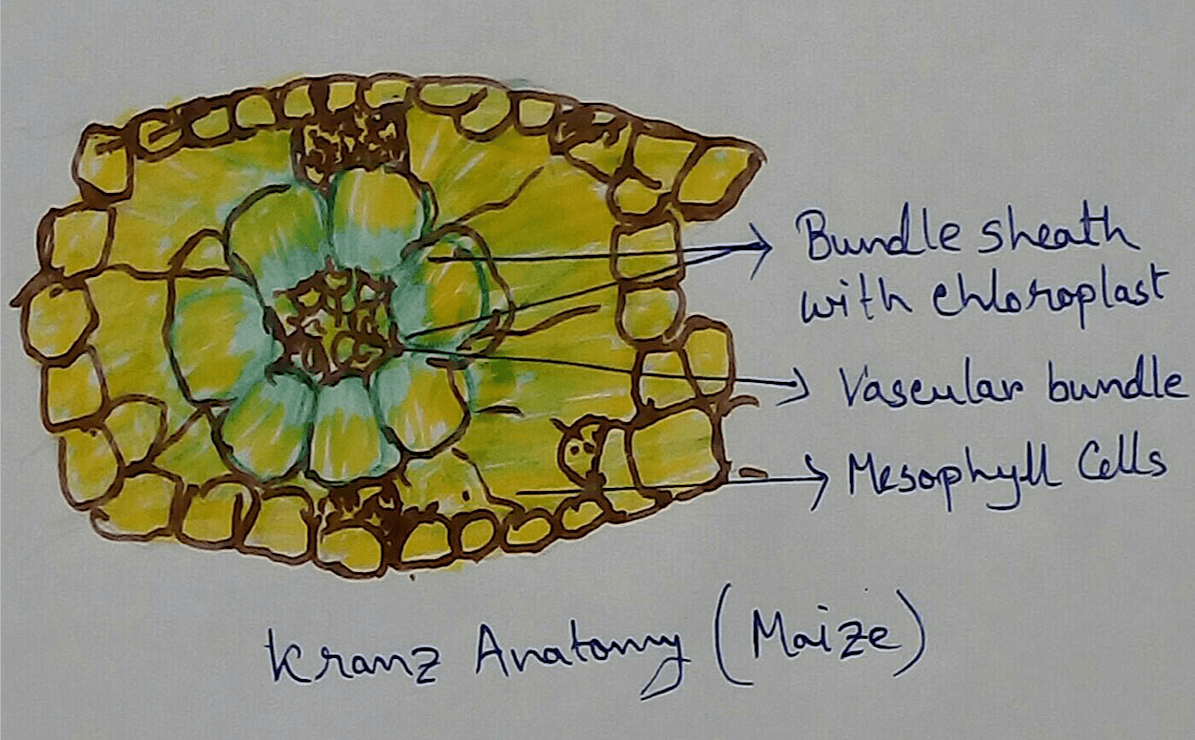





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.