What is a Cell?
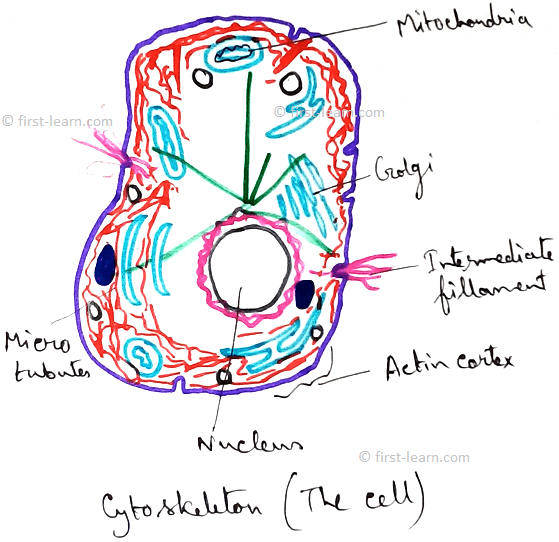
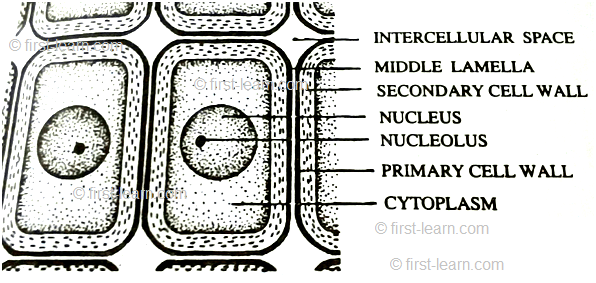
Cell is the structural and functional unit of life. It contains a centre which is called nucleus (as it controls the different functions and activities of cell). Plant cell is hexagonal or pentagonal is shape. Whereas animal cells are oval or round in shape. Plant cell contains cell wall which is found just outside the cell membrane. Human body is made up of trillion of cells. Cells are undergoes division to increase in number. Animal cell doesn’t contain any cell wall. Cells are consist of different organelles . These are mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, ribosome, centrosome etc.
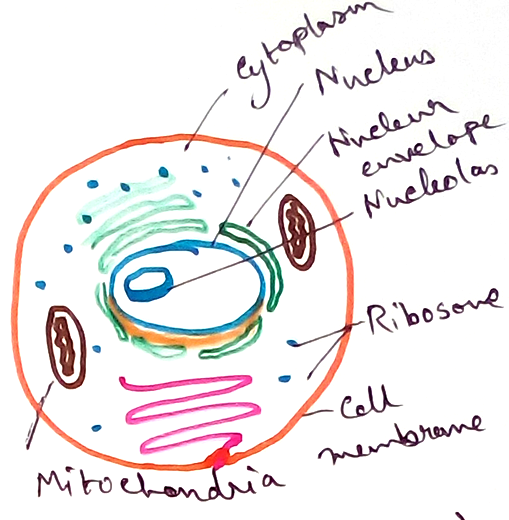
Cell is made up of cytoplasm and nucleus surrounded by cell membrane.
Cytoplasm - It is a belly like structure that contains nucleus and different organelles.
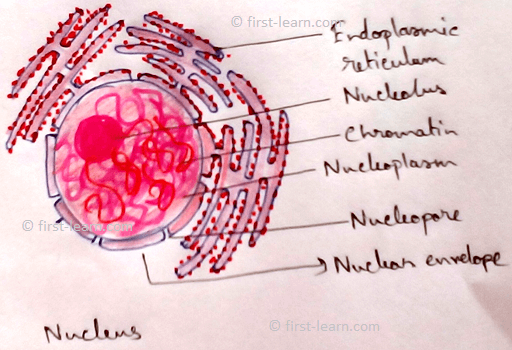
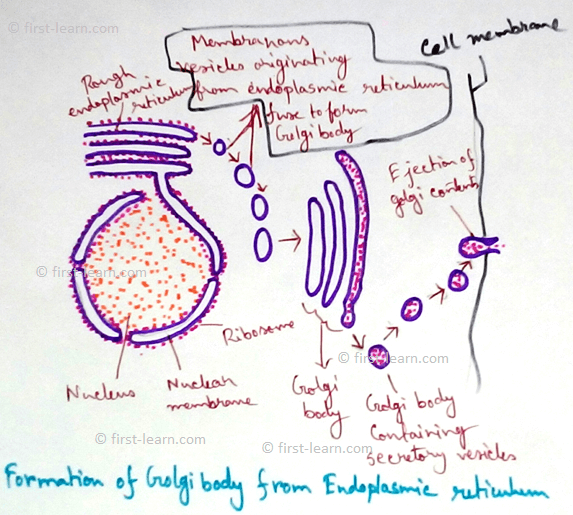
Nucleus - It is the main control centre of cell. It consists of nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nuclear reticulum, nucleoplasm. It contains genetic materials.
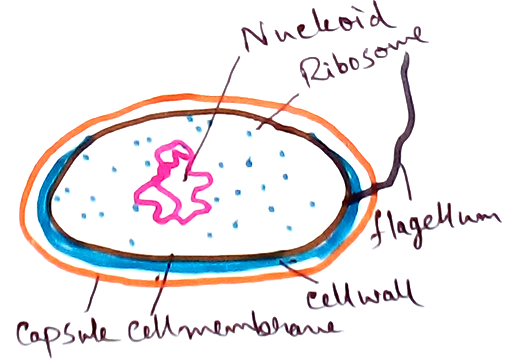
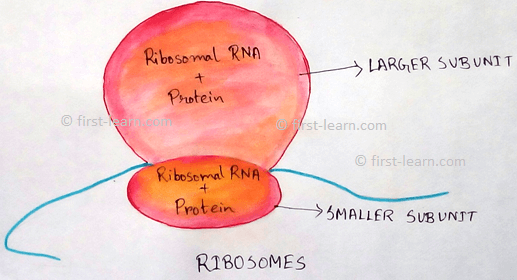
Ribosome - Associated with protein synthesis.
Mitochondria – Power House of cell that provides ATP.
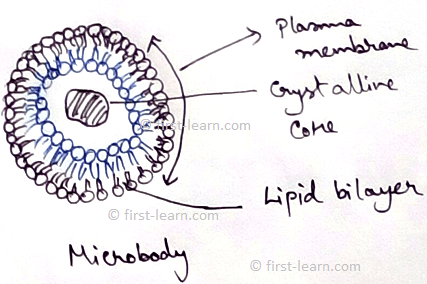
Lysosome and peroxisome - It is associated with destruction of different ergastic material of cells.
Endoplasmic reticulum - Rough endoplasmic reticulum contains ribosome and associated with protein synthesis. On the other hand smooth endoplasmic reticulum associated with fat and glucose synthesis.
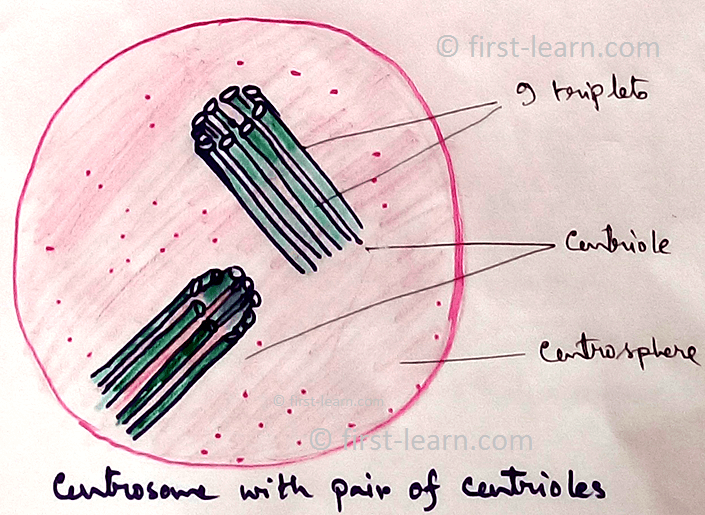
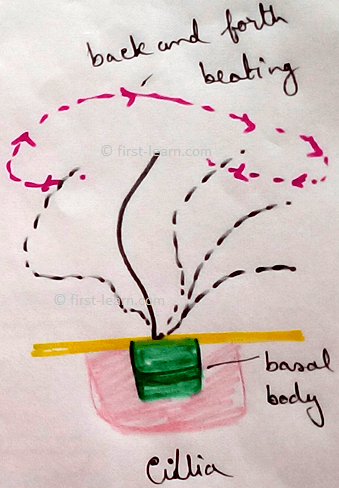
Centrosome - Centrioles are associated with producing spindle during cell division in animal cells.
Golgi body - Packaging of molecules for transport out of the cell.
Types of cell - According to the type of cell it can be divided into prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell.
Prokaryotic cell - These are premitive cell . This type of cells do not contain any well defined nucleus , membrane bound organelles. Their genetic material is scattered on the cytoplasm. Example of prokaryotic cell is bacteria.
Eukaryotic cell - This type of cells are modern or advanced cell with well defined membrane bound nucleus where chromosome are located. It also contains membrane bound cell organelles.Examples of eukaryotic cell is any plants and animals cells.
Functions of Cell
Cells have different functions. They are –
1. Building blocks of body- Cell is the structural and functional unit of body. It is called the building block of the body.
2. Give rise to different system –Different cells are associated to form tissues. Different tissues according to their function and structure associated to form together organs. Different organs have different purposes. Group of organs give rise to different system. All the systems together form organisms.
3. Takes part in absorption – Cells absorbed different nutrients from the food after digestion. Different types of specialised cells are there for absorption of food like microvilli, lacteal etc.
4. Transport different biomolecules- Cell membrane contains different gate and receptors for transport and movements of biomolecules.
5. Contains genetic material – Nucleus of cell contains genetic material called chromosome. Which contains genes (carry properties from one generation to other).
6. Help in providing nutrients to different parts of the body by transport.
7. Help in providing energy- Due to metabolism chemical energy that is converted into kinetic energy is stored in mitochondria in cell as ATP.
8. Play role in different metabolic activity- It contains different enzymes for metabolic activity.
From What is a Cell? to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Plants Around Us | Big & Small Plants | Shrubs & Herbs | Water Plants
Feb 03, 26 02:01 AM
We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things. They breathe and grow. They also reproduce. Most of the plants grow on land. Some plants grow in water. -
Formed Elements of Blood | Erythrocytes | ESR |Leukocytes |Neutrophils
Jan 15, 26 01:25 AM
Formed elements formed elements are constitute about 45 % of blood afeias haematocrit value packed cell volume mostly of red blood corpuscles and are of 3 types- erythrocytes, leukocytes and blood pla… -
What Is Plasma? | Blood Plasma | Proteins | Nutrients | Cholesterol
Nov 07, 25 10:29 AM
Blood is a mobile fluid which is a connective tissue and is derived from the mesoderm like cell any other connective tissue. Colour of blood is reddish and that flows inside the blood vessels by means… -
Disorders of Respiratory System | Tuberculosis | Pleurisy | Emphysema
Oct 28, 25 11:39 PM
Tuberculosis is very common disease and is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease causes different trouble in the respiration and infection of several parts of th… -
Regulation of Respiration | Respiratory Centres | Inspiratory Area |
Oct 14, 25 12:13 AM
Respiratory Centre is the area that controls the rate of respiration and it is observed to be located in medulla oblongata and pons. Respiratory Centre has the following will dispersed components like…







New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.