Explain about the Structure of Proteins
Definition of Protein: Proteins are one of the major components of food, associated with cellular structure and different physiological activities .
Components of Protein: Proteins are made up of amino acids. Each amino acids contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen. But sometimes other elements like - sulpher etc can remain attached with this molecules.
Types of amino acids – Amino acids are of different types- polar,nonpolar, basic, acid etc.
Structure of Protein:
Amino Acid: We can found 20 amino acids in the body. Among them each amino acids contains one -NH2 (amino group ) and one -COOH (carboxyl group). Peptides bond are formed between one amino and one carboxyl group. This peptide bond helps one amino acids to attach with others.
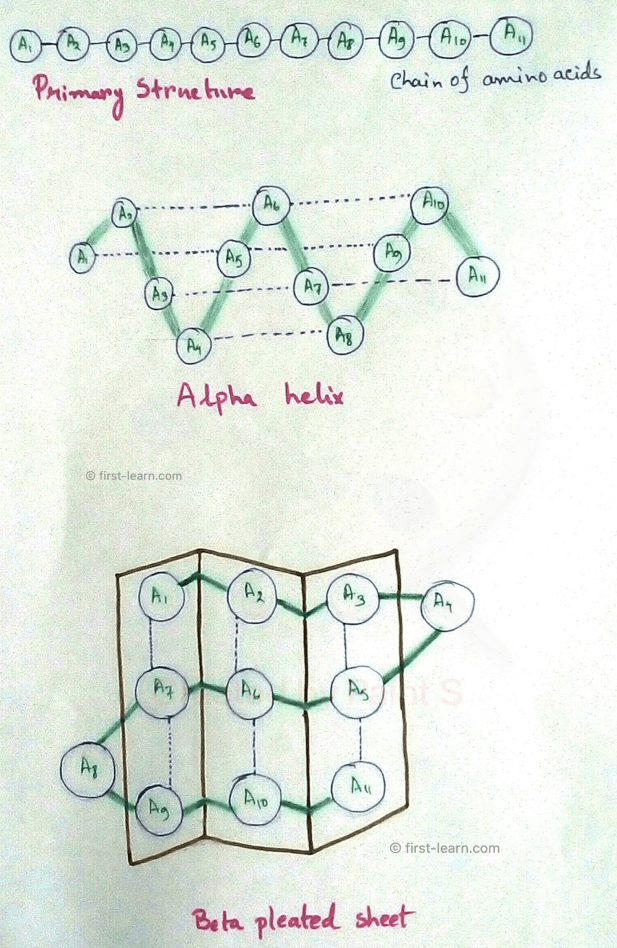
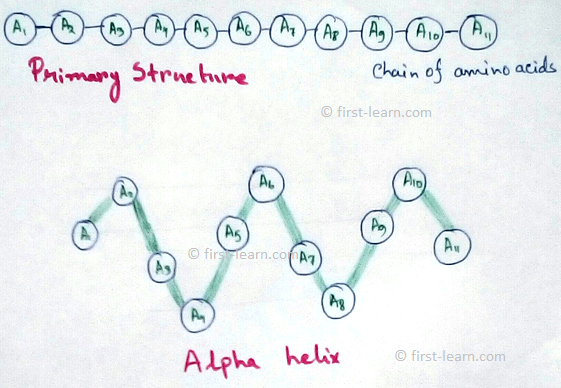
1. Primary Structure: Primary structures are the initial simplest structure of protein. There are 20 amino acids available in the environment which are combined in different sequence to produce different protein. Actually all the proteins are combination of amino acids with different sequence. When there are around 50 amino acid sequence it is called peptides, not protein. But when the number of amino acid increase more than 50 in number, then it is called proteins. In the primary structures amino acids are arranged in a chain .
2. Secondary Structure: Secondary structure of proteins are of two types – alpha helix and beta pleated sheet. Alpha helix are formed due to formation of hydrogen bonds between the amino acid molecules. Beta pleated sheets are formed by the arrangement of the beta strands. These beta strands form hydrogen bonds between them to produce secondary structures of protein. According to the arrangement of the strand beta sheet can be parallel or anti parallel. The ending of the polypeptide where -NH2 group is present is called N terminus and the end where -COOH group is present is called C terminal. Antiparallel beta strands are more stable than the parallel beta strands.
3. Tertiary Structure: The three dimensional structure of protein is known as tertiary structure which is the form where protein get maximum stabilization with minimum energy . In this form of structure protein folds itself in different pattern so that hydrophobic and non polar amino acids remain inside or inner part of the protein where they do not get exposed to the water. On the other hand acidic amino acids or basic amino acids are arranged on the upper surface of the protein to interact with the water. In the tertiary structure different bonds are formed between side chains of the polypeptide to stabilize this. These bonds can be disulphide bridge, salt bridges, ionic bridge. Amino acids like cysteine which contains sulphide group takes part in disulphide bridge development.
4. Quaternary Structure: Different polypeptides are joined together to form a salt brigde , large molecules of protein .In this structure protein subunits are formed which are large in size and are again produces different bonds between their suitable subunits for stabilized structure. Bonds those are involved in stabilization of proteins are hydrogen bond, disulphide bridge, salt bridges etc.
From Explain about the Structure of Proteins to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…
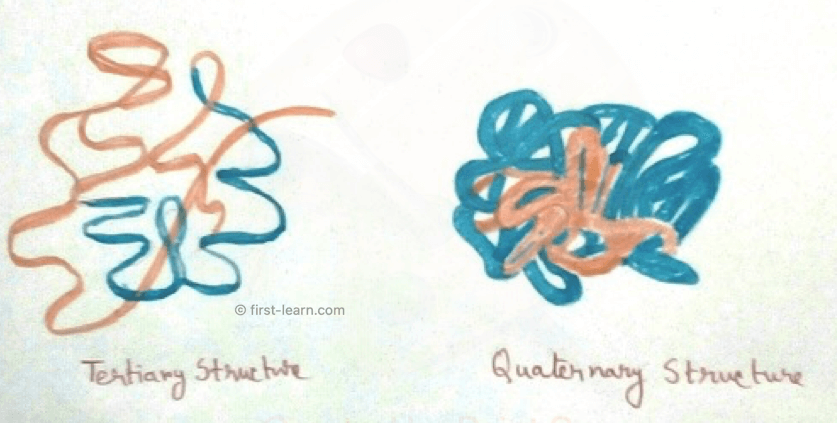







New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.