Our Earth
Our Earth is one of the nice planets of our solar system. The
Earth is the third planet from the sun. It is the only known planet that
supports life.
No life is found on any other planet except Earth. The earth was formed millions of years ago. At that time, it was a huge hot ball of rocks and gases. When the Earth was formed there was no life on it.
As year passed, the outer surface of the Earth cooled down because of the rain.
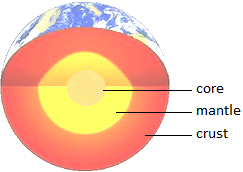
All of us live on the outer surface which is known as the
crust. But the Earth is not the same deep inside.
We think that the whole earth is cool. But, it is
not so. Only the outer surface of the Earth is cool while it is extremely hot
inside. Below the crust is the mantle, which is made up of very hot molten rock. In the centre of the Earth is a hot solid ball of many melted metals. This
central part of the Earth is called the core. It is the hottest part of the Earth.
We have heard of volcanoes giving out hot lava and causing great damage. Volcanoes are actually cracks or holes in the crust of the Earth. Molten rock, called magma is sometimes forced out from the mantle of the Earth through these cracks or holes. The magma that flows out is called lava. It is red hot and hardens to form rocks on cooling. This shows how hot the Earth is deep inside.
Shape of the Earth:
We often hear that the Earth is like a round ball. Actually, it is not perfectly round. It is slightly flattened at the top and bottom. It looks like a beautiful blue ball from outer space.
Rotation and Revolution of the Earth
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.