Photorespiration
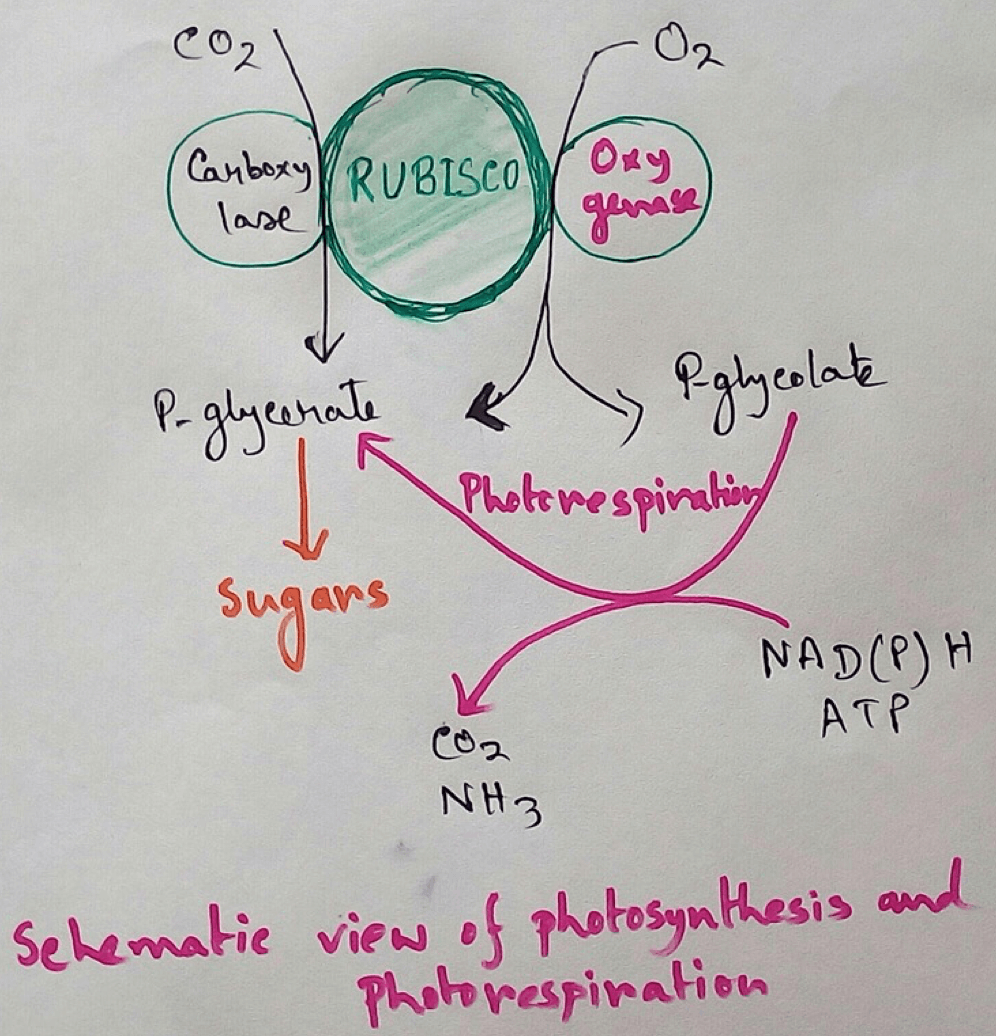
Photo respiration was first described by the Dicker and Tio in 1959. This photorespiration is also known as C2 cycle or oxidative photosynthetic carbon cycle. This is the process that are observed in some higher plants where Rubisco oxygenates RuBp that causes energy production by photosynthesis to be wasted.
Definition of Photo Respiration - Photo respiration is the process of plant metabolism where RuBisCo oxygenates RuBp (ribulose bis phosphate) and causing some of the energy wasted that produced during photosynthesis.
The desired reaction of the photorespiration is the addition of carbon dioxide to the RuBp for entry of the product to the Calvin- Benson cycle. In this reaction maximum of the RuBisCo add carbon dioxide to the RuBp and 25% of the RuBisCo add oxygen to the RuBp so that it cannot participate in the entry of Calvin – Benson cycle.
Location of Photo Respiration- Photorespiration is a light dependent process that takes place at the same time with photosynthesis in green plants. Photorespiration is a network of process which is executed by the metabolic exchanges between chloroplasts, leaf peroxisome and mitochondria.
Factors Affecting Photorespiration - there are some factors that affect photo respiration. These factors are –
1. High light intensity - High light intensity stimulate the photo respiration as photosynthesis takes place and the energy is stored in the leaves.
2. High temperature - At high temperature RuBisCo cannot differentiate between oxygen and carbon dioxide due to formation of the intermediate compound contains enediol group.
3. Ageing of leaf - As photorespiration is a process during photosynthesis, thus ageing of the leaf influence photorespiration. Rate of photosynthesis also depends on the ageing of leaf. Thus generation of energy also affected by the rate of respiration.
4. High Oxygen Concentration - High oxygen concentration stimulate rate of photo respiration as it has an affinity for the oxygen .
5. Substrate Specificity - As RubisCo add carbon dioxide or oxygen to the RuBp ,this gasses stimulates the reaction. But the availability matters as it upon that how fast the gasses could diffused to the area of reaction. If the gasses are not available at the zone of reaction then the rate of will be decreased.
6. Carbon Dioxide Concentration - There is an active form of RubisCo which is called enediol intermediate which participate in the reaction. It is estimated as the continuous rising of the carbon dioxide concentration may reduce the photorespiration by 50 % in the next 100 years.
Rubisco Oxygenate is a Waste of Energy Process - It is the waste full reaction because it produces 3 phosphoglycerate at reduced rate and higher metabolic cost with RuBp Carboxylase activity. Whereas photorespiratory carbon cycle results in the formation of glucose 3 phosphate and there is still loss of carbon, nitrogen as ammonia. This ammonia must be detoxified at substantial cost. For the photorespiration 1 molecule of ATP and NADPH is required.
Reaction of RuBisCo - Addition of molecular oxygen to the ribulose 1, 5 bis phosphate produces 3 Phospho glycerate and 2 phospho glycolate. Phosphoglyceric acid is the basic compound produced during photosynthesis and enters the Calvin – Benson cycle.
From Photorespiration to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…





New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.