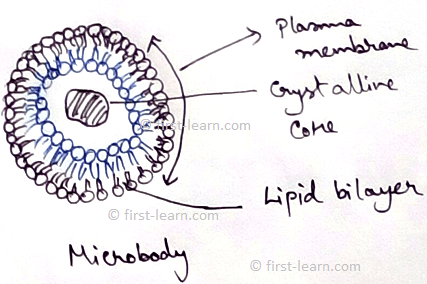
Microbodies
This in 1954 first was the first to observed microbodies. Microbodies are spherical or oval in shape with the diameter of 0.2 to 1.5 micrometer. It has outer covering with lipid and lipoprotein membrane. It contains different enzymes for catalase but do not contain any genetic materials. Thus they are unable to replicate. It participates in the preparatory and intermediate stages of biochemical reaction. It also causes degradation of alcohols, fats and amino acid. Microbodies are associated with detoxification as it contains different hydrolase, catalase enzymes for detoxification. It also contains the enzymes for photorespiration of plants.
Definition - Microbodies are single membrane bound, small vesicular bodies that found both in plant and animals, formed due to dilation of the endoplasmic reticulum (may remain joined).
Microbodies are single membrane bound small cell organelles which take part in the oxidation reactions, those are other than respiration. Microbodies are often possesses a crystalline core and granular matrix. These are of two types –peroxisome and glyoxisomes.
1. Peroxisome - In 1965 De Duve et al and in 1969 De Duve observed that the microbodies contain enzymes for peroxides synthesis. These include-
• Enzymes that are peroxide producing such as peroxidase, urate oxidase or uricase, amino acid oxidase.
• Peroxide causes destruction enzyme catalase.
Location of peroxide - Peroxisomes found widely in animal cells, protistans, fungi, eukaryotic algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes and higher plants. It is quite common in photosynthetic cells of plants. Beside this it is found in liver, kidney etc.
Function of peroxisome - They serve different types of function. These are –
Peroxisome contains oxidase enzymes which are able to degrade hydrogen peroxide means it is associated with metabolism of hydrogen peroxide.
They take part in the oxidative breakdown of extra biochemicals like purine, amino acids, alcohol, toxins, drugs.
In mesophyll tissue peroxisome interacts with chloroplasts and mitochondria to take part in photorespiration. This was observed by Tolbert et al in 1969. As the product glycolate is produced, peroxisome contains glycolate oxidase for metabolism of glycolate. The number of peroxisome can be 70 to 100 per mesophyll cell.
2. Glyoxisomes - Beevers in 1963, Briedenbach in 1967 observed glyoxisomes. These microbodies are observed in fat rich plant cells which take part in beta oxidation of fats and these microbodies also have performance in glyoxylate cycle. These enzymes are found in oil rich endosperm tissues of seeds. It may aid in germination of oil bearing seeds. It also involved in metabolism of stored lipids by conversion of fat into carbohydrates.Glyoxisomes possesses the enzyme catalase.
3. Glycosome - These are membrane bound organelles which contain enzymes and protein for glycogen metabolism. It is mainly found in liver. These enzymes are associated together to enclose in a molecule called glycosome. It is mainly using in drug therapy. It has specialized type of keratinoplast.
4. Hydrogenosome - It is universally accepted that this organelles was evolved from mitochondria. It is a membrane bound organelles which is generally found in fungi, ciliates, trichomonas. It can produce carbon dioxide, acetate, hydrogen, ATP etc. It also contains super oxide dismutase, dehydrogenase etc. It is mainly observed in anaerobic organism.
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…







New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.